Chapter Outline:
6.0 Introduction
6.1 Endpoint Security
6.2 Layer 2 Security Threats
6.3 Summary
Section 6.1: Endpoint Security
Upon completion of this section, you should be able to:
- Describe endpoint security and the enabling technologies.
- Explain how Cisco AMP is used to ensure endpoint security.
- Explain how Cisco NAC authenticates and enforces the network security policy.
Topic 6.1.1: Introducing Endpoint Security
Securing LAN Elements
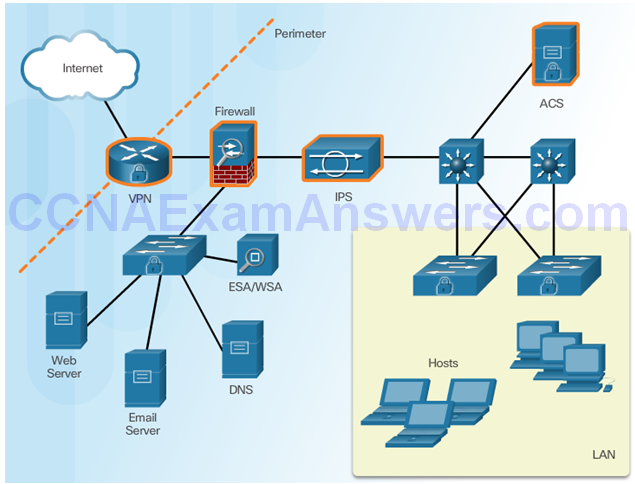
Traditional Endpoint Security
The Borderless Network

Securing Endpoints in the Borderless Network
- Post malware attack questions:
- Where did it come from?
- What was the threat method and point of entry?
- What systems were affected?
- What did the threat do?
- Can I stop the threat and root cause?
- How do we recover from it?
- How do we prevent it from happening again?
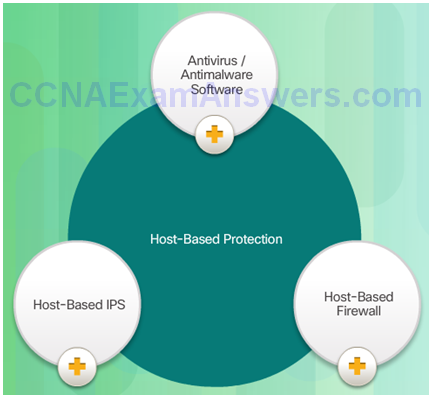
- Host-Based Protection:
- Antivirus/Antimalware
- SPAM Filtering
- URL Filtering
- Blacklisting
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
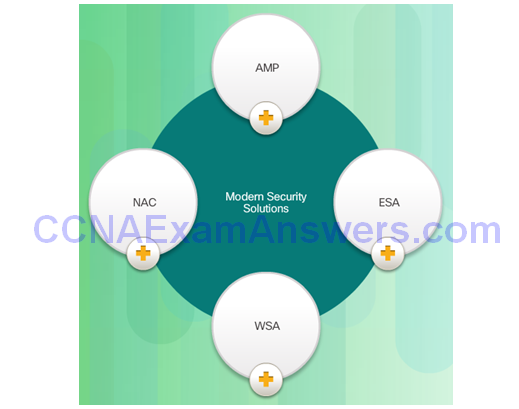
Modern Endpoint Security Solutions
Hardware and Software Encryption of Local Data

Topic 6.1.2: Antimalware Protection
Advanced Malware Protection

AMP and Managed Threat Defense
- Talos teams gather real-time threat intelligence from a variety of sources:
- 1.6 million deployed security devices, including firewall, IPS, web, and email appliances
- 150 million endpoints
- They then analyze this data:
- 100 TB of security intelligence daily
- 13 billion web requests per day
- 35% of the world’s enterprise email traffic
AMP for Endpoints
- AMP for Endpoints– AMP for Endpoints integrates with Cisco AMP for Networks to deliver comprehensive protection across extended networks and endpoints.
- AMP for Networks– Provides a network-based solution and is integrated into dedicated Cisco ASA Firewall and Cisco FirePOWER network security appliances.
- AMP for Content Security– This is an integrated feature in Cisco Cloud Web Security or Cisco Web and Email Security Appliances to protect against email and web-based advanced malware attacks.
Topic 6.1.3: Email and Web Security
Securing Email and Web

Cisco Email Security Appliance
Features and benefits of Cisco Email Security solutions:
- Global threat intelligence
- Spam blocking
- Advanced malware protection
- Outbound message control
Cisco Web Security Appliance
Client Initiates Web Request
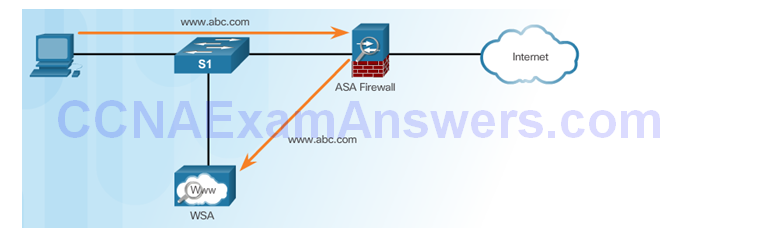
WSA Forwards Request
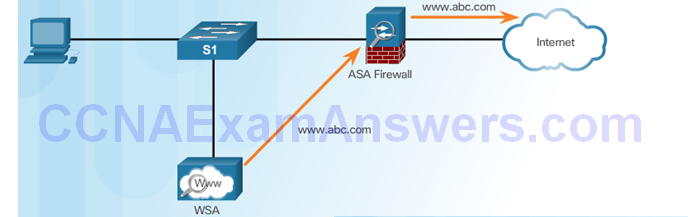
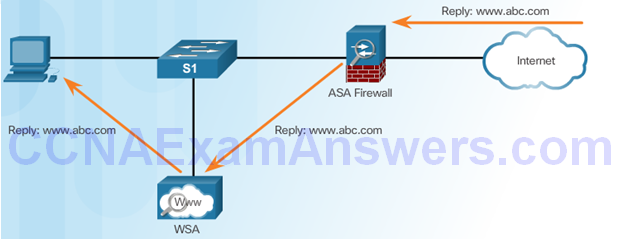
Reply Sent to WSA and Then To Client
Topic 6.1.4: Controlling Network Access
Cisco Network Admission Control
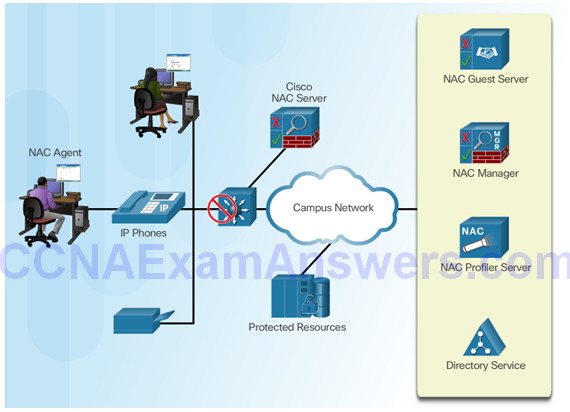
Cisco NAC Functions
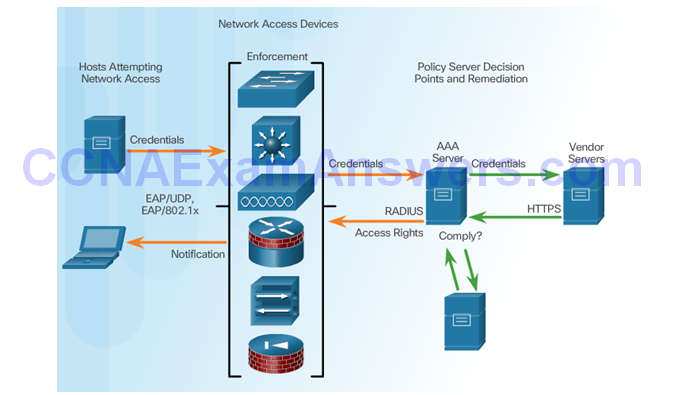
Cisco NAC Components
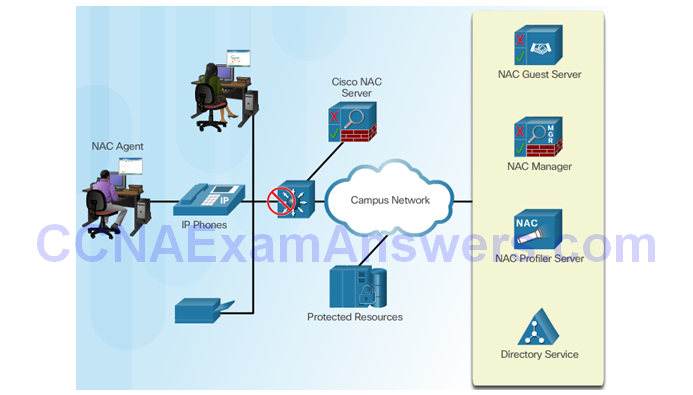
Network Access for Guests
Three ways to grant sponsor permissions:
- to only those accounts created by the sponsor
- to all accounts
- to no accounts (i.e., they cannot change any permissions)
Cisco NAC Profiler
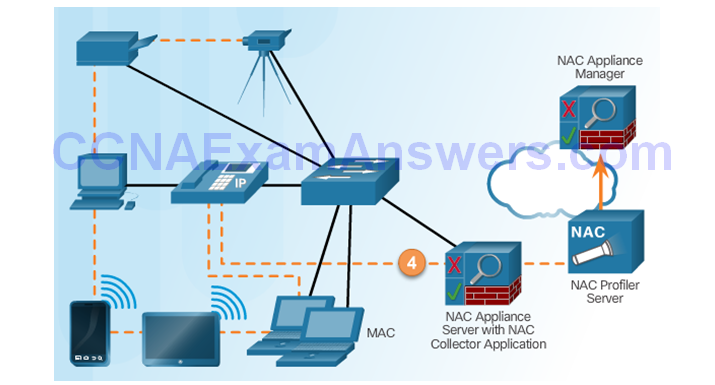
Section 6.2: Layer 2 Security Considerations
Upon completion of the section, you should be able to:
- Describe Layer 2 vulnerabilities.
- Describe CAM table overflow attacks.
- Configure port security to mitigate CAM table overflow attacks.
- Configure VLAN Truck security to mitigate VLAN hopping attacks.
- Implement DHCP Snooping to mitigate DHCP attacks.
- Implement Dynamic Arp Inspection to mitigate ARP attacks.
- Implement IP Source Guard to mitigate address spoofing attacks.
Topic 6.2.1: Layer 2 Security Threats
Describe Layer 2 Vulnerabilities
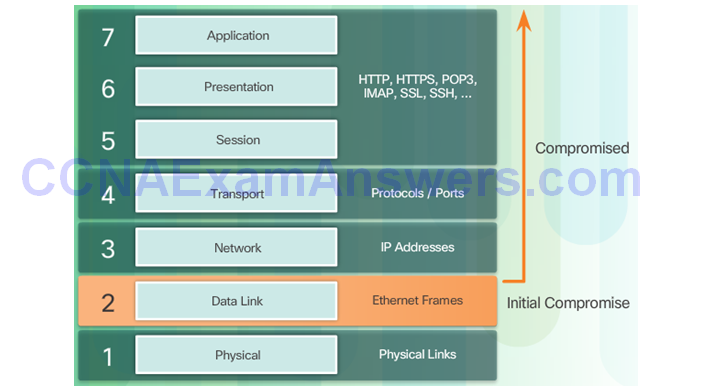
Switch Attack Categories
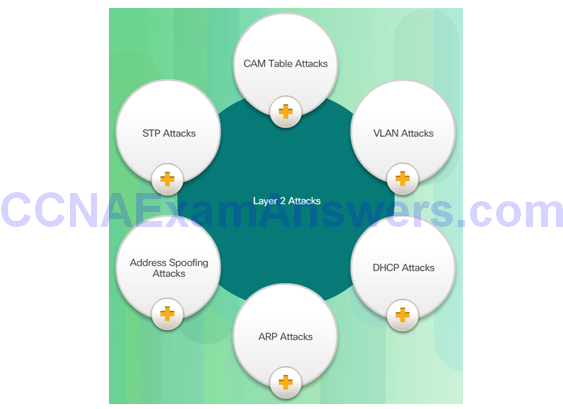
Topic 6.2.2: CAM Table Attacks
Basic Switch Operation
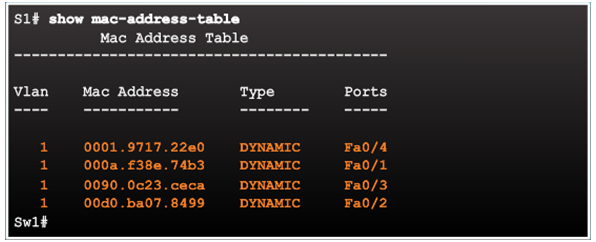
CAM Table Operation Example
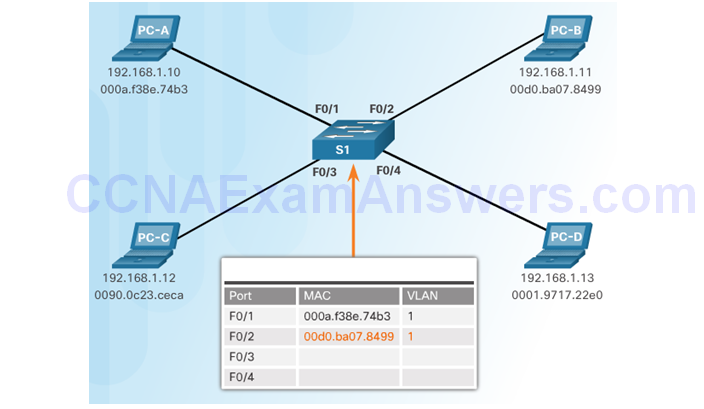
CAM Table Attack
Intruder Runs Attack Tool
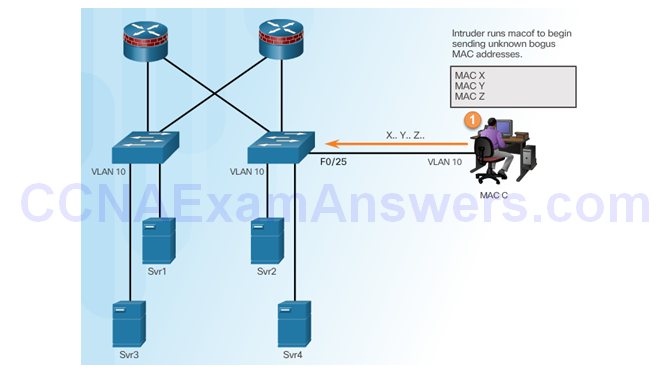
Fill CAM Table
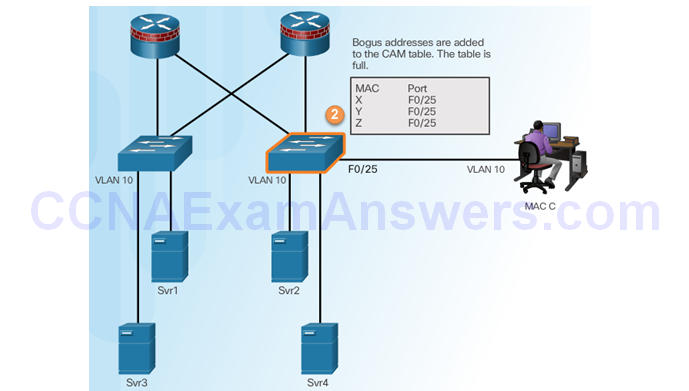
Switch Floods All Traffic
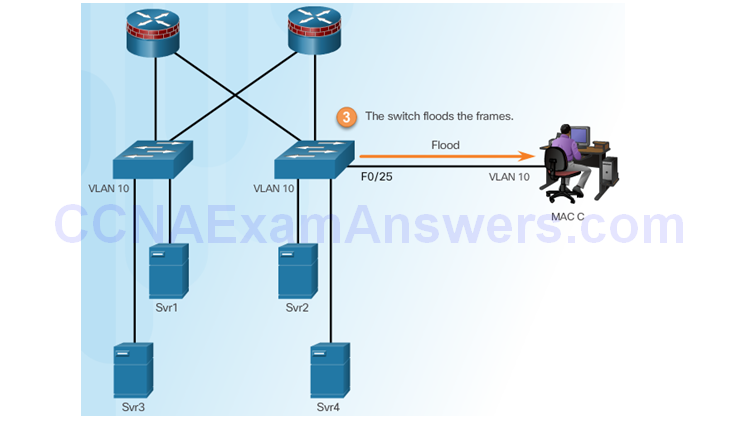
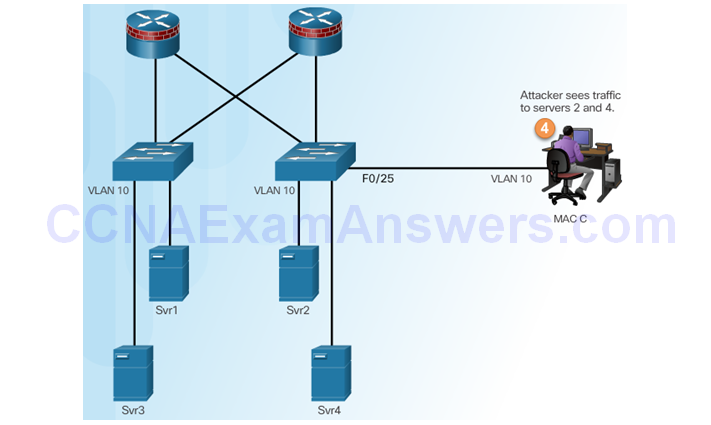
Attacker Captures Traffic
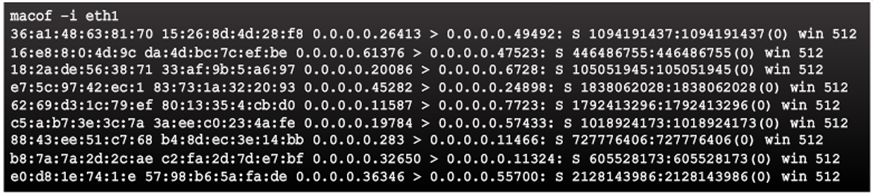
CAM Table Attack Tools
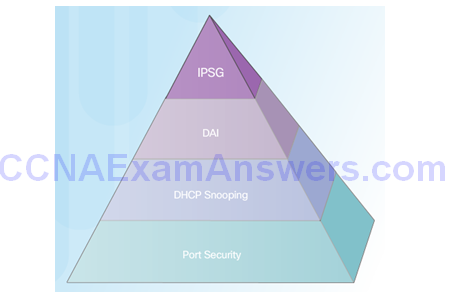
Topic 6.2.3: Mitigating CAM Table Attacks
Countermeasure for CAM Table Attacks
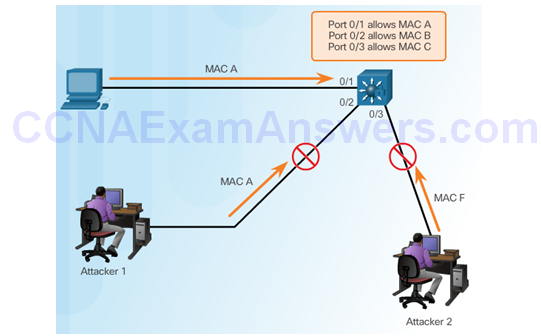
Port Security
Enabling Port Security

Verifying Port Security

Port Security Options

Enabling Port Security Options
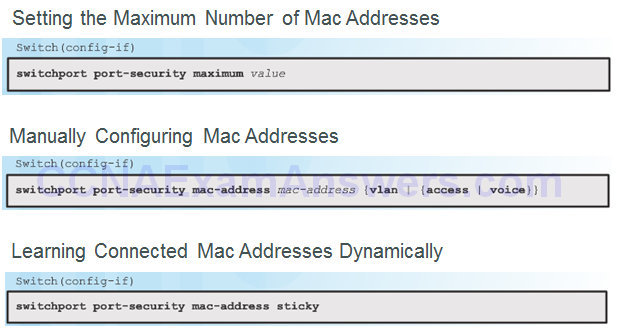
Port Security Violations
Security Violation Modes:
- Protect
- Restrict
- Shutdown
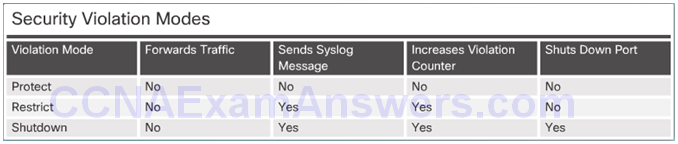
Port Security Aging
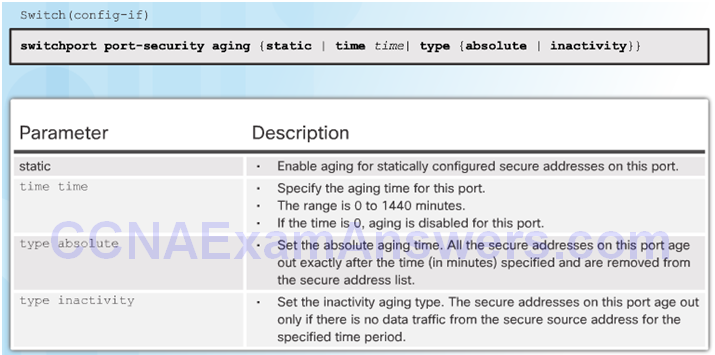
Port Security with IP Phones
SNMP MAC Address Notification
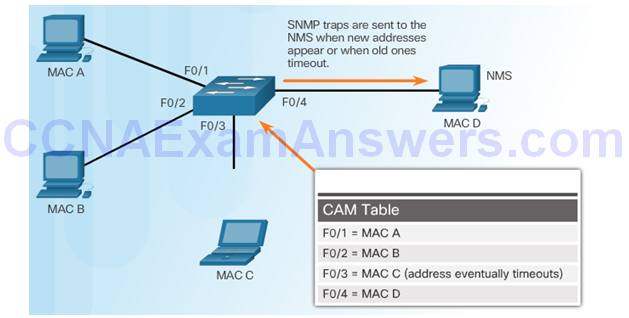
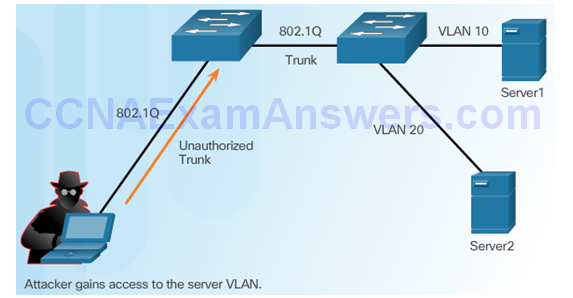
Topic 6.2.4: Mitigating VLAN Attacks
VLAN Hopping Attacks
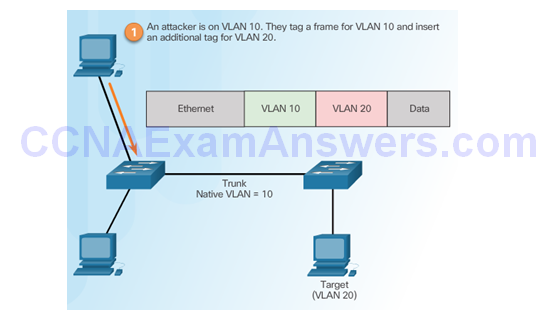
VLAN Double-Tagging Attack
Step 1 – Double Tagging Attack
Step 2 – Double Tagging Attack
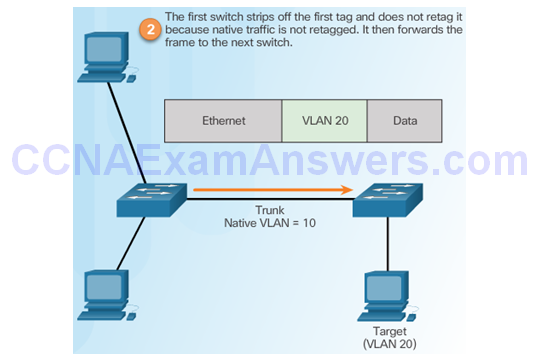
Step 3 – Double Tagging Attack
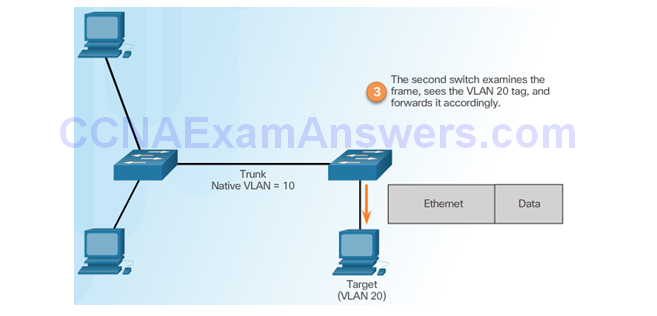
Mitigating VLAN Hopping Attacks

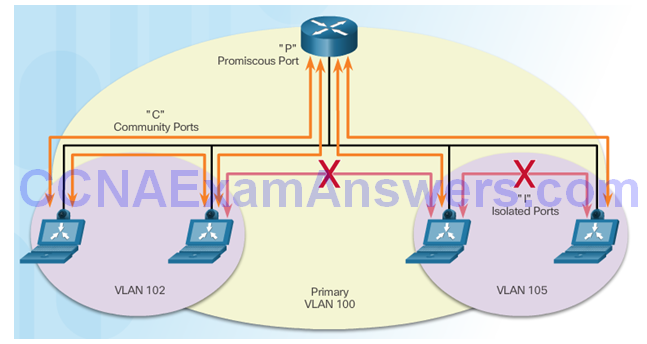
PVLAN Edge Feature
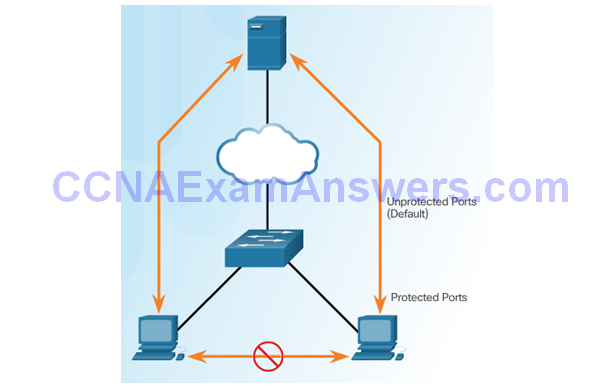
Verifying Protected Ports
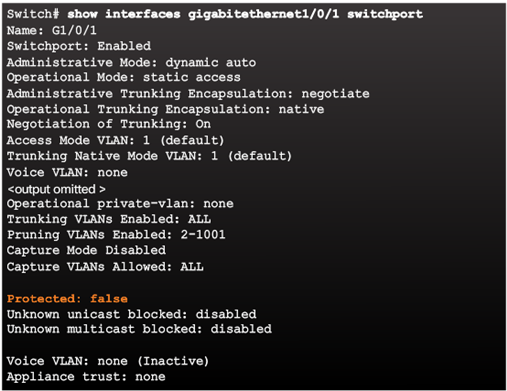
Private VLANs
Topic 6.2.5: Mitigating DHCP Attacks
DHCP Spoofing Attack
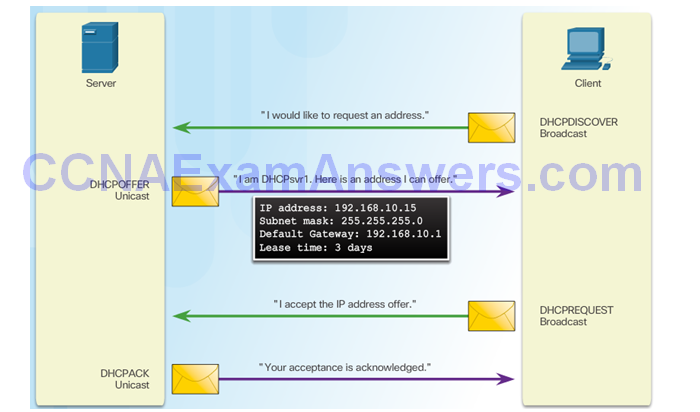
DHCP Starvation Attack
Attacker Initiates a Starvation Attack
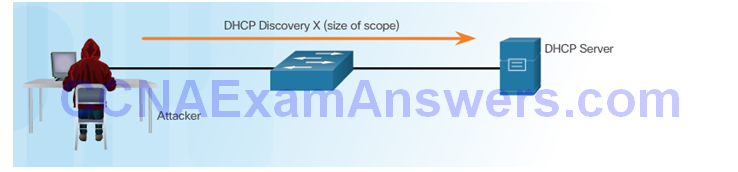
DHCP Server Offers Parameters
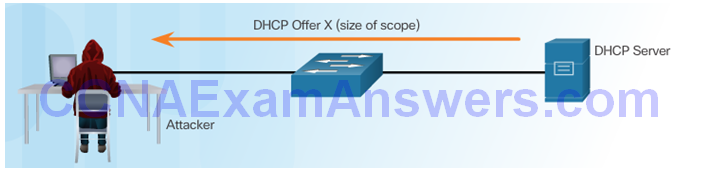
Client Requests all Offers
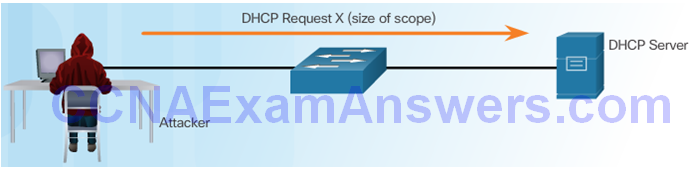
DHCP Server Acknowledges All Requests
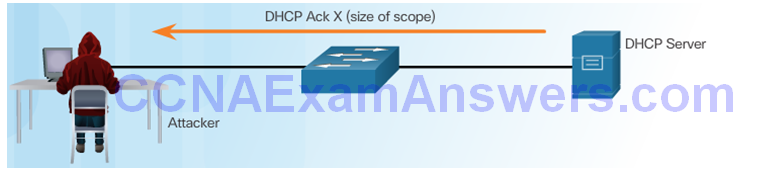
Mitigating VLAN Attacks
The switch will deny packets containing specific information:
- Unauthorized DHCP server messages from an untrusted port
- Unauthorized DHCP client messages not adhering to the snooping binding table or rate limits
- DHCP relay-agent packets that include option-82 information on an untrusted port
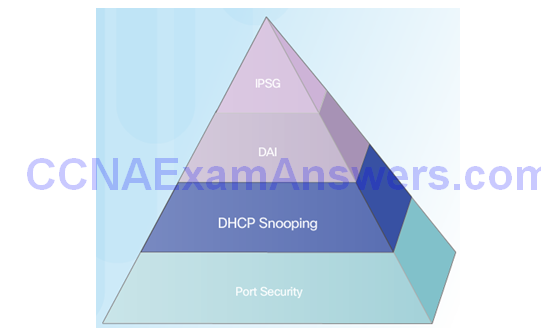
Configuring DHCP Snooping
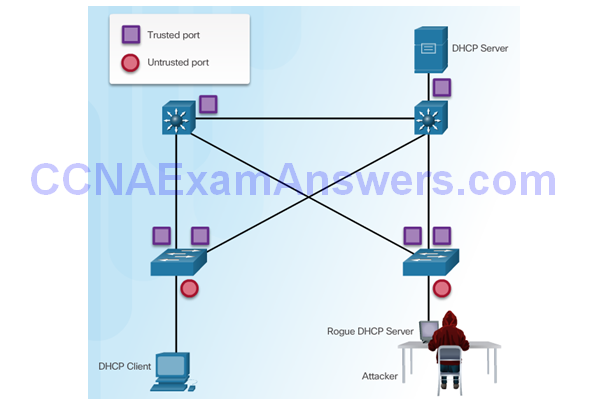
Configuring DHCP Snooping Example
DHCP Snooping Reference Topology

Configuring a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses
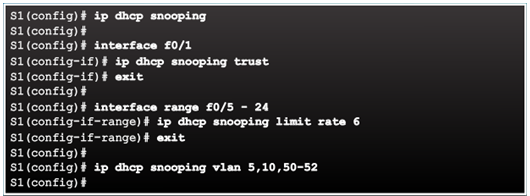
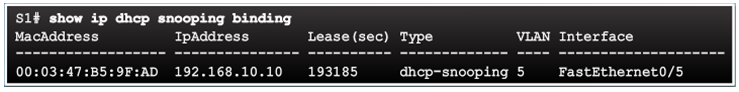
Verifying DHCP Snooping
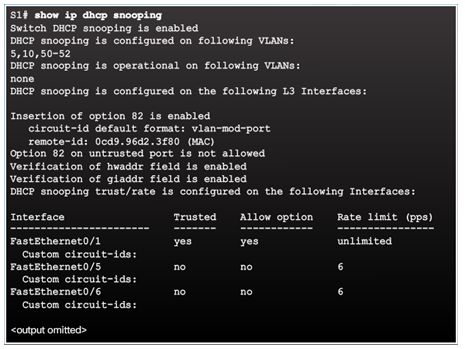
Configuring a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses
Topic 6.2.6: Mitigating ARP Attacks
ARP Spoofing and ARP Poisoning Attack

Mitigating ARP Attacks
Dynamic ARP Inspection:
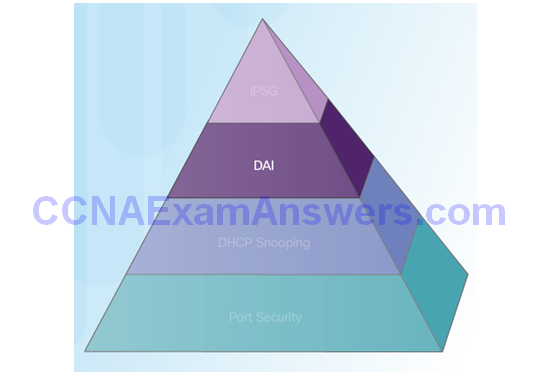
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection

Configuring DHCP Snooping Example
ARP Reference Topology
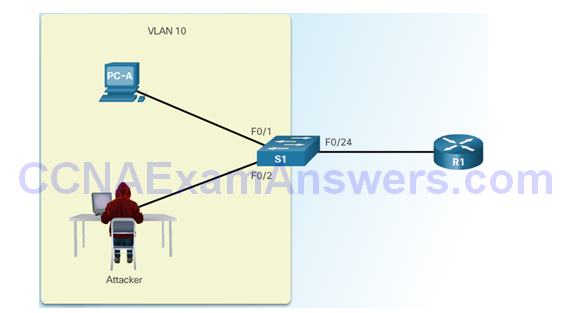
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection

Checking Source, Destination, and IP
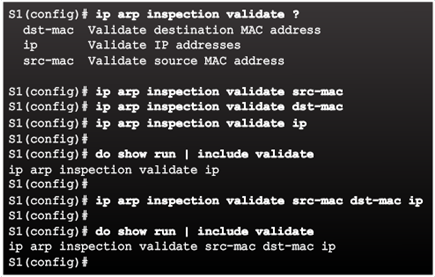
Topic 6.2.7: Mitigating Address Spoofing Attacks
Address Spoofing Attack
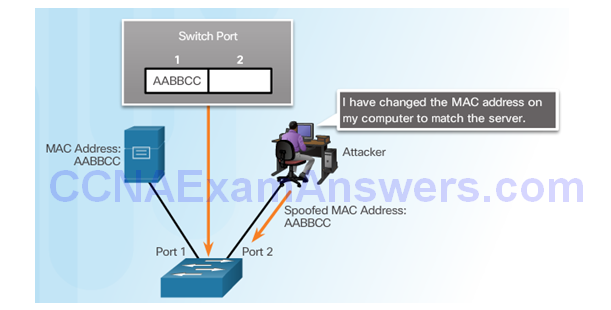
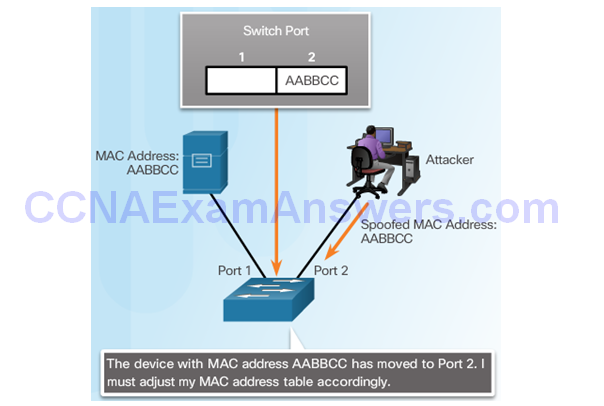
Mitigating Address Spoofing Attacks
For each untrusted port, there are two possible levels of IP traffic security filtering:
- Source IP address filter
- Source IP and MAC address filter
Configuring IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard Reference Topology
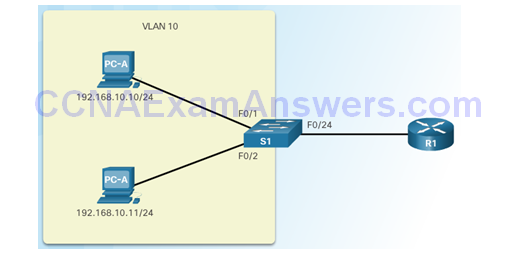
Configuring IP Source Guard

Checking IP Source Guard
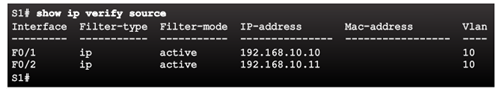
Topic 6.2.8: Spanning Tree Protocol
Introduction to the Spanning Tree Protocol
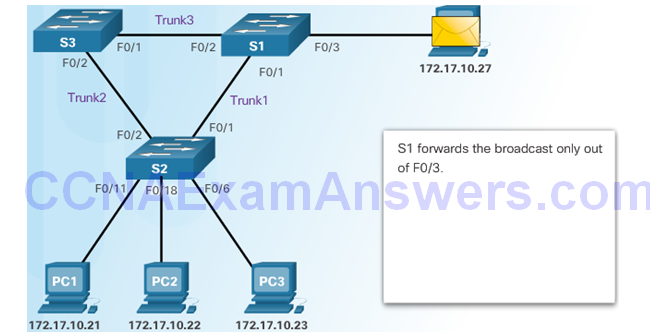
STP Port Roles
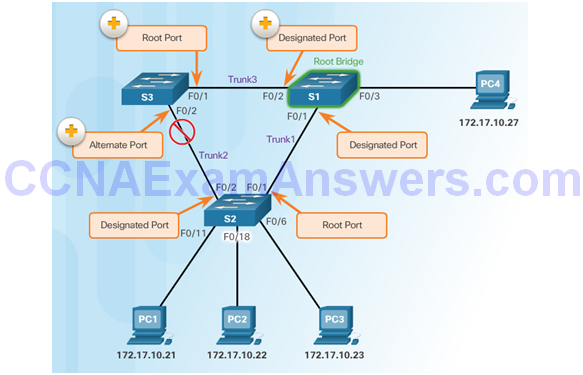
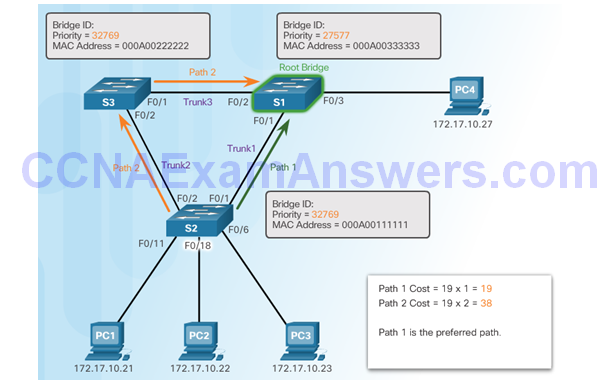
STP Root Bridge

STP Path Cost
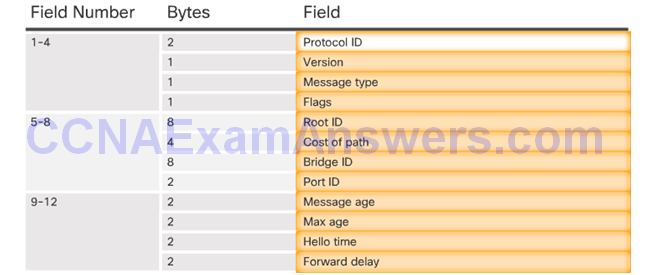
802.1D BPDU Frame Format
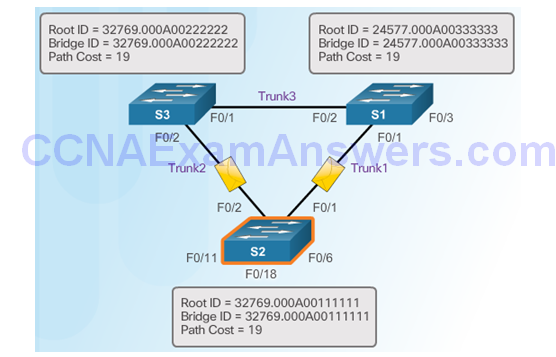
BPDU Propagation and Process
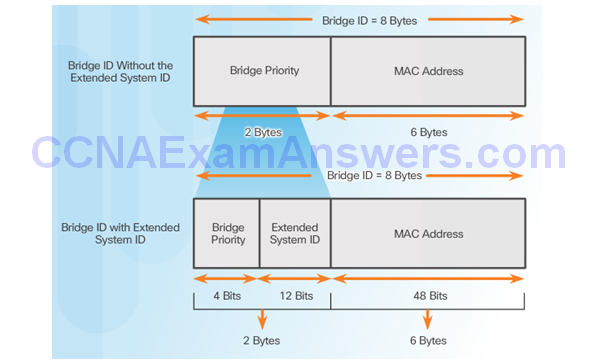
Extended System ID
Select the Root Bridge
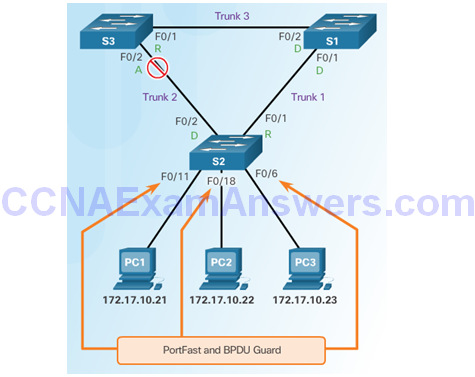
Topic 6.2.9: Mitigating STP Attacks
STP Manipulation Attacks
Spoofing the Root Bridge
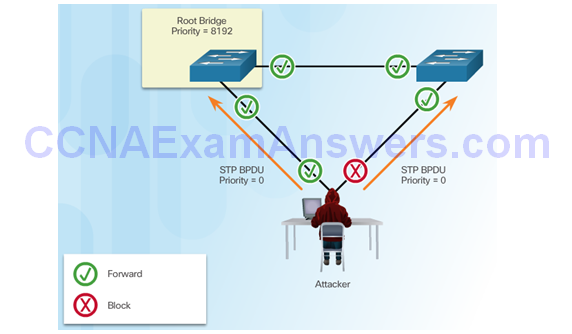
Successful STP Manipulation Attack
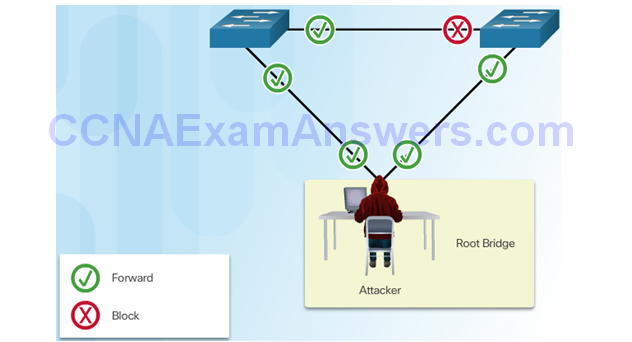
Mitigating STP Attacks
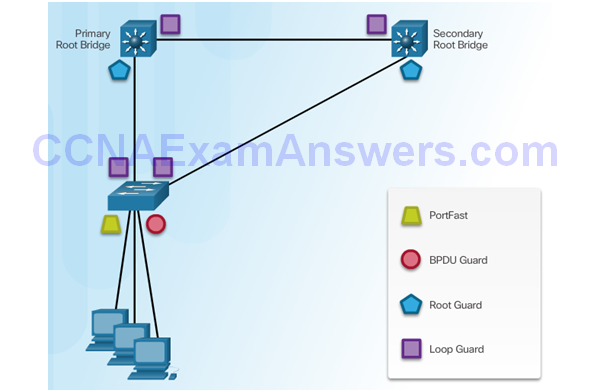
Configuring PortFast
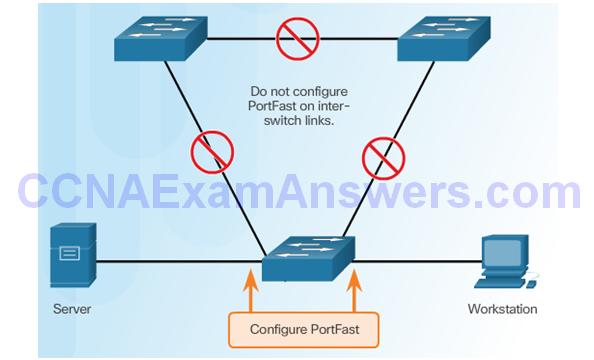
Configuring BDPU Guard
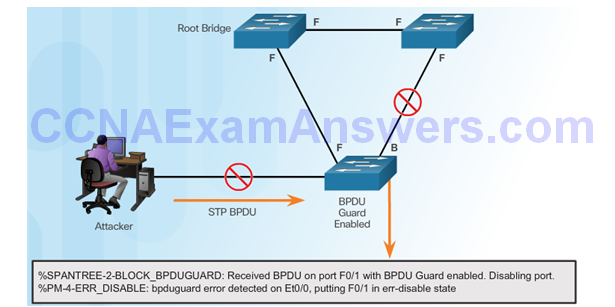
Configuring Root Guard
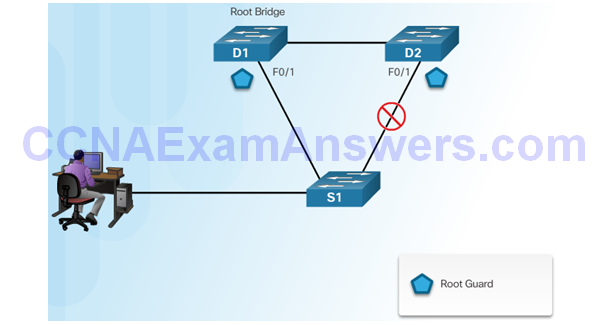
Configuring Loop Guard
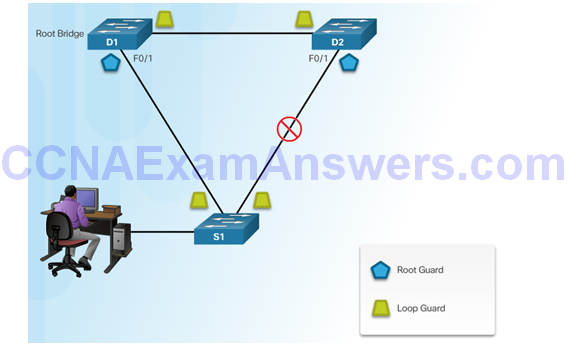
Section 6.3: Summary
Chapter Objectives:
- Explain endpoint security.
- Describe various types of endpoint security applications.
- Describe Layer 2 vulnerabilities.
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
[sociallocker id=”2293″][wpdm_package id=’3089′][/sociallocker]
