Chapter Outline:
1.0 Introduction
1.1 Securing Networks
1.2 Network Threats
1.3 Mitigating Threats
1.4 Summary
Section 1.1: Securing Networks
Upon completion of this section, you should be able to:
- Describe the current network security landscape.
- Explain how all types of networks need to be protected.
Topic 1.1.1: Current State of Affairs
Networks Are Targets
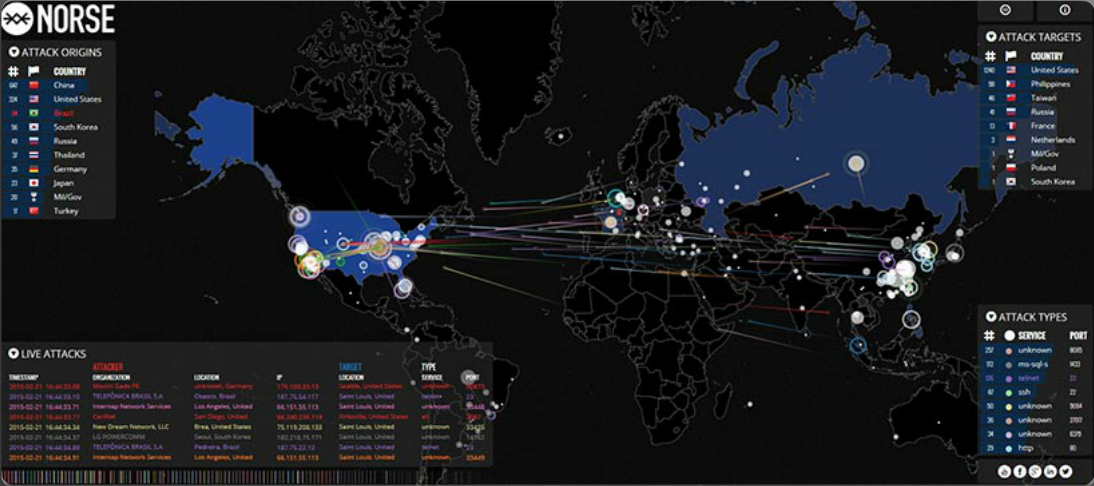
Drivers for Network Security
- Common network security terms:
- Threat
- Vulnerability
- Mitigation
- Risk
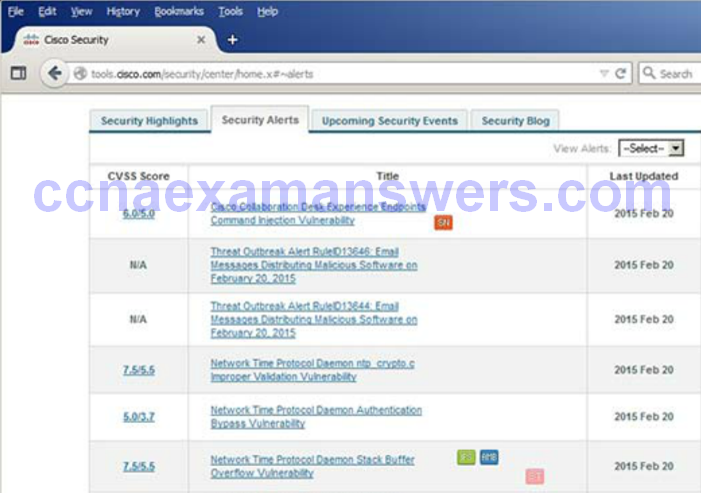
Vectors of Network Attacks
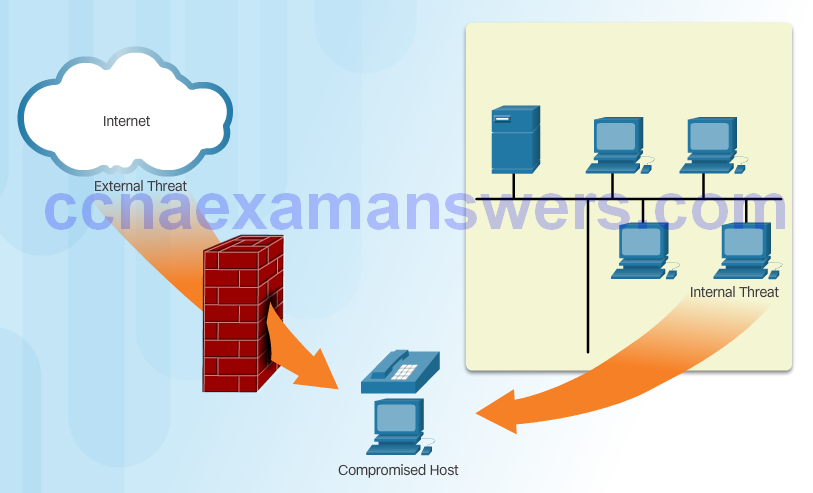
Data Loss
- Vectors of data loss:
- Email/Webmail
- Unencrypted Devices
- Cloud Storage Devices
- Removable Media
- Hard Copy
- Improper Access Control
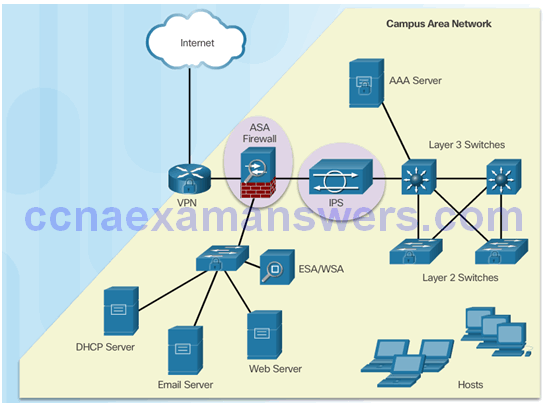
Topic 1.1.2: Network Topology Overview
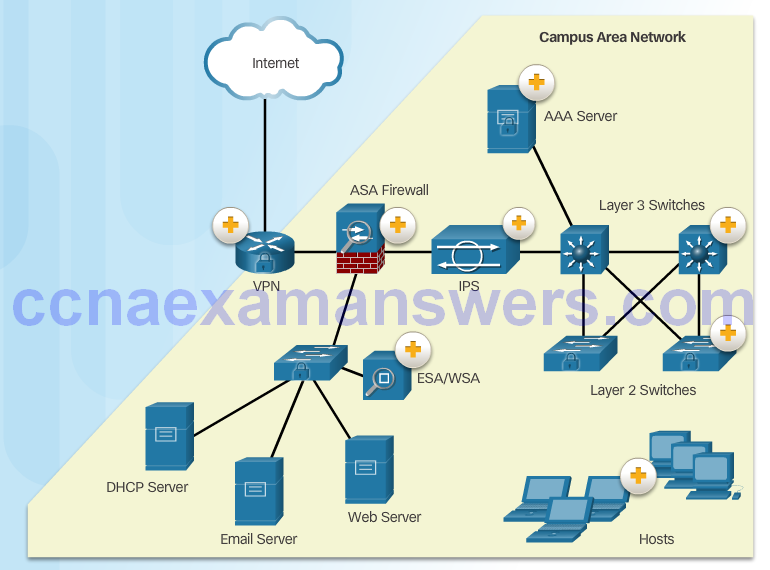
Campus Area Networks
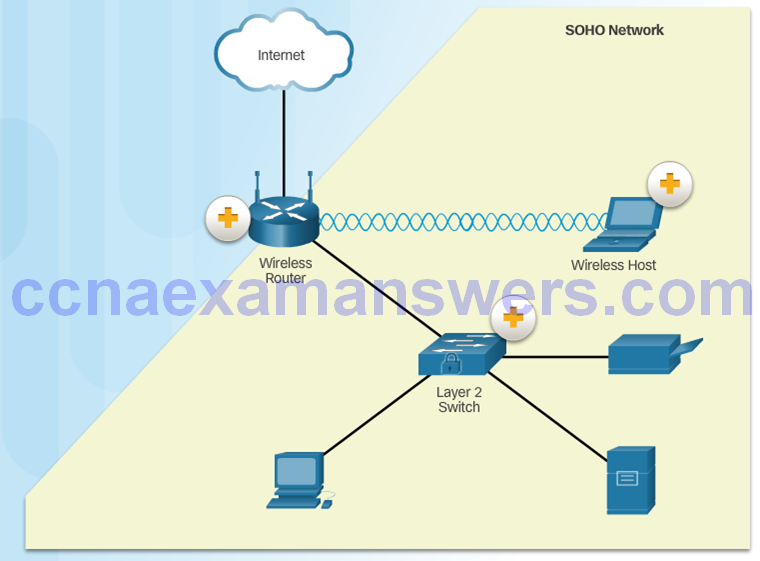
Small Office and Home Office Networks
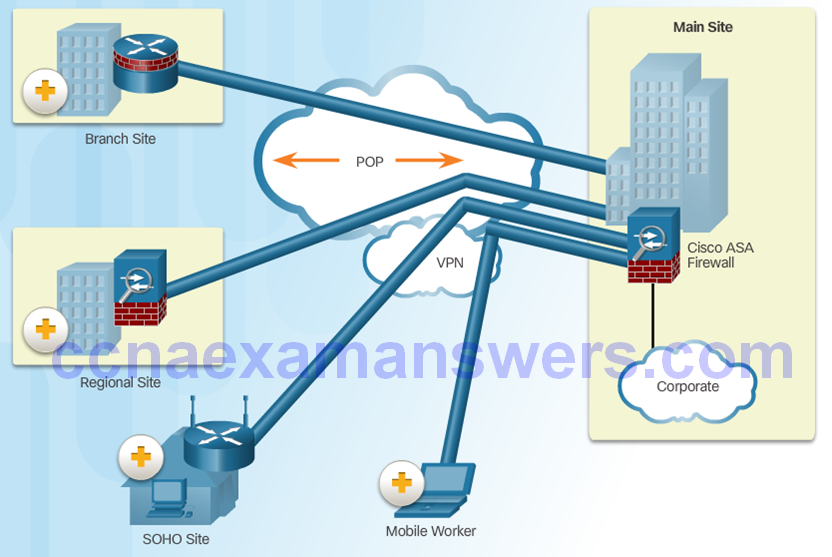
Wide Area Networks
Data Center Networks
- Outside perimeter security:
- On-premise security officers
- Fences and gates
- Continuous video surveillance
- Security breach alarms
- Inside perimeter security:
- Electronic motion detectors
- Security traps
- Continuous video surveillance
- Biometric access and exit sensors
Cloud and Virtual Networks
- VM-specific threats:
- Hyperjacking
- Instant On activation
- Antivirus storm
- Components of a secure data center:
- Secure segmentation
- Threat defense
- Visibility
The Evolving Network Border
- Critical MDM functions for BYOD network:
- Data encryption
- PIN enforcement
- Data wipe
- Data loss prevention
- Jailbreak/root detection
Section 1.2: Network Threats
Topic 1.2.1: Who is Hacking Our Networks?
- Modern hacking titles:
- Script Kiddies
- Vulnerability Brokers
- Hacktivists
- Cyber Criaminals
- State-Sponsored Hackers
Topic 1.2.2: Hacker Tools
Introduction of Attack Tools
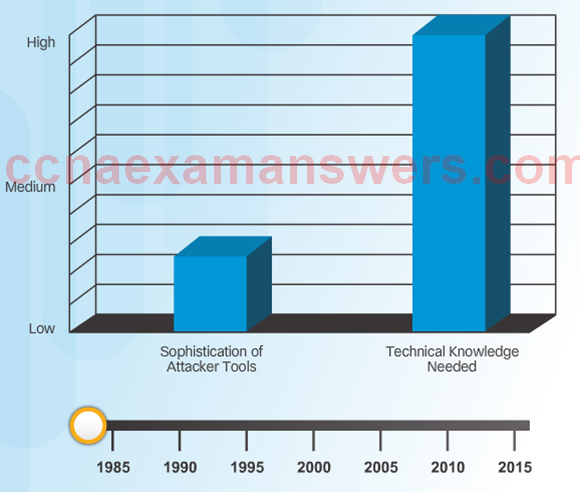
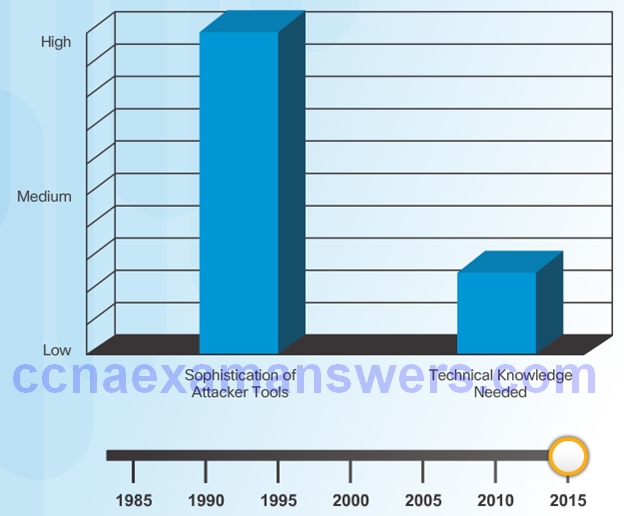
Evolution of Security Tools
- Penetration testing tools:
- Password crackers
- Wireless hacking
- Network scanning and hacking
- Packet crafting
- Packet sniffers
- Rootkit detectors
- Fuzzers to search vulnerabilities
- Forensic
- Debuggers
- Hacking operating systems
- Encryption
- Vulnerability exploitation
- Vulnerability Scanners
Categories of Attack Tools
- Network hacking attacks:
- Eavesdropping
- Data modification
- IP address spoofing
- Password-based
- Denial-of-service
- Man-in-the-middle
- Compromised-key
- Sniffer
Topic 1.2.3: Malware
Various Types of Malware


Viruses

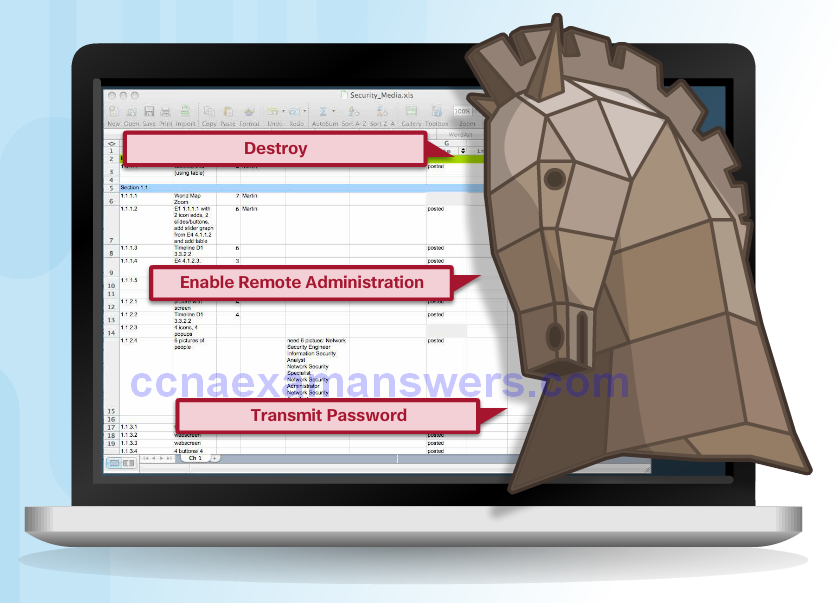
Trojan Horses
Trojan Horse Classification
- Classifications:
- Security software disabler
- Remote-access
- Data-sending
- Destructive
- Proxy
- FTP
- DoS
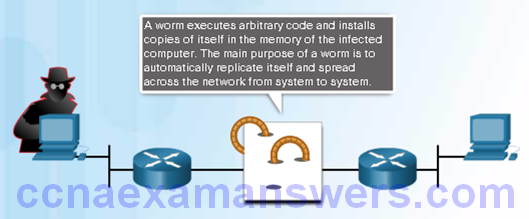
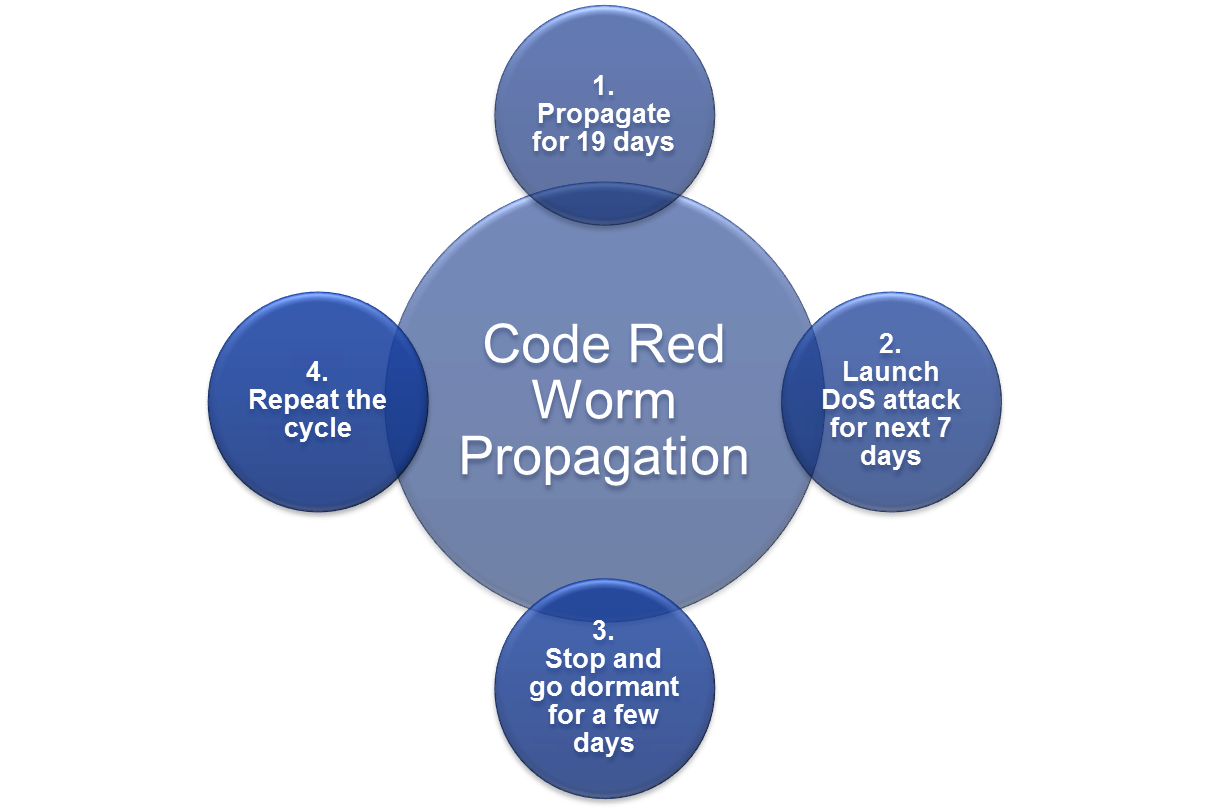
Worms
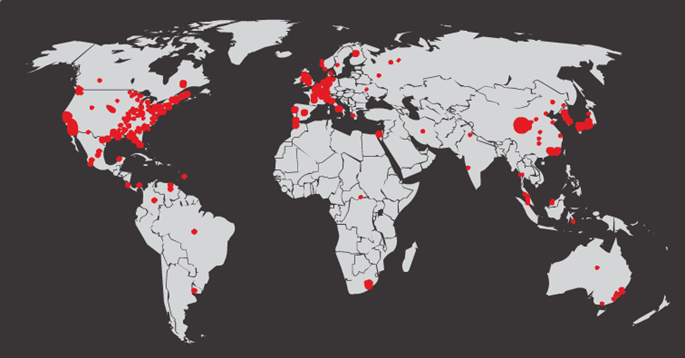
- Initial Code Red Worm Infection
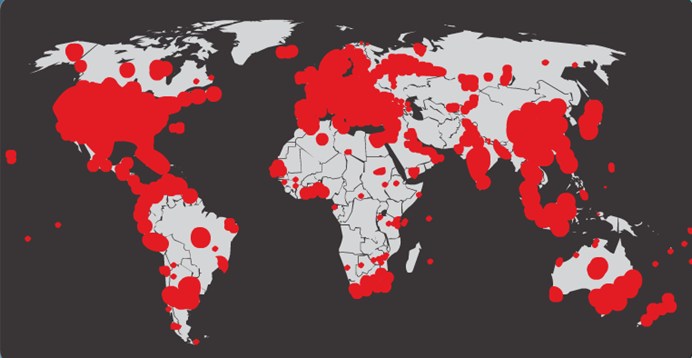
- Code Red Worm Infection 19 Hours Later
Worm Components
- Components:
- Enabling vulnerability
- Propagation mechanism
- Payload
Other Malware

Activity – Identify the Malware Type
Topic 1.2.4:Common Network Attacks
Types of Network Attacks
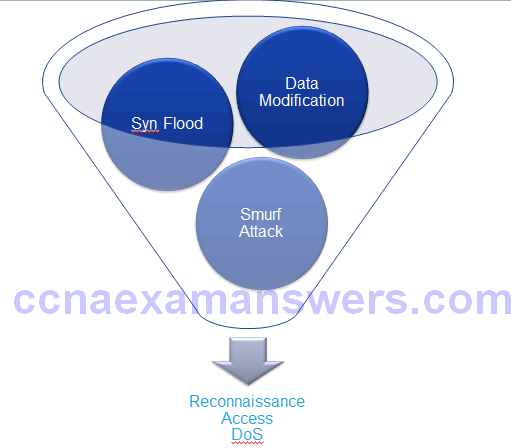
Reconnaissance Attacks
- Initial query of a target
- Ping sweep of the target network
- Port scan of active IP addresses
- Vulnerability scanners
- Exploitation tools

Sample Reconnaissance Attacks
Access Attacks
- A few reasons why hackers use access attacks:
- To retrieve data
- To gain access
- To escalate access privileges
- A few types of access attacks include:
- Password
- Trust exploitation
- Port redirection
- Man-in-the-middle
- Buffer overflow
- IP, MAC, DHCP spoofing
Social Engineering Attacks
- Pretexting
- Phishing
- Spearphishing
- Spam
- Tailgating
- Something for Something
- Baiting

Denial of Service Attacks
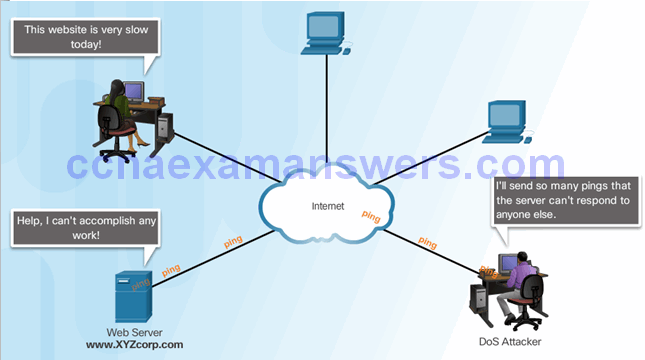
Types of DoS Attacks
DDoS Attacks
- Hacker builds a network of infected machines
- A network of infected hosts is called a botnet.
- The compromised computers are called zombies.
- Zombies are controlled by handler systems.
- Zombie computers continue to scan and infect more targets
- Hacker instructs handler system to make the botnet of zombies carry out the DDoS attack
Activity – Identify the Types of Attack
Lab – Social Engineering
Section 1.3: Mitigating Threats
- Upon completion of this section, you should be able to::
- Describe methods and resources to protect the networks.
- Describe a collection of domains for network security.
- Explain the purpose of the Cisco SecureX Architecture.
- Describe the techniques used to mitigate common network attacks.
- Explain how to secure the three functional areas of Cisco routers and switches.
Topic 1.3.1: Defending the Network
Network Security Professionals

Network Security Organizations

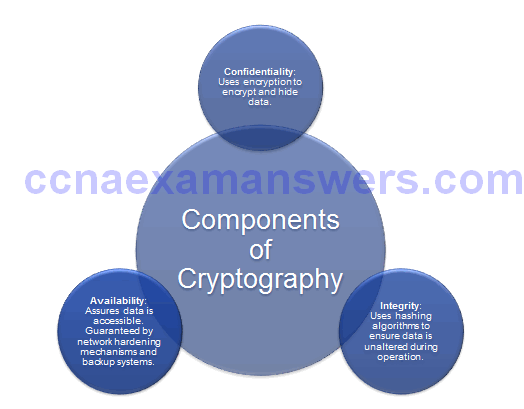
Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability
Topic 1.3.2: Domains of Network Security
Network Security Domains
- Risk assessment
- Security policy
- Organization of information security
- Asset management
- Human resources security
- Physical and environmental security
- Communications and operations management
- Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance
- Access control
- Information security incident management
- Business continuity management
- Compliance
Network Security Policy

Network Security Policy Objectives

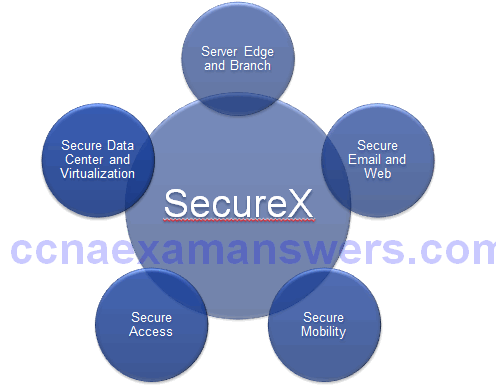
Topic 1.3.3: Introducing the Cisco SecureX Architecture
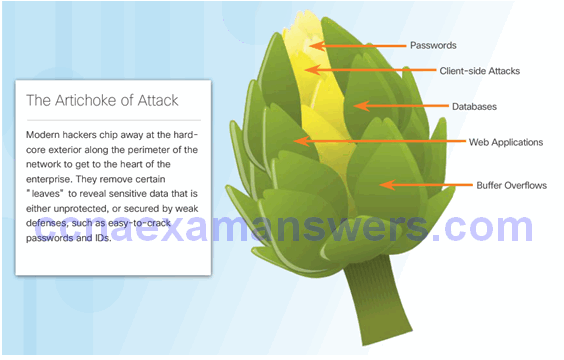
The Security Artichoke
Evolution of Network Security Tools
SecureX Product Families
SecureX Security Technology
- Cisco SecureX Architecture:
- Scanning engines
- Delivery mechanisms
- Security intelligence operations (SIO)
- Policy management consoles
- Next-generation endpoint
Centralized Context-Aware Network Scanning Element
- Defines security policies based on five parameters:
- Type of device being used for access
- Person’s identity
- Application in use
- Location
- Time of access

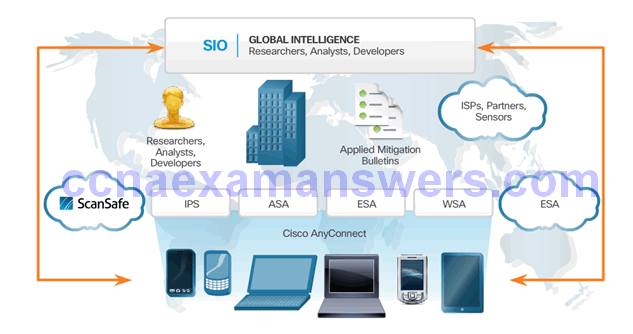
Cisco Security Intelligence Operations
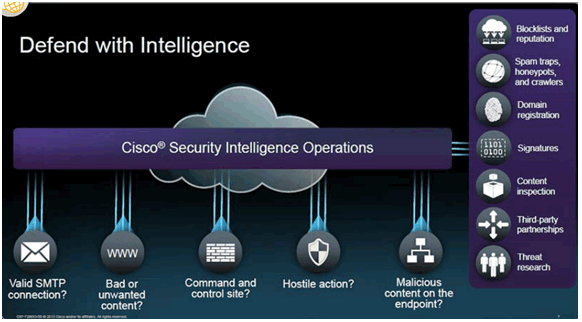
Topic 1.3.4: Mitigating Common Network Threats
Defending the Network
- Best practices:
- Develop a written security policy.
- Educate employees about the risks of social engineering, and develop strategies to validate identities over the phone, via email, or in person.
- Control physical access to systems.
- Use strong passwords and change them often.
- Encrypt and password-protect sensitive data.
- Implement security hardware and software.
- Perform backups and test the backed up files on a regular basis.
- Shut down unnecessary services and ports.
- Keep patches up-to-date by installing them weekly or daily to prevent buffer overflow and privilege escalation attacks.
- Perform security audits to test the network.
Mitigating Malware

Mitigating Worms
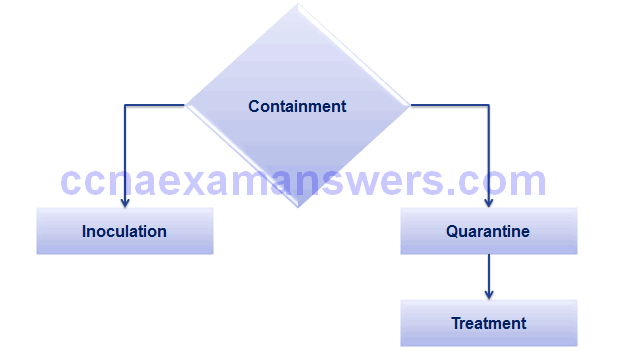
Mitigating Reconnaissance Attacks

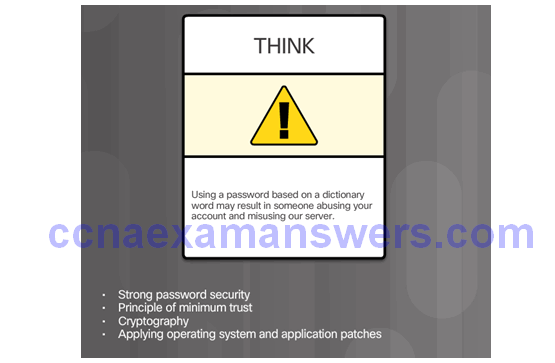
Mitigating Access Attacks
Mitigating DoS Attacks

Topic 1.3.5: Cisco Network Foundation Protection Framework
NFP Framework
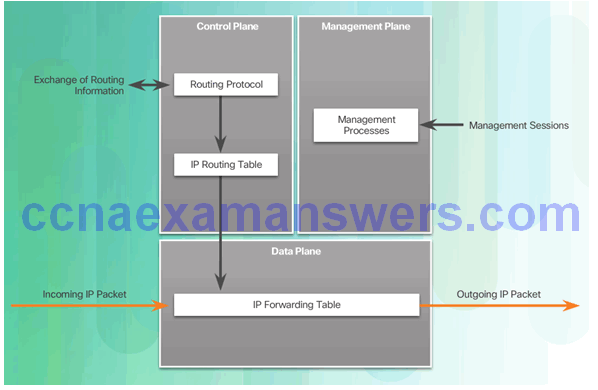
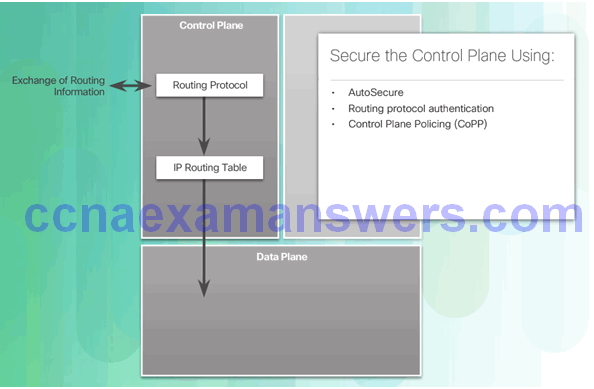
Securing the Control Plane
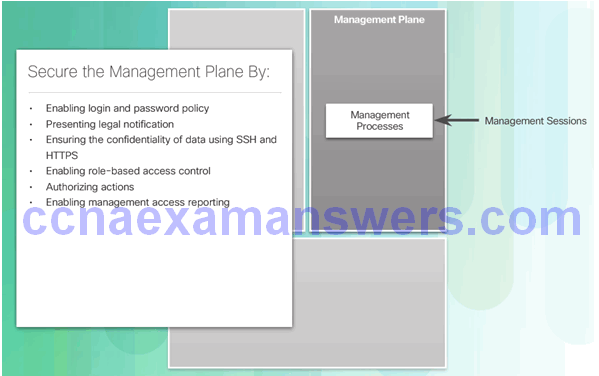
Securing the Management Plane
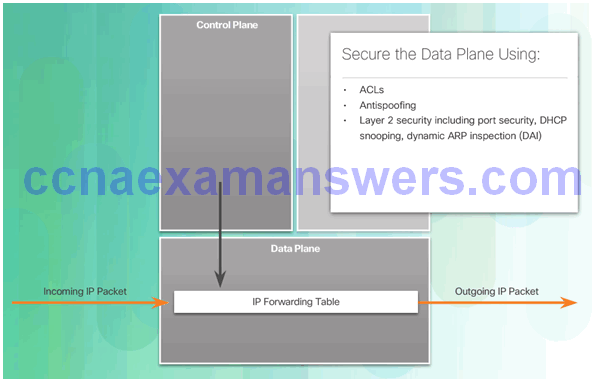
Securing the Data Plane
Activity – Identify Characteristics of the NFP Framework
Section 1.4: Summary
- Chapter Objectives:
- Explain network security.
- Describe various types of threats and attacks.
- Explain tools and procedures to mitigate the effects of malware and common network attacks.
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
[sociallocker id=”2293″][wpdm_package id=’2761′][/sociallocker]
