CCNA 4 Chapter 6 Exam Answers
-
A network administrator is deploying QoS with the ability to provide a special queue for voice traffic so that voice traffic is forwarded before network traffic in other queues. Which queuing method would be the best choice?
FIFO
WFQ
LLQ*
CBWFQ -
What are two characteristics of DiffServ QoS model? (Choose two.)
can divide network traffic into classes based on business requirements*
the easiest QoS model to deploy
delivers end to end QoS
uses the Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) to signal QoS requirements
groups all TCP flows into a single class* -
For classifying packets into classes with CBWFQ, what is the purpose of configuring a maximum packet limit for a class?
to control the maximum number of packets that can be received each second on an ingress interface
to control the maximum number of packets allowed in a single queue*
to control the maximum number of packets that can be forwarded each second on an egress interface
to control the maximum number of packets allowed to be discarded -
A network engineer is selecting a QoS method to control congestion on a VPN tunnel link between the headquarters site and a branch office. Which queuing method cannot be used to classify and control VPN traffic?
FIFO
LLQ
CBWFQ
WFQ* -
An administrator has mastered the use of access control lists (ACLs) and wants to deploy QoS by defining different traffic classes through the use of ACLs. Which queuing method provides this functionality?
CBWFQ*
WFQ
FCFS
FIFO -
Which queuing algorithm has only a single queue and treats all packets equally?
LLQ
FIFO*
WFQ
CBWFQ -
When QoS is implemented in a converged network, which two factors can be controlled to improve network performance for real-time traffic? (Choose two.)
packet addressing
delay*
jitter*
packet routing
link speed -
A network engineer performs a ping test and receives a value that shows the time it takes for a packet to travel from a source to a destination device and return. Which term describes the value?
bandwidth
latency*
priority
jitter -
What are two characteristics of voice traffic? (Choose two.)
Dropped voice packets are not retransmitted.*
Voice traffic requires at least 384 kbs of bandwidth.
Voice traffic latency should not exceed 150 ms.*
Voice traffic is unpredictable and inconsistent.
Voice traffic consumes lots of network resources. -
How does a Cisco router using tail drop handle congestion when a traffic queue becomes full?
The router will remove the packet in the front of the queue, move all other packets forward, and insert the just arrived packet at the end.
The router will drop any packet that arrives at the end of the queue.*
The router will remove the most recent data placed in the queue to make space for an arriving packet.
The router will only drop non delay-sensitive data that is close to the end of the queue. -
What are two characteristics of the best-effort QoS model? (Choose two.)
It treats all network packets in the same way.*
It allows end hosts to signal their QoS needs to the network.
It uses a connection-oriented approach with QoS.
It provides preferential treatment for voice packets.
It does not provide a delivery guarantee for packets.* -
What role do network devices play in the IntServ QoS model?
Network devices use QoS on a hop-by-hop basis to provide excellent scalability.
Network devices ensure that resources are available before traffic is allowed to be sent by a host through the network.*
Network devices are configured to service multiple classes of traffic and handle traffic as it may arrive.
Network devices provide a best-effort approach to forwarding traffic. -
Which QoS model is very resource intensive and provides the highest guarantee of QoS?
IntServ*
DiffServ
soft QoS
best-effort -
In QoS models, which type of traffic is commonly provided the most preferential treatment over all other application traffic?
voice traffic*
web traffic
email
file transfers -
What are two approaches to prevent packet loss due to congestion on an interface? (Choose two.)
Decrease buffer space.
Disable queuing mechanisms.
Increase link capacity.*
Drop lower-priority packets.*
Prevent bursts of traffic. -
What two fields are available in IPv4 and IPv6 headers to mark packets for QoS? (Choose two.)
Type of Service*
Priority
Traffic Class*
VLAN ID
Class of Service -
What is the benefit of deploying Layer 3 QoS marking across an enterprise network?
Layer 3 marking can be carried in the 802.1Q fields.
Layer 3 marking can carry the QoS information end-to-end.*
Layer 3 marking can be used to carry non-IP traffic.
Layer 3 marking can carry QoS information on switches that are not IP aware. -
Which QoS technology provides congestion avoidance by allowing TCP traffic to be throttled before buffers become full and tail drops occur?
traffic policing
best-effort
first-in, first-out
weighted random early detection* -
Refer to the exhibit. As traffic is forwarded out an egress interface with QoS treatment, which congestion avoidance technique is used?
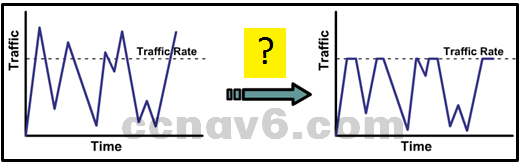
traffic shaping
weighted random early detection
classification and marking
traffic policing* -
Which QoS model uses the DSCP bits to mark packets and provides 64 possible classes of service?
best-effort
IntServ
DiffServ*
FIFO -
Which QoS technique retains excess packets in a separate queue for later transmission?
classifying
shaping*
queuing
marking
