Chapter Outline:
7.0 Introduction
7.1 Cryptographic Services
7.2 Basic Integrity and Authenticity
7.3 Confidentiality
7.4 Public Key Cryptography
7.5 Summary
Section 7.1: Cryptographic Services
Upon completion of this section, you should be able to:
- Explain the requirements of secure communications including integrity, authentication, and confidentiality.
- Explain cryptography.
- Describe cryptoanalysis.
- Describe cryptology.
Topic 7.1.1: Securing Communications
Authentication, Integrity, and Confidentiality
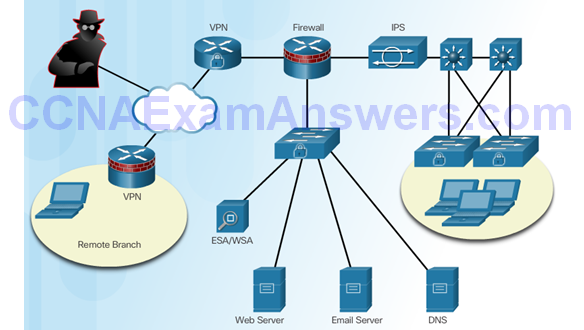
Authentication

Data Integrity

Data Confidentiality

Topic 7.1.2: Cryptography
Creating Ciphertext
Ciphertext can be creating using several methods:
- Transposition
- Substitution
- One-time pad
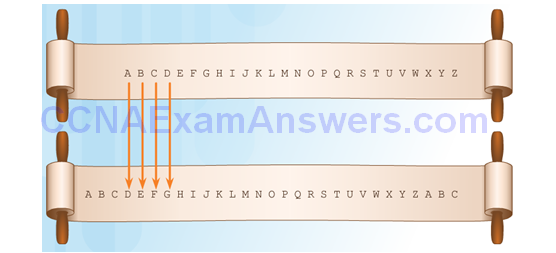
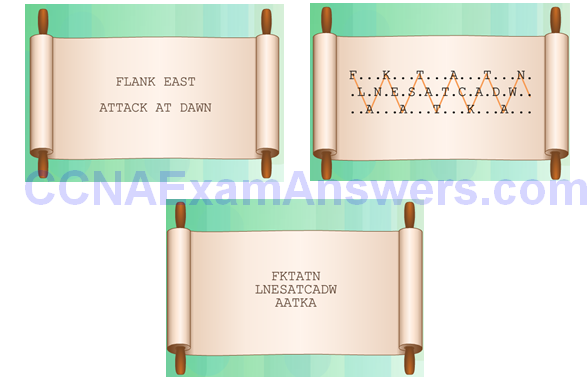
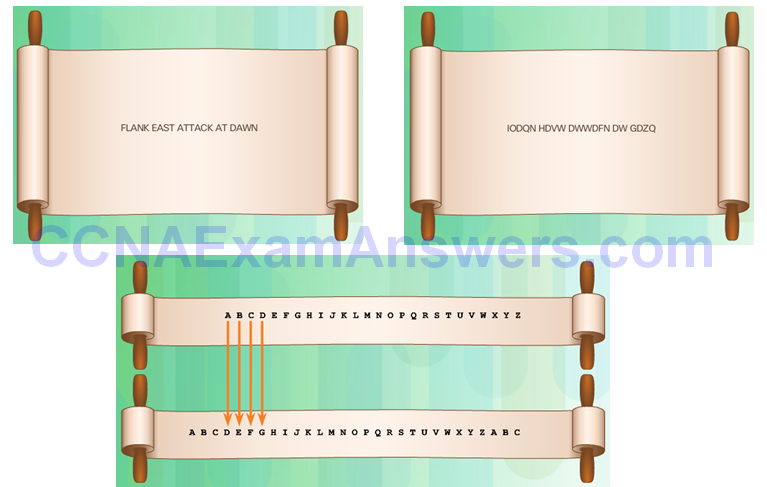
Transposition Ciphers
Substitution Ciphers
One-Time Pad Ciphers
Topic 7.1.3: Cryptanalysis
Cracking Code

Methods for Cracking Code
Methods used for cryptanalysis:
- Brute-force method
- Ciphertext method
- Known-Plaintext method
- Chosen-Plaintext method
- Chosen-Ciphertext method
- Meet-in-the-Middle method

Methods for Cracking Code
Frequency Analysis of the English Alphabet
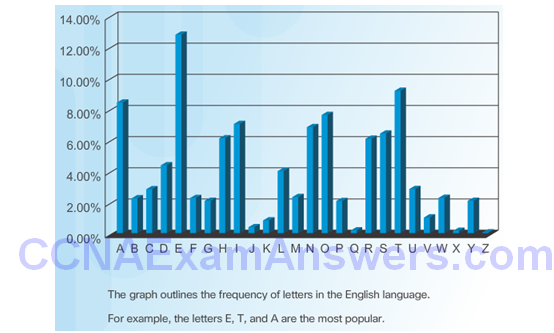
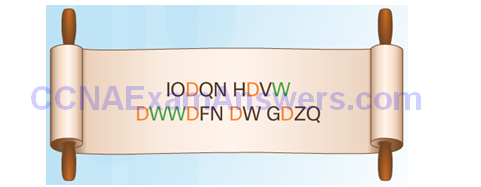
Deciphering Using Frequency Analysis
Topic 7.1.4: Cryptology
Making and Breaking Secret Codes
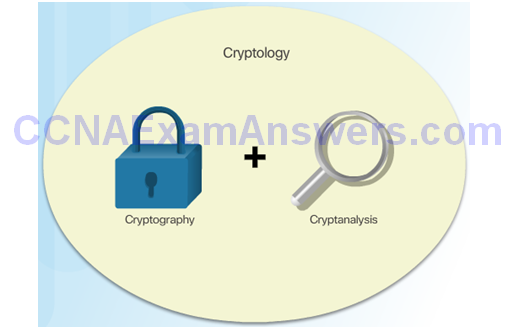
Cryptanalysis
The Secret is in the Keys
Section 7.2: Basic Integrity and Authenticity
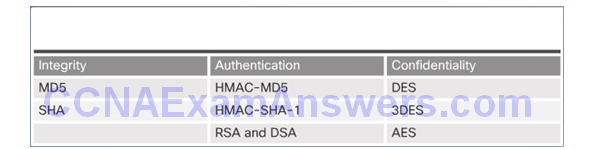
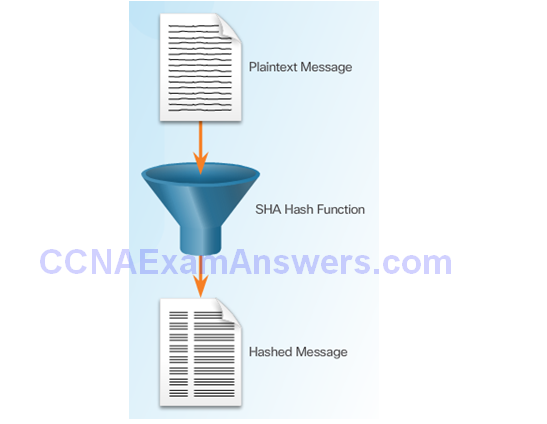
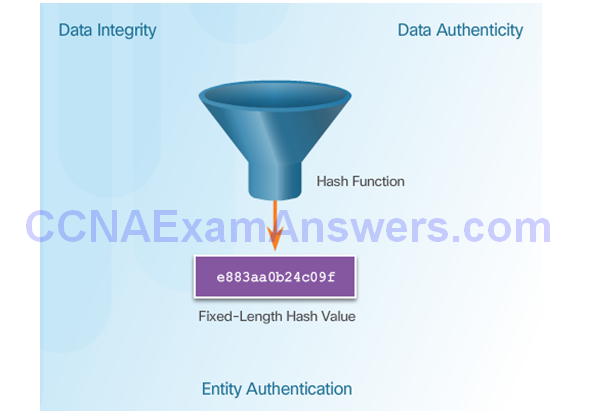
Topic 7.2.1: Cryptographic Hashes
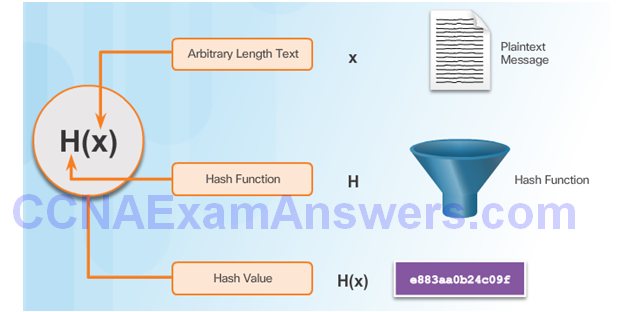
Cryptographic Hash Function
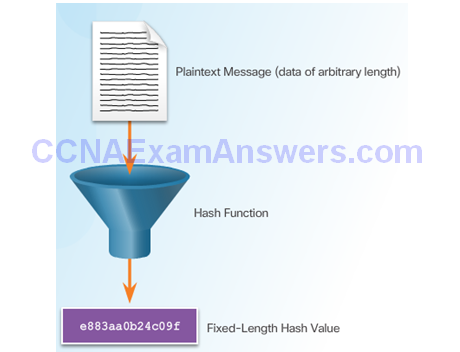
Cryptographic Hash Function Properties
Well-Known Hash Functions
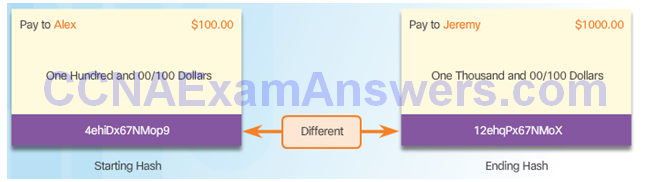
Topic 7.2.2: Integrity with MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-2
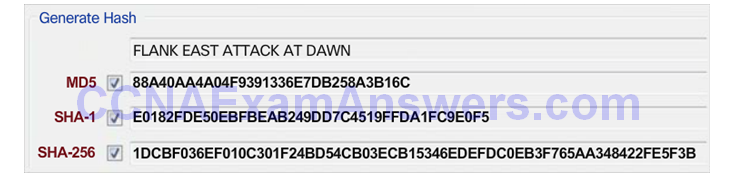
Message Digest 5 Algorithm

Secure Hash Algorithm
MD5 Versus SHA
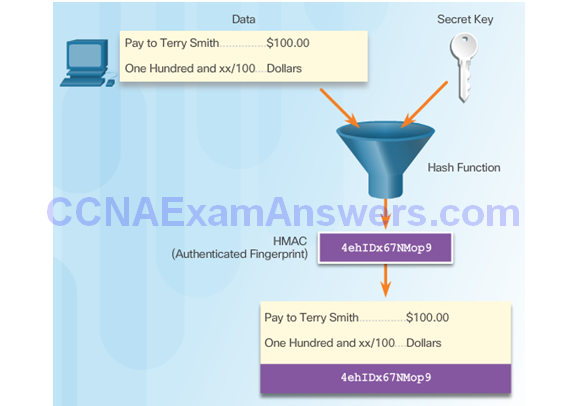
Topic 7.2.3: Authenticity with HMAC
Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code
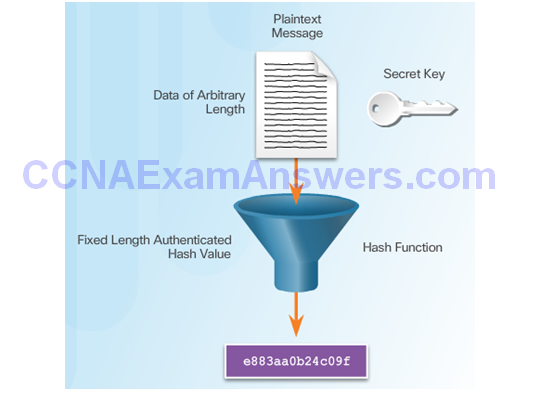
HMAC Operation
Hashing in Cisco Products
Topic 7.2.4: Key Management
Characteristics of Key Management

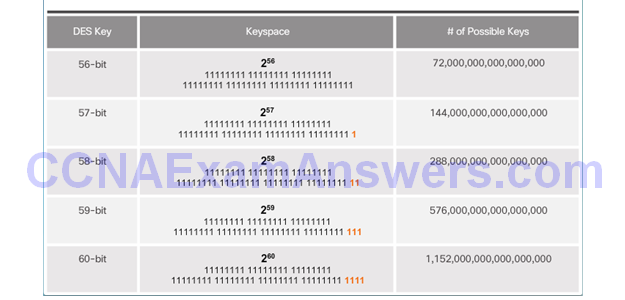
Key Length and Keyspace
The Keyspace
Types of Cryptographic Keys
Types of cryptographic keys:
- Symmetric keys
- Asymmetric keys
- Digital signatures
- Hash keys
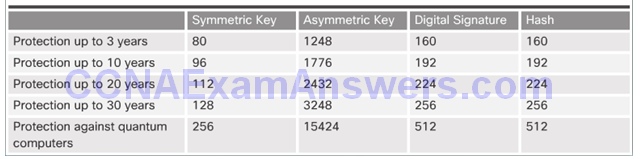
Choosing Cryptographic Keys

Section 7.3: Confidentiality
Topic 7.3.1: Encryption
Two Classes of Encryption Algorithms
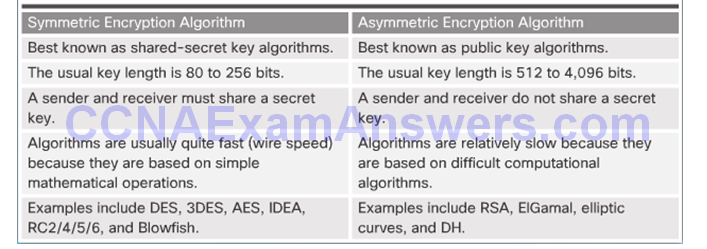
Symmetric and Asymmetric Encryption
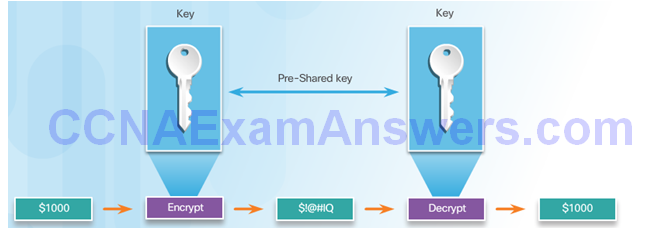
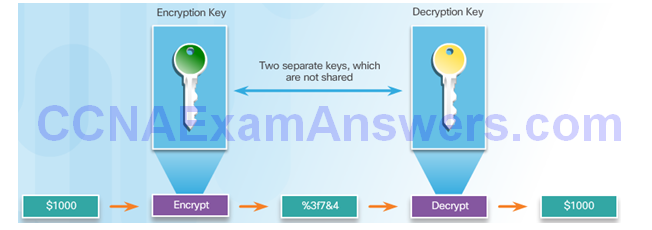
Symmetric Encryption
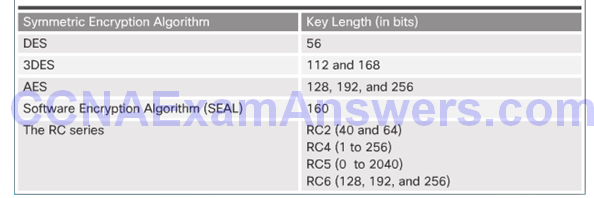
Symmetric Block Ciphers and Stream Ciphers

Choosing an Encryption Algorithm

Topic 7.3.2: Data Encryption Standard
DES Symmetric Encryption
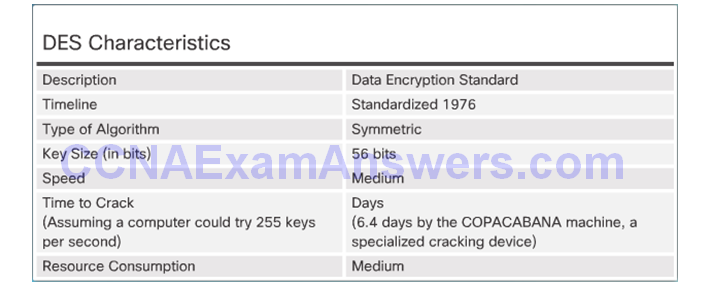
DES Summary

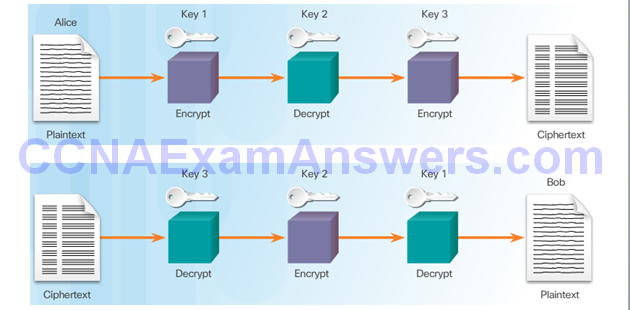
Improving DES with 3DES
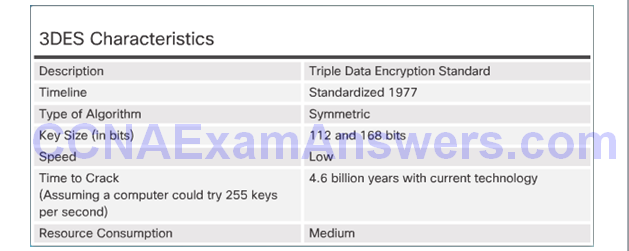
3DES Operation
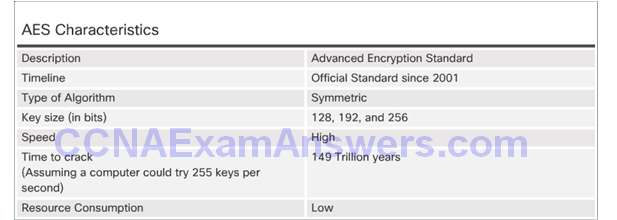
AES Origins
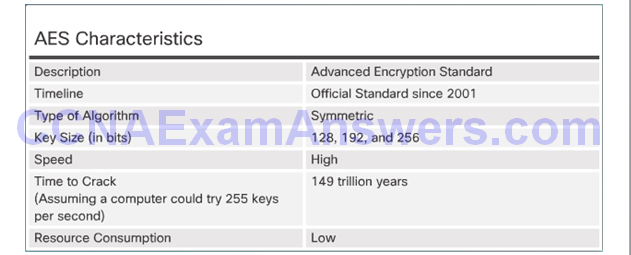
AES Summary

Topic 7.3.3: Alternate Encryption Algorithms
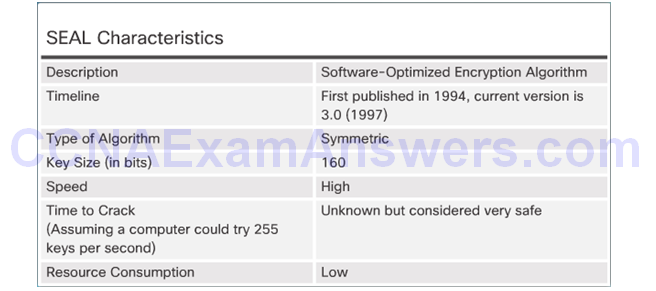
Software-Optimized Encryption Algorithm (SEAL)
SEAL has several restrictions:
- The Cisco router and the peer must support IPsec.
- The Cisco router and the other peer must run an IOS image that supports encryption.
- The router and the peer must not have hardware IPsec encryption.
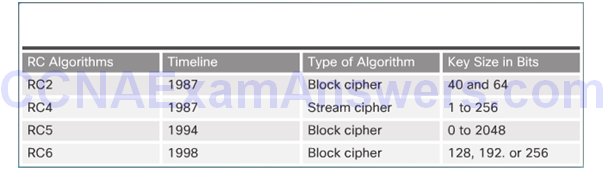
RC Algorithms
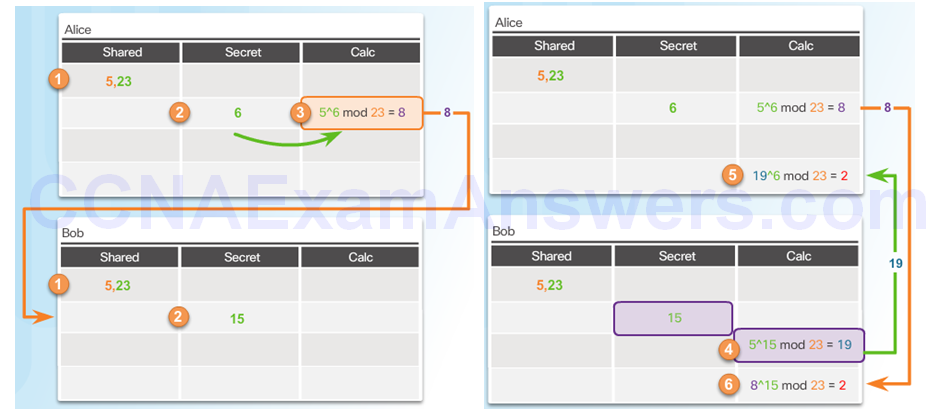
Topic 7.3.4: Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
Diffie-Hellman (DH) Algorithm
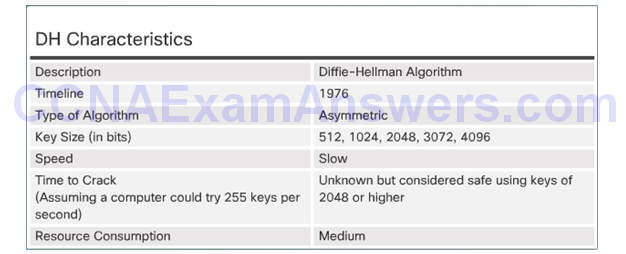
DH Operation
Section 7.4: Public Key Cryptography
Topic 7.4.1: Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Encryption
Asymmetric Key Algorithms
Four protocols that use asymmetric key algorithms:
- Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
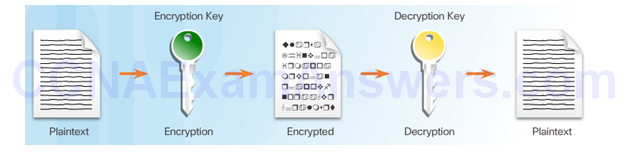
Public Key + Private Key = Confidentiality

Private Key + Public Key = Authenticity

Asymmetric Algorithms
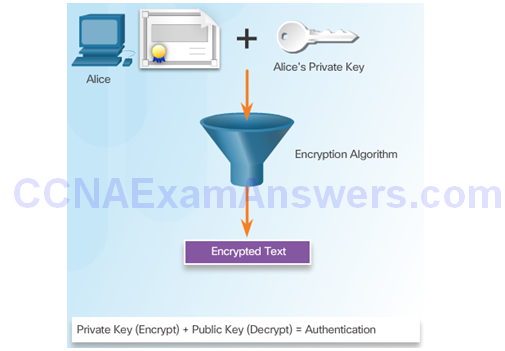
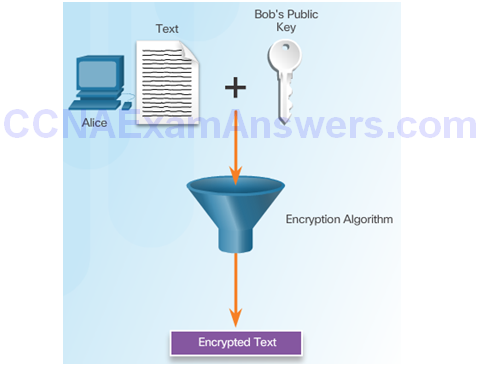
Alice Encrypts Message Using Bob’s Public Key
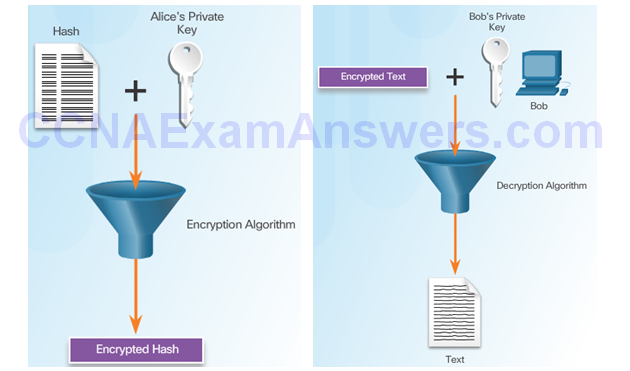
Alice Encrypts A Hash Using Bob’s Public Key
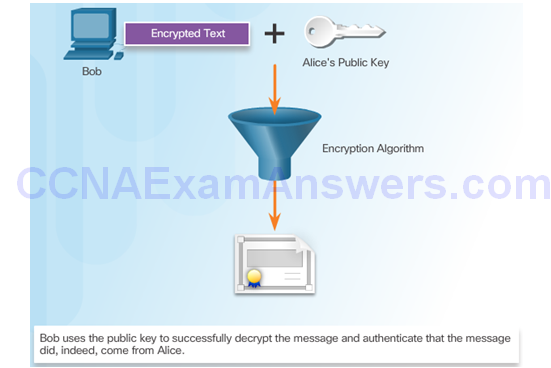
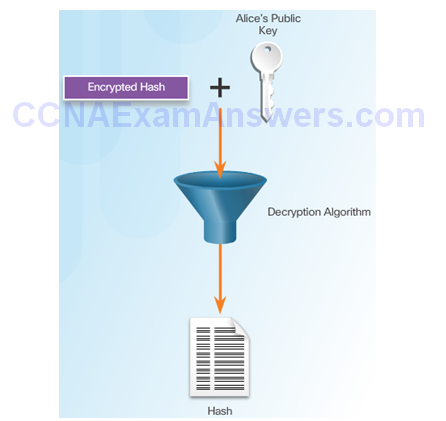
Bob Uses Alice’s Public Key to Decrypt Hash
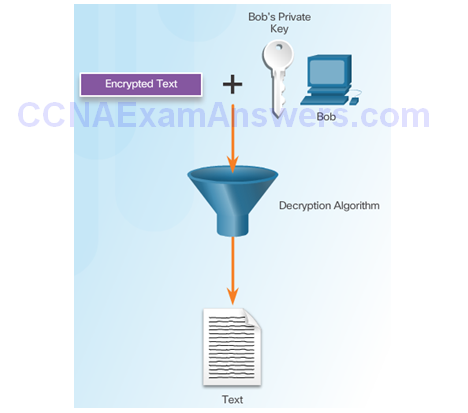
Bob Uses His Public Key to Decrypt Message
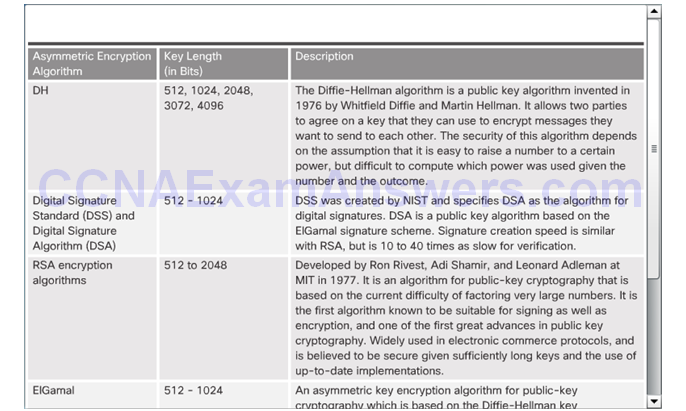
Types of Asymmetric Algorithms
Topic 7.4.2: Digital Signatures
Using Digital Signatures
Digital Signature Properties:
- Signature is authentic
- Signature is unalterable
- Signature is not reusable
- Signature cannot be repudiated
Code Signing
Digitally signing code provides several assurances about the code:
- The code is authentic and is actually sourced by the publisher.
- The code has not been modified since it left the software publisher.
- The publisher undeniably published the code.
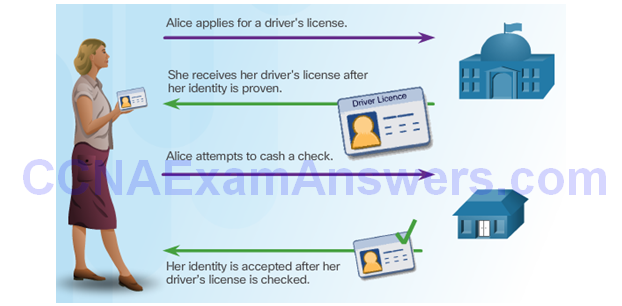
Digital Certificates

Using Digital Certificates
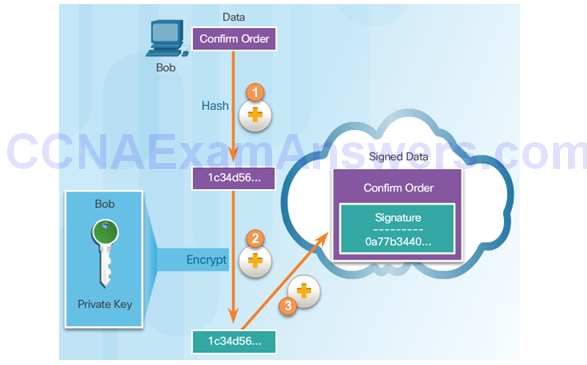
Sending a Digital Certificate
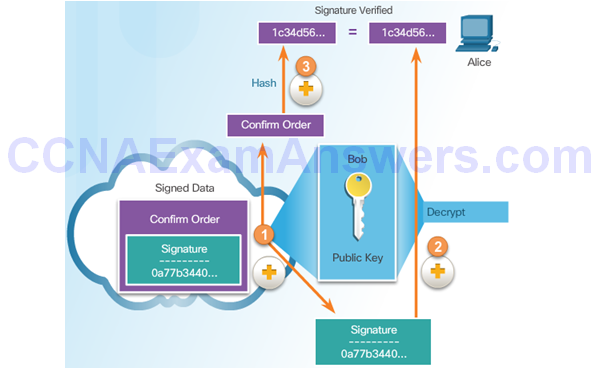
Receiving a Digital Certificate
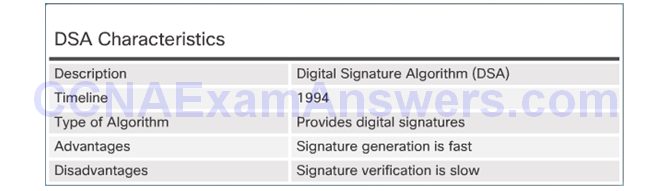
Digital Signature Algorithms
DSA Scorecard
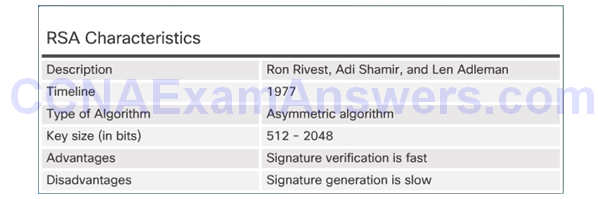
RSA Scorecard
Topic 7.4.3: Public Key Infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure Overview
PKI Framework
Elements of the PKI Framework

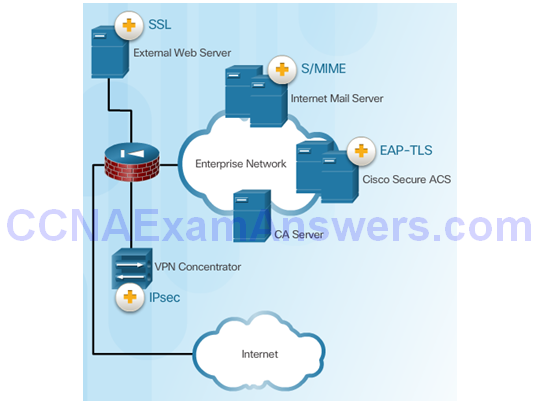
PKI Example
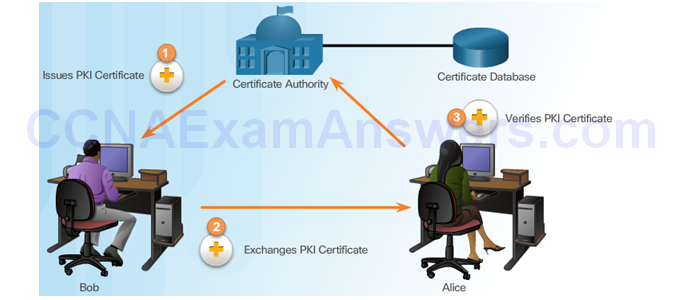
Certificate Authorities
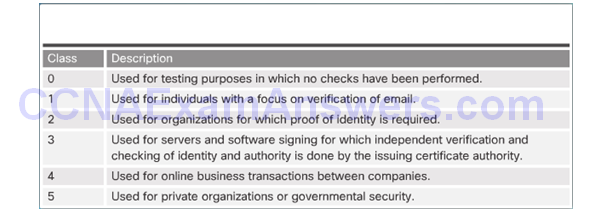
Interoperability of Different PKI Vendors
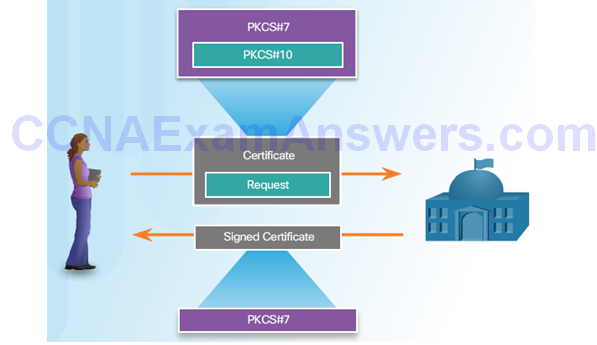
Public-Key Cryptography Standards

Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol
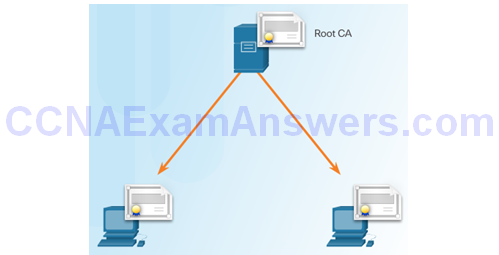
PKI Topologies
Single-Root PKI Topology
Cross Certified CA
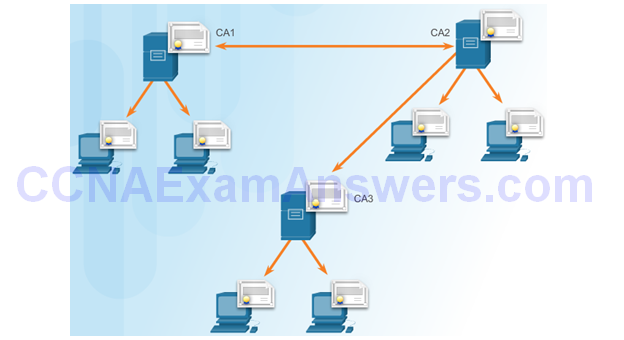
Hierarchical CA
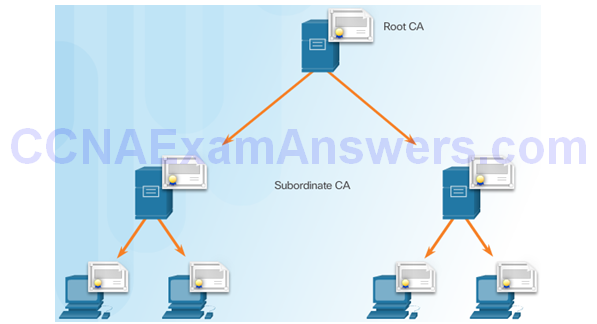
Registration Authority
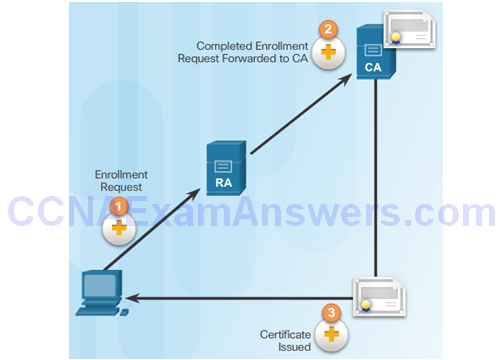
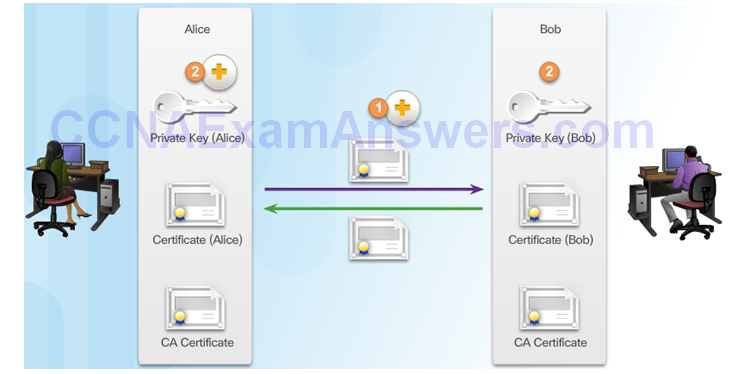
Digital Certificates and CAs
Retrieving CA Certificates
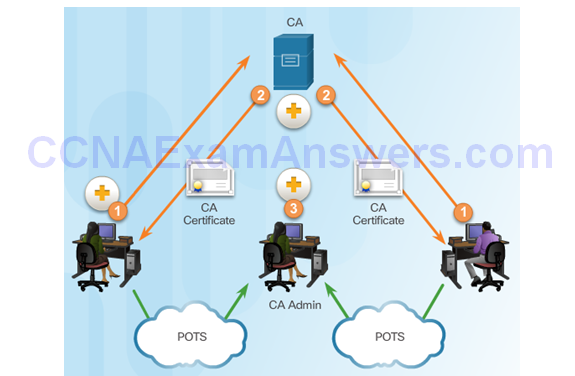
Submitting Certificate Requests to the CA
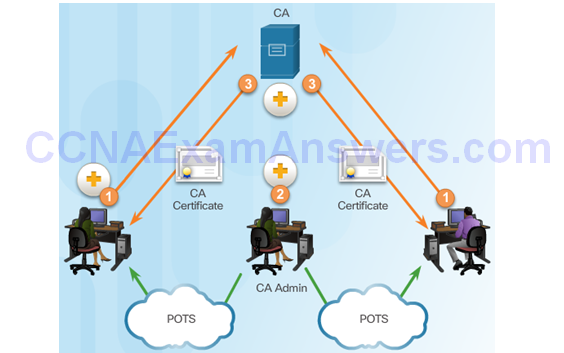
Peers Authenticate Each Other
Section 7.5: Summary
Chapter Objectives:
- Explain the areas of cryptology.
- Explain to two kinds of encryption algorithms.
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
[sociallocker id=”2293″][wpdm_package id=’3168′][/sociallocker]
