Modules 14 – 15: Network Application Communications Exam – ITN ( Version 7.00) – Network Application Communications Exam Answers
1. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1 . What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- beyond scope of the source address
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
2. A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- beyond scope of the source address
- no route to destination
3. A user issues a ping 10.10.14.67 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0. What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
4. Which protocol supports Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) for dynamic assignment of IPv6 addresses to a host?
- ARPv6
- DHCPv6
- ICMPv6
- UDP
5. Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description. (Not all options are used.)

6. A technician uses the ping 127.0.0.1 command. What is the technician testing?
- the TCP/IP stack on a network host
- connectivity between two adjacent Cisco devices
- connectivity between a PC and the default gateway
- connectivity between two PCs on the same network
- physical connectivity of a particular PC and the network
7. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is trying to troubleshoot connectivity between PC1 and PC2 and uses the tracert command from PC1 to do it. Based on the displayed output, where should the administrator begin troubleshooting?
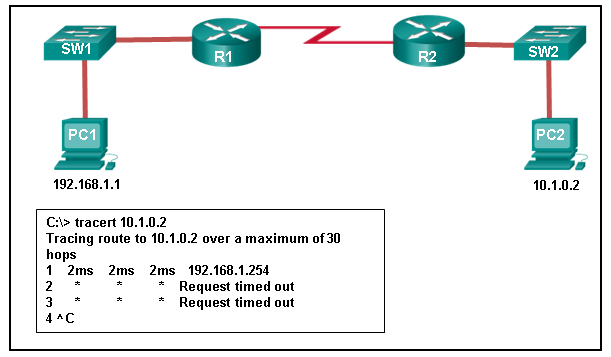
- PC2
- R1
- SW2
- R2
- SW1
8. Which protocol is used by the traceroute command to send and receive echo-requests and echo-replies?
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Telnet
- TCP
9. Which ICMPv6 message is sent when the IPv6 hop limit field of a packet is decremented to zero and the packet cannot be forwarded?
- network unreachable
- time exceeded
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
10. A user executes a traceroute over IPv6. At what point would a router in the path to the destination device drop the packet?
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches 255
- when the value of the Hop Limit field reaches zero
- when the router receives an ICMP time exceeded message
- when the target host responds with an ICMP echo reply message
11. What is the purpose of ICMP messages?
- to inform routers about network topology changes
- to ensure the delivery of an IP packet
- to provide feedback of IP packet transmissions
- to monitor the process of a domain name to IP address resolution
12. What source IP address does a router use by default when the traceroute command is issued?
- the highest configured IP address on the router
- a loopback IP address
- the IP address of the outbound interface
- the lowest configured IP address on the router
13. Match each description with an appropriate IP address. (Not all options are used.)
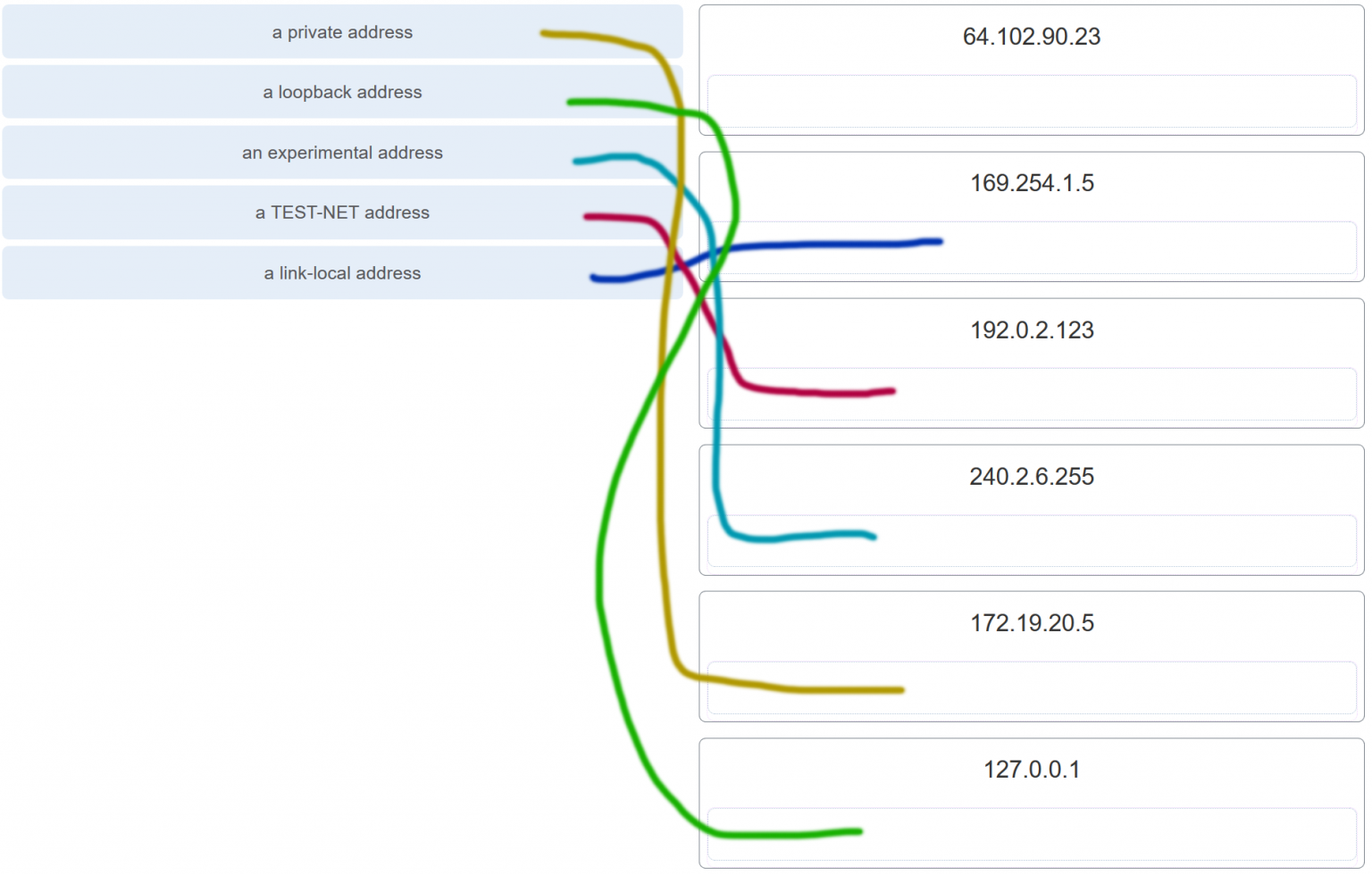
14. A user issues a ping 192.135.250.103 command and receives a response that includes a code of 1. What does this code represent?
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- network unreachable
15. Which subnet would include the address 192.168.1.96 as a usable host address?
- 192.168.1.64/26
- 192.168.1.32/27
- 192.168.1.32/28
- 192.168.1.64/29
16. Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
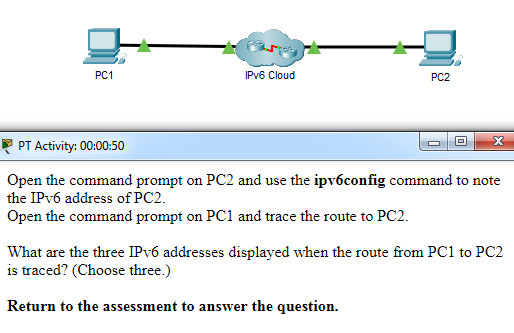
What are the three IPv6 addresses displayed when the route from PC1 to PC2 is traced? (Choose three.)
- 2001:DB8:1:1::1
- 2001:DB8:1:1::A
- 2001:DB8:1:2::2
- 2001:DB8:1:2::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::1
- 2001:DB8:1:3::2
- 2001:DB8:1:4::1
17. A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- a specially defined group of hosts
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- all hosts on the Internet
18. A host is transmitting a unicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- one specific host
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts on the Internet
- the closest neighbor on the same network
19. A user issues a ping fe80:65ab:dcc1::100 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4. What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
20. A user issues a ping 198.133.219.8 command and receives a response that includes a code of 0 . What does this code represent?
- network unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
21. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:3040:114::88 command and receives a response that includes a code of 4 . What does this code represent?
- port unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
22. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2. What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
- network unreachable
23. What is the prefix length notation for the subnet mask 255.255.255.224?
- /25
- /26
- /27
- /28
24. How many valid host addresses are available on an IPv4 subnet that is configured with a /26 mask?
- 254
- 190
- 192
- 62
- 64
25. Which subnet mask would be used if 5 host bits are available?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
26. A network administrator subnets the 192.168.10.0/24 network into subnets with /26 masks. How many equal-sized subnets are created?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 64
27. Match the subnetwork to a host address that would be included within the subnetwork. (Not all options are used.)
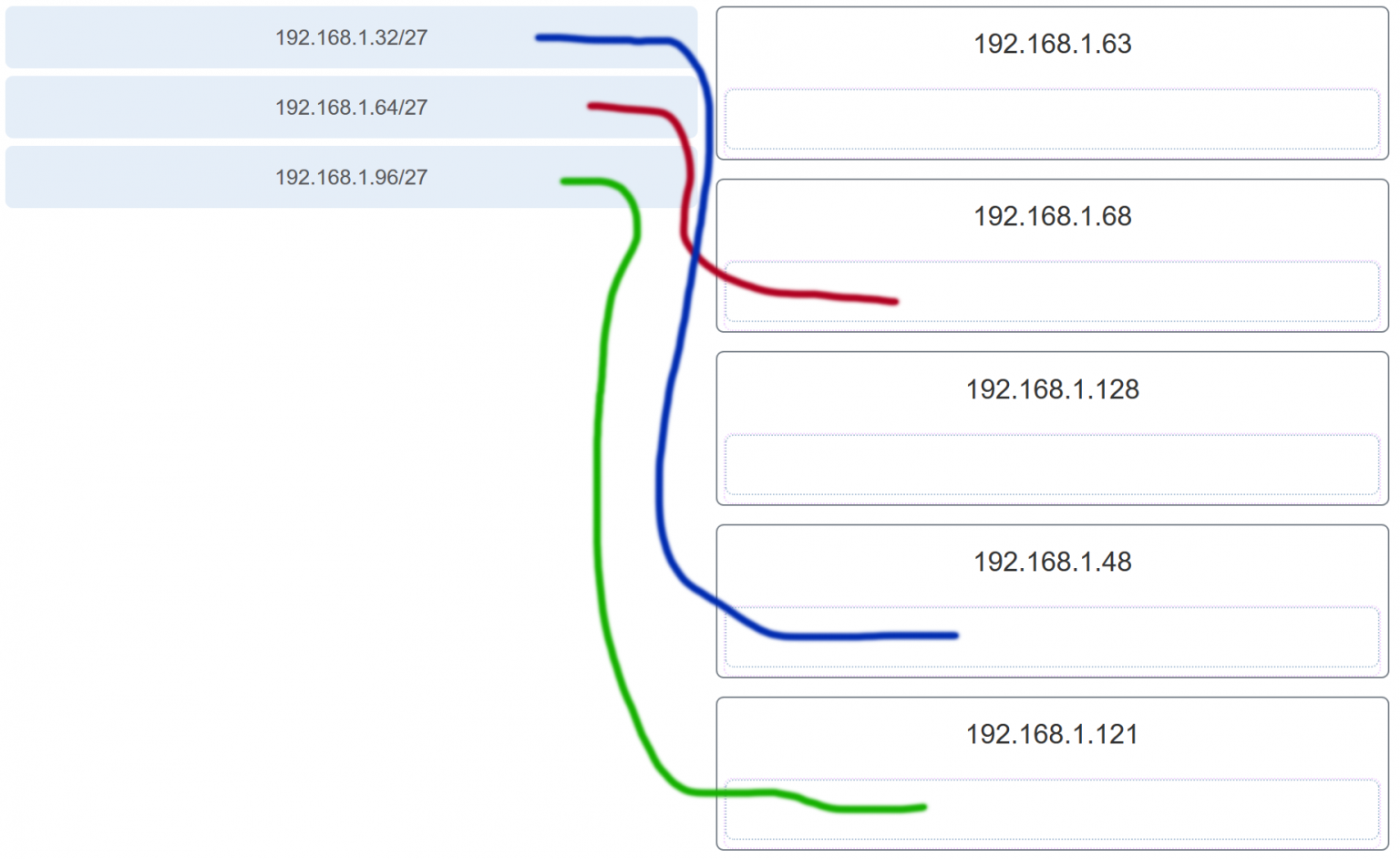
28. An administrator wants to create four subnetworks from the network address 192.168.1.0/24. What is the network address and subnet mask of the second useable subnet?
- subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.32
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.64
subnet mask 255.255.255.240 - subnetwork 192.168.1.128
subnet mask 255.255.255.192 - subnetwork 192.168.1.8
subnet mask 255.255.255.224
29. How many bits must be borrowed from the host portion of an address to accommodate a router with five connected networks?
- two
- three
- four
- five
30. How many host addresses are available on the 192.168.10.128/26 network?
- 30
- 32
- 60
- 62
- 64
31. How many host addresses are available on the network 172.16.128.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.252.0?
- 510
- 512
- 1022
- 1024
- 2046
- 2048
32. Match each IPv4 address to the appropriate address category. (Not all options are used.)
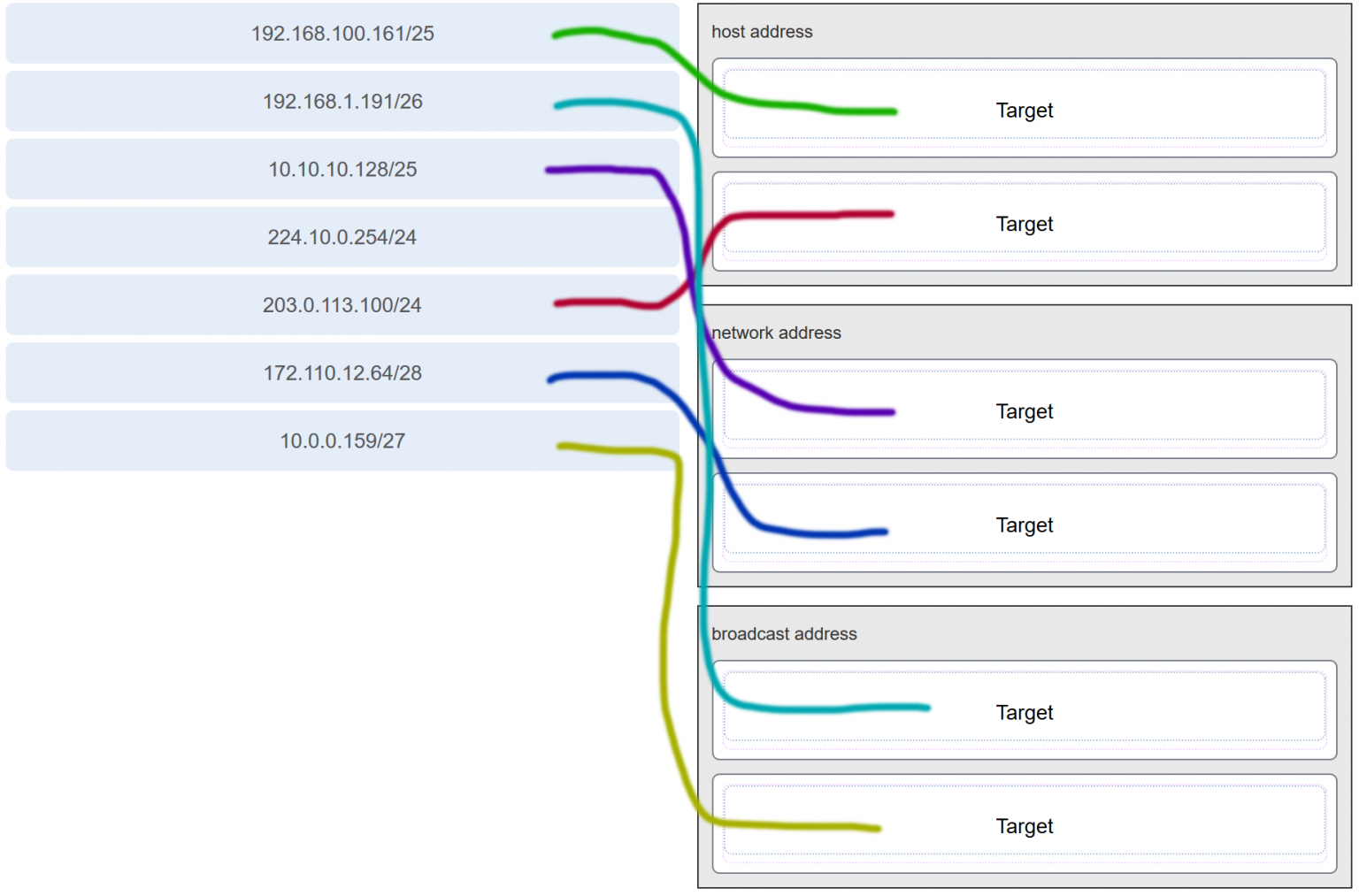
33. What three blocks of addresses are defined by RFC 1918 for private network use? (Choose three.)
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 100.64.0.0/14
- 169.254.0.0/16
- 239.0.0.0/8
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
34. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator must send a message to everyone on the router A network. What is the broadcast address for network 172.16.16.0/22?
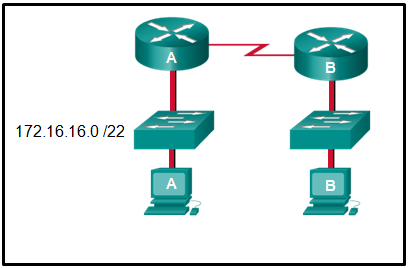
- 172.16.16.255
- 172.16.20.255
- 172.16.19.255
- 172.16.23.255
- 172.16.255.255
35. A site administrator has been told that a particular network at the site must accommodate 126 hosts. Which subnet mask would be used that contains the required number of host bits?
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.128
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.240
36. Refer to the exhibit. Considering the addresses already used and having to remain within the 10.16.10.0/24 network range, which subnet address could be assigned to the network containing 25 hosts?
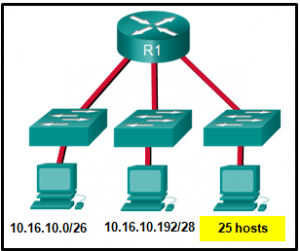
- 10.16.10.160/26
- 10.16.10.128/28
- 10.16.10.64/27
- 10.16.10.224/26
- 10.16.10.240/27
- 10.16.10.240/28
10.16.10.64/27
10.16.10.96/27
10.16.10.128/27
10.16.10.160/27
37. What is the usable number of host IP addresses on a network that has a /26 mask?
- 256
- 254
- 64
- 62
- 32
- 16
38. Which address prefix range is reserved for IPv4 multicast?
- 240.0.0.0 – 254.255.255.255
- 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
- 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255
- 127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
39. Refer to the exhibit. Match the network with the correct IP address and prefix that will satisfy the usable host addressing requirements for each network.
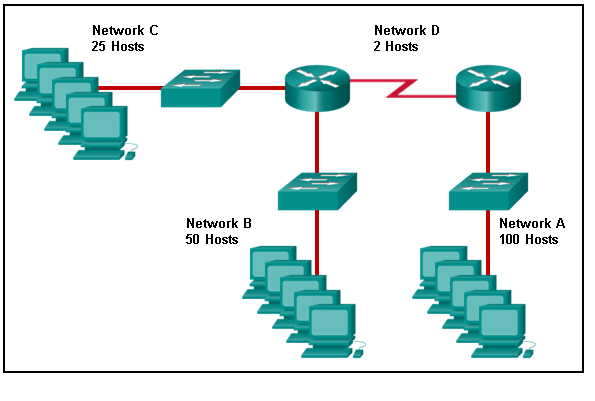
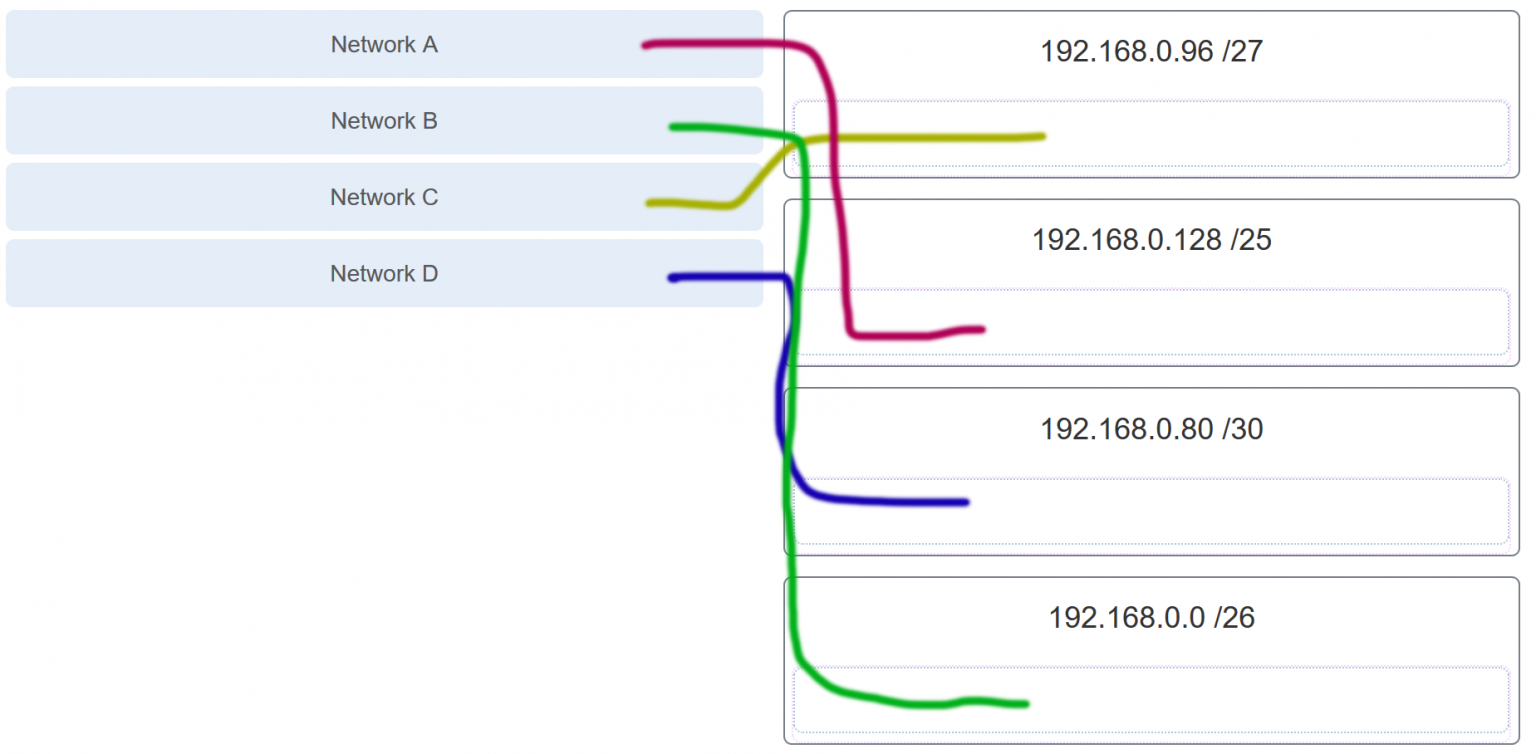
Network B needs to use 192.168.0.0 /26, which yields 64 host addresses.
Network C needs to use 192.168.0.96 /27, which yields 32 host addresses.
Network D needs to use 192.168.0.80/30, which yields 4 host addresses.
40. A high school in New York (school A) is using videoconferencing technology to establish student interactions with another high school (school B) in Russia. The videoconferencing is conducted between two end devices through the Internet. The network administrator of school A configures the end device with the IP address 209.165.201.10. The administrator sends a request for the IP address for the end device in school B and the response is 192.168.25.10. Neither school is using a VPN. The administrator knows immediately that this IP will not work. Why?
- This is a loopback address.
- This is a link-local address.
- This is a private IP address.
- There is an IP address conflict.
41. Which three addresses are valid public addresses? (Choose three.)
- 198.133.219.17
- 192.168.1.245
- 10.15.250.5
- 128.107.12.117
- 172.31.1.25
- 64.104.78.227
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
42. A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
43. A company has a network address of 192.168.1.64 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.192. The company wants to create two subnetworks that would contain 10 hosts and 18 hosts respectively. Which two networks would achieve that? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.1.16/28
- 192.168.1.64/27
- 192.168.1.128/27
- 192.168.1.96/28
- 192.168.1.192/28
44. Which address is a valid IPv6 link-local unicast address?
- FEC8:1::FFFF
- FD80::1:1234
- FE80::1:4545:6578:ABC1
- FE0A::100:7788:998F
- FC90:5678:4251:FFFF
45. Which of these addresses is the shortest abbreviation for the IP address: 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB:0000:0000:0057?
- 3FFE:1044::AB::57
- 3FFE:1044::00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0:0:00AB::0057
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::57
- 3FFE:1044:0000:0000:00AB::0057
1. Omit any leading 0s (zeros) in any hextet.
2. Replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros with a double colon (::) .
3. The double colon (::) can only be used once within an address.
46. A network administrator has received the IPv6 prefix 2001:DB8::/48 for subnetting. Assuming the administrator does not subnet into the interface ID portion of the address space, how many subnets can the administrator create from the /48 prefix?
- 16
- 256
- 4096
- 65536
47. Given IPv6 address prefix 2001:db8::/48, what will be the last subnet that is created if the subnet prefix is changed to /52?
- 2001:db8:0:f00::/52
- 2001:db8:0:8000::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f::/52
- 2001:db8:0:f000::/52
48. Consider the following range of addresses:
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A0:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A1:0000::
2001:0DB8:BC15:00A2:0000::
…
2001:0DB8:BC15:00AF:0000::
The prefix-length for the range of addresses is /60 .
49. What type of IPv6 address is FE80::1?
- loopback
- link-local
- multicast
- global unicast
50. Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnet portion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the site subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the sub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the subnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site?
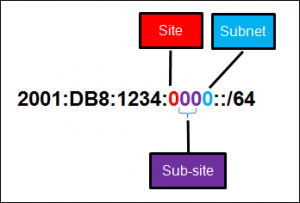
Refer to the exhibit. A company is deploying an IPv6 addressing scheme for its network. The company design document indicates that the subnetportion of the IPv6 addresses is used for the new hierarchical network design, with the s ite subsection to represent multiple geographical sites of the company, the s ub-site section to represent multiple campuses at each site, and the s ubnet section to indicate each network segment separated by routers. With such a scheme, what is the maximum number of subnets achieved per sub-site ?
- 0
- 4
- 16
- 256
51. What is used in the EUI-64 process to create an IPv6 interface ID on an IPv6 enabled interface?
- the MAC address of the IPv6 enabled interface
- a randomly generated 64-bit hexadecimal address
- an IPv6 address that is provided by a DHCPv6 server
- an IPv4 address that is configured on the interface
52. What is the prefix for the host address 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12AB::1/64?
- 2001:DB8:BC15
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:1
- 2001:DB8:BC15:A:12
53. An IPv6 enabled device sends a data packet with the destination address of FF02::1. What is the target of this packet?
- the one IPv6 device on the link that has been uniquely configured with this address
- all IPv6 enabled devices on the local link or network
- only IPv6 DHCP servers
- only IPv6 configured routers
54. Match the IPv6 address with the IPv6 address type. (Not all options are used.)

2001:DB8::BAF:3F57:FE94 is a global unicast address.
FF02::1 is the all node multicast address. Packets sent to this address will be received by all IPv6 hosts on the local link.
::1 is the IPv6 loopback address.
There are no examples of link local or unique local addresses provided.
55. Which IPv6 prefix is reserved for communication between devices on the same link?
- FC00::/7
- 2001::/32
- FE80::/10
- FDFF::/7
56. Which type of IPv6 address refers to any unicast address that is assigned to multiple hosts?
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- anycast
57. What are two types of IPv6 unicast addresses? (Choose two.)
- multicast
- loopback
- link-local
- anycast
- broadcast
58. Which service provides dynamic global IPv6 addressing to end devices without using a server that keeps a record of available IPv6 addresses?
- stateful DHCPv6
- SLAAC
- static IPv6 addressing
- stateless DHCPv6
59. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 3. What does this code represent?
- address unreachable
- network unreachable
- host unreachable
- protocol unreachable
60. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- the closest neighbor on the same network
61. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
62. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- all hosts with the same IP address
- all hosts on the Internet
63. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- one specific host
- directly connected network devices
- all hosts on the Internet
64. A host is transmitting a multicast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- a specially defined group of hosts
- all hosts in the same subnet
- directly connected network devices
- the closest neighbor on the same network
65. A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- the closest neighbor on the same network
- directly connected network devices
66. A host is transmitting a broadcast. Which host or hosts will receive it?
- all hosts in the same subnet
- one specific host
- all hosts on the Internet
- directly connected network devices
67. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
68. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
69. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
70. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
71. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
72. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
73. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
74. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
75. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
76. Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
77. A user issues a ping 2001:db8:FACE:39::10 command and receives a response that includes a code of 2 . What does this code represent?
- beyond scope of the source address
- communication with the destination administratively prohibited
- address unreachable
- no route to destination
