16.5.2 Lab – Secure Network Devices
Topology
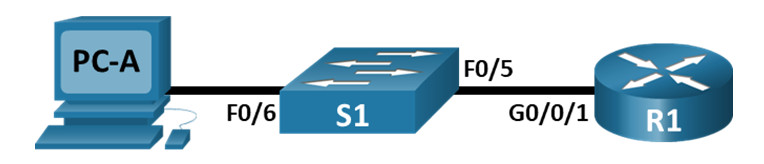
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S1 | VLAN 1 | 192.168.1.11 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 2: Configure Basic Security Measures on the Router
- Part 3: Configure Basic Security Measures on the Switch
Background / Scenario
It is recommended that all network devices be configured with at least a minimum set of best practice security commands. This includes end user devices, servers, and network devices, such as routers and switches.
In this lab, you will configure the network devices in the topology to accept SSH sessions for remote management. You will also use the IOS CLI to configure common, basic best practice security measures. You will then test the security measures to verify that they are properly implemented and working correctly.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as the interface IP addresses, device access, and passwords on the devices.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices shown in the topology and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Initialize and reload the router and switch.
Step 3: Configure the router and switch.
a. Console into the device and enable privileged EXEC mode.
b. Assign the device name according to the Addressing Table.
c. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were hostnames.
d. Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
e. Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
f. Assign cisco as the VTY password and enable login.
g. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
h. Configure and activate the G0/0/1 interface on the router using the information contained in the Addressing Table.
i. Configure the default SVI on the switch with the IP address information according to the Addressing Table.
j. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
Step 4: Configure PC-A.
a. Configure PC-A with an IP address and subnet mask.
b. Configure a default gateway for PC-A.
Step 5: Verify network connectivity.
Ping R1 and S1 from PC-A. If any of the pings fail, troubleshoot the connection.
Part 2: Configure Basic Security Measures on the Router
Step 1: Configure security measures.
a. Encrypt all clear-text passwords.
b. Configure the system to require a minimum 12-character password.
c. Change the passwords (privileged exec, console, and vty) to meet the new length requirement.
1) Set the privileged exec password to $cisco!PRIV*
2) Set the console password to $cisco!!CON*
3) Set the vty line password to $cisco!!VTY*
d. Configure the router to accept only SSH connections from remote locations
1) Configure the username SSHadmin with an encrypted password of 55HAdm!n2020
2) The router’s domain name should be set to ccna-lab.com
3) The key modulus should be 1024 bits.
e. Set security and best-practice configurations on the console and vty lines.
1) Users should be disconnected after 5 minutes of inactivity.
2) The router should not allow vty logins for 2 minutes if 3 failed login attempts occur within 1 minute.
Part 3: Configure security measures.
Step 1: Verify that all unused ports are disabled.
Router ports are disabled by default, but it is always prudent to verify that all unused ports are in an administratively down state. This can be quickly checked by issuing the show ip interface brief command. Any unused ports that are not in an administratively down state should be disabled using the shutdown command in interface configuration mode.
R1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/0/1 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up Serial0/1/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down Serial0/1/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Step 2: Verify that your security measures have been implemented correctly.
a. Use Tera Term on PC-A to telnet to R1.
Does R1 accept the Telnet connection? Explain.
No, the connection is refused. Telnet was disabled with the transport input ssh command.
b. Use Tera Term on PC-A to SSH to R1.
Does R1 accept the SSH connection?
Yes
c. Intentionally mistype the user and password information to see if login access is blocked after two attempts.
What happened after you failed to login the second time?
The connection to R1 was disconnected. If you attempt to reconnect within 30 seconds, the connection will be refused.
d. From your console session on the router, issue the show login command to view the login status. In the example below, the show login command was issued within the 120 second login blocking period and shows that the router is in Quiet-Mode. The router will not accept any login attempts for 111 more seconds.
R1# show login
A default login delay of 1 seconds is applied.
No Quiet-Mode access list has been configured.
All successful login is logged.
Router enabled to watch for login Attacks.
If more than 3 login failures occur in 60 seconds or less,
logins will be disabled for 120 seconds.
Router presently in Quiet-Mode.
Will remain in Quiet-Mode for 111 seconds.
Denying logins from all sources.
e. After the 120 seconds has expired, SSH to R1 again and login using the SSHadmin username and 55HAdm!n2020 for the password.
After you successfully logged in, what was displayed?
The R1 –MOTD banner.
f. Enter privileged EXEC mode and use $cisco!PRIV* for the password.
If you mistype this password, are you disconnected from your SSH session after three failed attempts within 60 seconds? Explain.
No. The login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 command only monitors session login attempts on VTY lines.
g. Issue the show running-config command at the privileged EXEC prompt to view the security settings you have applied.
Part 4: Configure Basic Security Measures on the Switch
Step 1: Configure security measures.
a. Encrypt all clear-text passwords.
b. Configure the system to require a minimum 12 character password
c. Change the passwords (privileged exec, console, and vty) to meet the new length requirement.
1) Set the privileged exec password to $cisco!PRIV*
2) Set the console password to $cisco!!CON*
3) Set the vty line password to $cisco!!VTY*
d. Configure the switch to accept only SSH connections from remote locations.
1) Configure the username SSHadmin with an encrypted password of 55HAdm!n2020
2) The switches domain name should be set to ccna-lab.com
3) The key modulus should be 1024 bits.
e. Set security and best-practice configurations on the console and vty lines.
1) Users should be disconnected after 5 minutes of inactivity.
2) The switch should not allow logins for 2 minutes if 3 failed login attempts occur within 1 minute.
f. Disable all of the unused ports.
Step 2: Verify all unused ports are disabled.
Switch ports are enabled, by default. Shut down all ports that are not in use on the switch.
a. You can verify the switch port status using the show ip interface brief command.
S1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 192.168.1.11 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/4 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/5 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/6 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/7 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/8 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/9 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/10 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/11 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/12 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/13 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/14 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/15 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/16 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/17 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/18 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/19 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/20 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/21 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/22 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/23 unassigned YES unset down down FastEthernet0/24 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset down down GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset down down
b. Use the interface range command to shut down multiple interfaces at a time
S1(config)# interface range f0/1–4 , f0/7-24 , g0/1-2 S1(config-if-range)# shutdown S1(config-if-range)# end
c. Verify that all inactive interfaces have been administratively shut down.
S1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol Vlan1 192.168.1.11 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/4 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/5 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/6 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/7 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/8 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/9 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/10 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/11 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/12 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/13 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/14 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/15 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/16 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/17 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/18 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/19 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/20 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/21 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/22 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/23 unassigned YES unset administratively down down FastEthernet0/24 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down GigabitEthernet0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Step 3: Verify that your security measures have been implemented correctly.
a. Verify that Telnet has been disabled on the switch.
b. SSH to the switch and intentionally mistype the user and password information to see if login access is blocked.
c. After the 30 seconds has expired, SSH to S1 again and log in using the SSHadmin username and 55HAdm!n2020 for the password.
Did the banner appear after you successfully logged in?
Yes
d. Enter privileged EXEC mode using $cisco!PRIV* as the password.
e. Issue the show running-config command at the privileged EXEC prompt to view the security settings you have applied.
Reflection Questions
1. The password cisco command was entered for the console and VTY lines in your basic configuration in Part 1. When is this password used after the best practice security measures have been applied?
This password will not be used any longer. Even though the password command still appears in the line sections of the running-config, this command was disabled as soon as the login local command was entered for those lines.
2. Are preconfigured passwords shorter than 10 characters affected by the security passwords min-length 12 command?
No. The security passwords min-length command only affects passwords that are entered after this command is issued. Any pre-existing passwords remain in effect. If they are changed, they will need to be at least 12 characters long.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1#sho run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3876 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! security passwords min-length 12 enable secret 5 $1$BmR8$GYubrKoVQHVy5jWU918MX/ ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip domain name ccna-lab.com ! ! login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 login on-success log ! ! subscriber templating ! ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! ! crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-950245734 enrollment selfsigned subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-950245734 revocation-check none rsakeypair TP-self-signed-950245734 ! ! crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-950245734 certificate self-signed 01 3082032E 30820216 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 05050030
Switch S1
no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$/Dix$FQPskX.44rHEKUDhJvJI40 ! username SSHadmin secret 5 $1$2ens$10nrX3Vj14Ofk.oMKtTrQ1 no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! ! no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name ccna-lab.com login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 ! ! spanning-tree mode pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending! ! interface FastEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 ! interface FastEthernet0/6 ! interface FastEthernet0/7 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan1 ip address 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 ! ip default-gateway 192.168.1.1 ip http server ip http secure-server ! ! banner motd ^C Unauthorized Access Is Prohibited ^C ! line con 0 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 145311021F07256A650B1C1B68 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 5 0 password 7 08654F471A1A0A56533D383D60 login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login ! end

there is no commands to do required actions.. 0/5