CCNA 3 Practice Skills PT Assessment Packet Tracer
[tabs][tab title=”Type A (v6.0)”]
CCNA Routing and Switchingz Scaling Networks
Practice Skills Assessment – EIGRP
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
1. Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
2. Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
3. Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Introduction
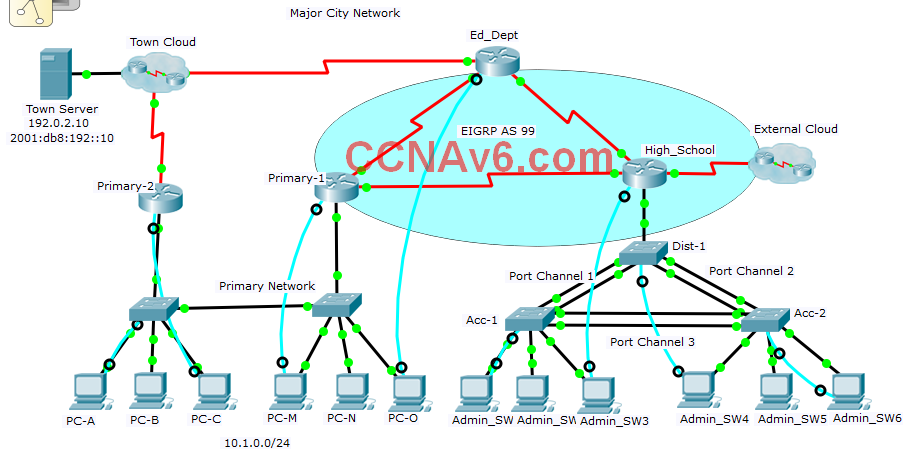
In this practice skills assessment, you will configure the Major City network with EIGRP routing and enhanced switching. The network is configured with both IPv4 and IPv6 on all devices. This will allow you to implement routing in both EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6. Your goal is to achieve full connectivity between all LAN hosts and the remote Town Server in both IPv4 and IPv6. For a full list of tasks, see below.
You are not required to configure the following:
• The Primary network switches
• Most of the network hosts and the Town Server
• The Town Cloud
All IOS device configurations should be completed from a direct terminal connection to the device console.
You will practice and be assessed on the following skills:
• Configuration of IPv4 and IPv6 default routes
• Configuration of EIGRP for IPv4
• Configuration of EIGRP for IPv6
• Customization of EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6
You will configure specific devices with the following:
Router Ed_Dept:
• IPv4 and IPv6 default route
• EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6
• Router ID
• Interface bandwidth
• Redistribution of default routes
Router Primary-1:
• EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6
• HSRP
• Interface bandwidth
• EIGRP for IPv4 passive interface
Router Primary-2:
• IPv4 default route
• HSRP
Router High_School:
• EIGRP for IPv4 and EIGRP for IPv6
• Router ID
• Interface bandwidth
• EIGRP for IPv4 passive interfaces
Switch Dist-1:
• RPVST+ activation
• RPVST primary root bridge priority
• EtherChannel channel groups
• Static trunking with native VLAN
• DTP
• VTP
Switch Acc-1:
• RPVST+ activation
• PortFast
• BPDU Guard
• EtherChannel channel groups
• Static trunking with native VLAN
• DTP
• VTP
Switch Acc-2:
• RPVST+ activation
• RPVST secondary root bridge priority
• EtherChannel channel groups
• Static trunking with native VLAN
• DTP
• VTP
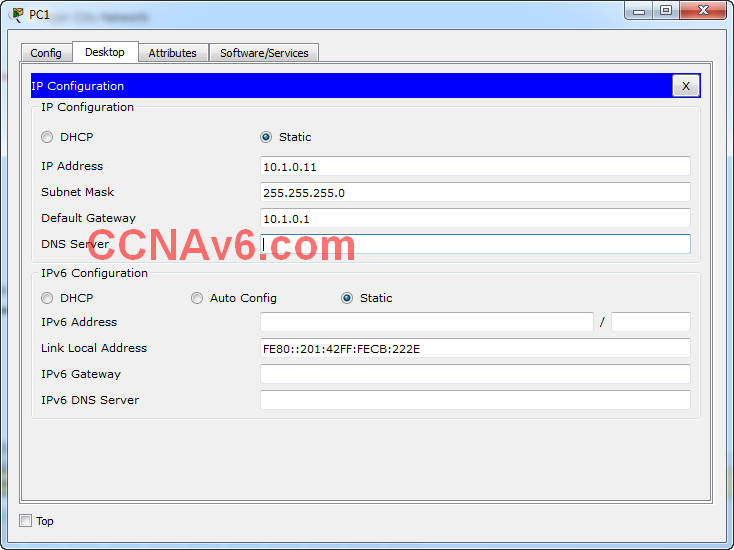
PC PC-A:
• Default gateway
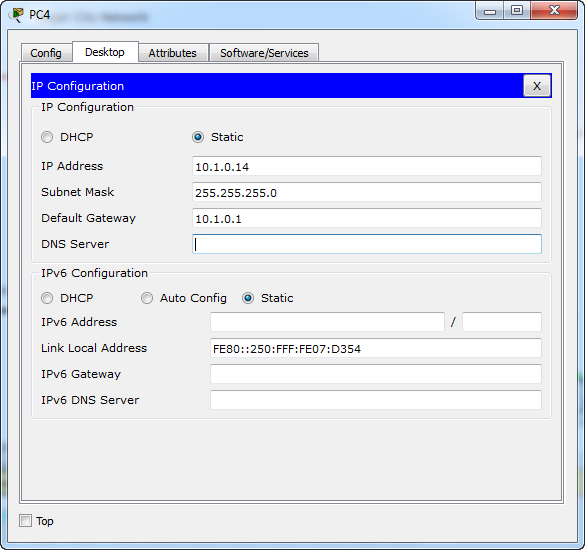
PC PC-M:
• Default gateway
Addressing Table
Use the following addresses to configure the network. Some addresses are preconfigured on devices that you are not required to configure, and are provided for reference purposes only.
| Device | Interface | Address Information |
| Ed_Dept (DataCenter) |
S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.9/30 |
| 2001:DB8:1A::1/64 FE80::1 link local |
||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.21/30 | |
| 2001:DB8:1B::1/64 FE80::1 link local |
||
| S0/1/0 | 203.0.113.18/30 | |
| 2001:DB8:99::2/64 FE80::1 link local |
||
| Primary-1 (Hospital_1) (CCNAv6.com) |
S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.10/30 |
| 2001:DB8:1A::2/64 FE80::2 link local |
||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.33/30 | |
| 2001:DB8:2::1/64 FE80::2 link local |
||
| G0/0 | 10.1.0.3/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:20::3/64 FE80::2 link local |
||
| Primary-2 (Clinic_10) |
S0/0/0 | 203.0.113.22/30 |
| 2001:DB8:100::2/64 FE80::22 link local |
||
| G0/0 | 10.1.0.2/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:20::2/64 FE80::22 link local |
||
| High_School (Hospital_2) |
S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.34/30 |
| 2001:DB8:2::2/64 FE80::3 link local |
||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.22/30 | |
| 2001:DB8:1B::2/64 FE80::3 link local |
||
| S0/1/0 | 2001:DB8:E::2/64 | |
| G0/0.10 | 10.10.0.1/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:3:10::1/64 FE80::3 link local |
||
| G0/0.15 | 10.15.0.1/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:3:15::1/64 FE80::3 link local |
||
| G0/0.20 | 10.20.0.1/24 | |
| 2001:DB8:3:20::1/64 FE80::3 link local |
||
| External (Remote) |
N/A | 2001:DB8:E::1/64 |
Instructions
Part I: EIGRP and HSRP Configuration
Step 1-1: Configure default static routes.
1. Configure IPv4 and IPv6 default static routes on the Ed_Dept router to the Town Cloud. Use the outgoing interface value in your configuration.
2. Configure the Primary-2 router with an IPv4 default route to the Town Cloud using the outgoing interface value.
Step 1-2: Configure EIGRP for IPv4
On the Ed_Dept, Primary-1, and High_School routers only, configure EIGRP for IPv4.
1. Use an AS number of 99 for all EIGRP routers.
2. Activate routing for the appropriate networks. Use inverse masks that specify only addresses within the networks.
3. Set the router IDs as follows:
– Ed_Dept: 1.1.1.1
– Primary-1: 2.2.2.2
– High_School: 3.3.3.3
Step 1-3: Configure EIGRP for IPv6.
Configure EIGRP for IPv6 on the Ed_Dept, Primary-1, and High_School routers.
1. Use an AS number of 99 for all EIGRP routers.
2. Activate routing for the appropriate networks. Note that router Primary-2 does not use EIGRP routing.
3. Set the router IDs as follows:
– Ed_Dept: 1.1.1.1
– Primary-1: 2.2.2.2
– High_School: 3.3.3.3
Important: Your EIGRP for IPv6 configuration can only be checked for this assessment indirectly. After you have completed your configuration, in order to get credit for EIGRP for IPv6 routing, you must do the following:
1. On host PC-B, go to the Desktop tab and open the Command Prompt.
2. Enter telnet 2001:DB8:E::1
3. If your EIGRP for IPv6 configuration is correct, you should be able to reach the External router with the address above. Authenticate your Telnet session with the password cisco.
4. Move to privileged EXEC mode using the password admin.
5. Activate the G0/0 interface of the router.
6. Exit the Telnet session.
In your score report, for EIGRP for IPv6 interface activation, you will see an item for activation of the router External G0/0 interface. If you got this item correct, you have correctly activated EIGRPv6 on the required routers.
Step 1-4: Customize EIGRP for IPv4 operation.
Customize EIGRP for IPv4 as follows:
1. Set the interface bandwidth for the two EIGRP interfaces on router Ed_Dept to match the interface clock speed.
2. Set the interface bandwidth for the serial interfaces on routers Primary-1 and High_School to match the bandwidth of the interfaces on router Ed_Dept.
3. Configure all LAN interfaces, both physical and virtual, so that EIGRP messages are not sent into the LANs.
4. Configure Ed_Dept so that the static default route is automatically shared with the other EIGRP routers.
Step 1-5: Customize EIGRP for IPv6 operation.
Configure the Ed_Dept router to automatically share the IPv6 static route with the other EIGRP for IPv6 routers.
Step 1-6: Configure HSRP as follows:
Configure the Primary-1 and Primary-2 routers with HSRP. In this scenario, the hosts on the Primary network are to be dual-homed. In other words, if the active Primary-1 router fails, the Primary network hosts will use the Primary-2 router as their gateway. Although connectivity to the rest of the Major City network will not be available, the hosts will be able to access the Internet through the Primary-2 router, because HSRP will switch to using it as the default gateway for the hosts. You will configure Primary-1 as the active router, and Primary-2 as the backup using HSRP.
Requirements:
1. Configure router Primary-1 with HSRP as follows:
– The group number is 1.
– Virtual gateway IP address: 10.1.0.1
– The router should immediately become the active router.
– The priority should be 150.
2. Configure router Primary-2 as follows:
– Virtual gateway IP address: 10.1.0.1
– Leave all other HSRP values at the default.
3. In order for the Primary-2 router to provide connectivity to the Internet, it requires a default route to be configured as you are directed in Step 1-1 above. This router is not configured with EIGRP.
4. Configure hosts PC-A and PC-M with the correct default gateway addresses.
Part II: Enhanced Switching Technologies
Step 2-1: Configure link aggregation with EtherChannel.
Configure the three EtherChannel links between switches Dist-1, Acc-1, and Acc-2:
| Port Channel | Device | Interfaces |
| 1 | Dist-1 | Fa0/3 Fa0/4 |
| Acc-1 | Fa0/3 Fa0/4 |
|
| 2 | Dist-1 | Fa0/5 Fa0/6 |
| Acc-2 | Fa0/5 Fa0/6 |
|
| 3 | Acc-1 | Fa0/1 Fa0/2 |
| Acc-2 | Fa0/1 Fa0/2 |
1. Configure EtherChannels with the LACP protocol using the information in the table.
2. Both sides of the channel should ask if the other side is willing to participate in the channel.
Step 2-2: Configure Trunking.
Configure trunking as follows:
1. The trunk between High_School and Dist-1 should be active.
2. The trunk between High_School and Dist-1 should use the native VLAN value preconfigured on High_School.
3. Configure all of the port channel interfaces as static trunks with the appropriate native VLAN.
4. Disable DTP negotiation on all of the trunks.
Step 2-3: Configure VTP.
Configure switches Dist-1, Acc-1, and Acc-2 with VTP as follows:
1. Switch Dist-1 should be the only VTP server in the domain.
2. The other switches in the domain should be configured as clients.
Use the following values:
– VTP domain: TownEd
– VTP Password: TWE_123!
Note: In order for the VLANs to be distributed from the VTP server to the client switches, you may need to take action to increment the VTP revision number. This can be done by adding and deleting a VLAN on the VTP server after the switches in the domain have complete VTP configurations and trunking is operating correctly.
Step 2-4: Configure RPVST.
Configure switches Dist-1, Acc-1, and Acc-2 with RPVST+ as follows:
1. All of the switches should use Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol.
2. Switch Dist-1 should be configured as the root bridge for VLANs 10, 15, and 20 with a priority value of 24576.
3. Switch Acc-2 should be configured as the secondary root bridge for VLANs 10, 15, and 20 with a priority value of 28672.
4. Switch Acc-1 should be left with its default priority.
Step 2-5: Configure PortFast and BPDU Guard.
Configure only switch Acc-1 as follows:
1. Configure all of the access ports that are assigned to VLANs with BPDU Guard.
2. Configure the same ports with PortFast.
If EIGRP is configured properly, full adjacencies should be formed between all routers in the EIGRP AS. The hosts on the LANs should be able to communicate with the hosts on all other LANs and the Town Server using both IPv4 and IPv6.
Answers
NOTE: Use cable Console to connect PCs and Routers (Switchs)

DateCenter/Ed_Dept Router:
R1name>en R1name#conf ter R1name(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0 R1name(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing R1name(config)#ipv6 route ::/0 s0/1/0 R1name(config)#router eigrp 99 R1name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.8 0.0.0.3 R1name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.20 0.0.0.3 R1name(config-router)#eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1 R1name(config-router)#exit R1name(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 99 R1name(config-rtr)#eigrp router-id 1.1.1.1 R1name(config-rtr)#no shutdown R1name(config-rtr)#exit R1name(config)#int s0/0/0 R1name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R1name(config-if)#int s0/0/1 R1name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R1name(config-if)#exit R1name(config)#int s0/1/0 R1name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R1name(config-if)#exit R1name(config)#int s0/0/0 R1name(config-if)#bandwidth 2000 R1name(config-if)#exit R1name(config)#int s0/0/1 R1name(config-if)#bandwidth 2000 R1name(config-if)#exit R1name(config)#router eigrp 99 R1name(config-router)#redistribute static R1name(config-router)#exit R1name(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 99 R1name(config-rtr)#redistribute static R1name(config-rtr)#
Clinic_10/Primary-2 Router:
R2-2name>en R2-2name#conf ter R2-2name(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0/0 R2-2name(config)#int g0/0 R2-2name(config-if)#standby 1 ip 10.1.0.1 R2-2name(config-if)#standby version 2
Hospital_1/Primary-1 Router
R2name>en R2name#conf ter R2name(config)#router eigrp 99 R2name(config-router)#network 10.1.0.0 0.0.0.255 R2name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.8 0.0.0.3 R2name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.32 0.0.0.3 R2name(config-router)#eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 R2name(config-router)#exit R2name(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing R2name(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 99 R2name(config-rtr)#eigrp router-id 2.2.2.2 R2name(config-rtr)#no shutdown R2name(config-rtr)#exit R2name(config)#int s0/0/1 R2name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R2name(config-if)#int s0/0/0 R2name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R2name(config-if)#int g0/0 R2name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R2name(config-if)#exit R2name(config)#int s0/0/0 R2name(config-if)#bandwidth 2000 R2name(config-if)#exit R2name(config)#router eigrp 99 R2name(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0 R2name(config-router)#exit R2name(config)#int g0/0 R2name(config-if)#standby 1 ip 10.1.0.1 R2name(config-if)#standby 1 preempt R2name(config-if)#standby 1 priority 150 R2name(config-if)#standby version 2
Hospital_2 / High_School Router
R3name>en R3name#conf ter R3name(config)#router eigrp 99 R3name(config-router)#network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.255 R3name(config-router)#network 10.15.0.0 0.0.0.255 R3name(config-router)#network 10.20.0.0 0.0.0.255 R3name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.20 0.0.0.3 R3name(config-router)#network 192.168.100.32 0.0.0.3 R3name(config-router)#eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 R3name(config-router)#exit R3name(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing R3name(config)#ipv6 router eigrp 99 R3name(config-rtr)#eigrp router-id 3.3.3.3 R3name(config-rtr)#no shutdown R3name(config-rtr)#exit R3name(config)#int g0/0.10 R3name(config-subif)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-subif)#int g0/0.15 R3name(config-subif)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-subif)#int g0/0.20 R3name(config-subif)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-subif)#exit R3name(configpv6 eigrp)#int s0/0/0 R3name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-if)#int s0/0/1 R3name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-if)#int s0/1/0 R3name(config-if)#ipv6 eigrp 99 R3name(config-if)#exit R3name(config)#int s0/0/1 R3name(config-if)#bandwidth 2000 R3name(config-if)#exit R3name(config)#router eigrp 99 R3name(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0.10 R3name(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0.15 R3name(config-router)#passive-interface g0/0.20 R3name(config-router)#exit R3name(config)#int g0/0 R3name(config-if)#no sh R3name(config-if)#
Net_1 / Dist-1 Switch
Change VTP domain and VTP Password to match your exam
S1name>en S1name#conf ter S1name(config)#int range f0/3-4 S1name(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode active S1name(config-if-range)#int range f0/5-6 S1name(config-if-range)#channel-group 2 mode active S1name(config-if-range)#exit S1name(config)#int g0/1 S1name(config-if)#no shutdown S1name(config-if)#int g0/1 S1name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S1name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1name(config-if)#int g0/1 S1name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S1name(config-if)#int range f0/3-4 S1name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S1name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 1 S1name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S1name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S1name(config-if)#int range f0/5-6 S1name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S1name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 2 S1name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S1name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S1name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S1name(config-if)#exit S1name(config)#vtp mode server S1name(config)#vtp domain TownEd S1name(config)#vtp password TWE_123! S1name(config)#vtp version 2 S1name(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S1name(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10,15,20 priority 24576
FL_1 Switch / Acc-1 Switch:
Change VTP domain and VTP Password to match your exam
S2name>en S2name#conf ter S2name(config)#int range f0/3-4 S2name(config-if-range)#channel-group 1 mode active S2name(config-if-range)#int range f0/1-2 S2name(config-if-range)#channel-group 3 mode active S2name(config-if-range)#exit S2name(config)#int range f0/3-4 S2name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S2name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 1 S2name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S2name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S2name(config-if)#int range f0/1-2 S2name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S2name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 3 S2name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S2name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S2name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S2name(config-if)#exit S2name(config)#vtp mode client S2name(config)#vtp domain TownEd S2name(config)#vtp password TWE_123! S2name(config)#vtp version 2 S2name(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S2name(config)#int range f0/10-24 S2name(config-if-range)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable S2name(config-if-range)#spanning-tree portfast
Fl_2 Switch / Acc-2 Switch
Change VTP domain and VTP Password to match your exam
S3name> S3name>en S3name#conf ter S3name(config)#int range f0/5-6 S3name(config-if-range)#channel-group 2 mode active S3name(config-if-range)#int range f0/1-2 S3name(config-if-range)#channel-group 3 mode active S3name(config-if-range)#exit S3name(config-if-range)# S3name(config)#int range f0/5-6 S3name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S3name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 2 S3name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S3name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S3name(config-if)#int range f0/1-2 S3name(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk S3name(config-if-range)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3name(config-if-range)#int port-channel 3 S3name(config-if)#switchport mode trunk S3name(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 99 S3name(config-if)#switchport nonegotiate S3name(config-if)#exit S3name(config)#vtp mode client S3name(config)#vtp domain TownEd S3name(config)#vtp password TWE_123! S3name(config)#spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst S3name(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10,15,20 priority 28672
On host PC-B, go to the Desktop tab and open the Command Prompt.
– Enter telnet 2001:DB8:E::1
– Authenticate your Telnet session with the password cisco.
– Move to privileged EXEC mode using the password admin.
External>en External#conf ter External(config)#int g0/0 External(config-if)#no sh
Hosts PC-A / PC-M:
Gateway IP address: 10.1.0.1
Download Full: pka file, PDF file and Answers – 100% Score
[sociallocker id=”8545″]
Password unzip: ccnav6.com
[wpdm_package id=’10122′][/sociallocker][/tab] [tab title=”Type B (v5.03)”]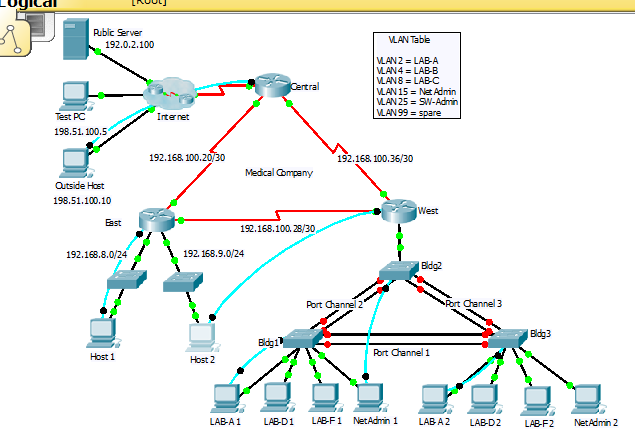
CCNA 3 Routing and Switching – Scaling Networks
EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment – Packet Tracer
t
A few things to keep in mind while completing this activity:
- Do not use the browser Back button or close or reload any exam windows during the exam.
- Do not close Packet Tracer when you are done. It will close automatically.
- Click the Submit Assessment button in the browser window to submit your work.
Introduction
In Part I of this practice skills assessment, you will configure routing and ACLs. You will configure dynamic routing with EIGRP for IPv4 and static and default routes. In addition, you will configure two access control lists.
In Part II of this practice skills assessment, you will configure the Medical Company network with RPVST+, port security, EtherChannel, DHCP, VLANs and trunking, and routing between VLANs. In addition you will perform an initial configuration on a switch, secure unused switch ports and secure SVIs. You will also control access to the switch management network with an access control list.
All IOS device configurations should be completed from a direct terminal connection to the device console from an available host.
Some values that are required to complete the configurations have not been given to you. In those cases, create the values that you need to complete the requirements. These values may include certain IP addresses, passwords, interface descriptions, banner text, and other values.
For the sake of time, many repetitive but important configuration tasks have been omitted from this activity. Many of these tasks, especially those related to device security, are essential elements of a network configuration. The intent of this activity is not to diminish the importance of full device configurations.
You will practice and be assessed on the following skills:
- Configuration of initial device settings
- IPv4 address assignment and configuration
- Configuration and addressing of device interfaces
- Configuration of the EIGRP for IPv4 routing protocol
- Configuration of a default route
- Configuration of ACL to limit device access
- Configuration of switch management settings including SSH
- Configuration of port security
- Configuration of unused switch ports according to security best practices
- Configuration of RPVST+
- Configuration of EtherChannel
- Configuration of a router as a DHCP server
- Configuration of VLANs and trunks
- Configuration of routing between VLANs
You are required to do the following:
East:
- Configure initial device settings.
- Configure interfaces with IPv4 addresses, descriptions, and other settings.
- Configure and customize EIGRP for IPv4.
Central:
- Configure interfaces with IPv4 addresses, descriptions, and other settings.
- Configure and customize EIGRP for IPv4.
- Configure named and numbered ACLs.
- Configure and propagate a default route through EIGRP for IPv4.
West:
- Configure interfaces with IPv4 addresses, descriptions, and other settings.
- Configure DHCP pools and excluded addresses.
- Configure routing between VLANs.
- Configure EIGRP for IPv4.
- Configure EIGRP for IPv4 route summarization.
- Configure an ACL to limit access to the switch management network.
Bldg1:
- Create and name VLANs.
- Configure EtherChannel.
- Configure trunking.
- Assign access ports to VLANs.
- Configure remote management settings.
- Activate and configure RPVST+.
- Secure unused switch ports.
- Configure port security.
Bldg2:
- Create and name VLANs.
- Configure EtherChannel.
- Configure trunking.
- Assign access ports to VLANs.
- Configure remote management settings with SSH.
- Activate RPVST+.
Bldg3:
- Create and name VLANs.
- Configure EtherChannel.
- Configure trunking.
- Assign access ports to VLANs.
- Configure remote management settings.
- Activate and configure RPVST+.
Internal PC hosts:
- Configure as DHCP clients.
- Assign Static IPv4 addresses where indicated.
Tables
Note: You are provided with the networks that interfaces should be configured on. Unless you are told to do differently in the detailed instructions below, you are free to choose the host addresses to assign.
Addressing Table:
| Device | Interface | Network | Configuration Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| East | S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.20/30 | any address in the network |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.28/30 | any address in the network | |
| G0/0 | 192.168.8.0/24 | first host address | |
| G0/1 | 192.168.9.0/24 | first host address | |
| Central | S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.20/30 | any address in the network |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.36/30 | any address in the network | |
| S0/1/0 | 203.0.113.16/29 | (The first address in this network is already in use on the ISP router. Any other address in the network can be assigned to this interface.) | |
| West | S0/0/0 | 192.168.100.28/30 | any address in the network |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.100.36/30 | any address in the network | |
| G0/1.2 | 10.10.2.0/24 | first address in the network | |
| G0/1.4 | 10.10.4.0/24 | first address in the network | |
| G0/1.8 | 10.10.8.0/24 | first address in the network | |
| G0/1.15 | 10.10.15.0/24 | first address in the network | |
| G0/1.25 | 10.10.25.0/24 | first address in the network | |
| Bldg1 | SVI | 10.10.25.0/24 | the highest address in the network |
| Bldg2 | SVI | 10.10.25.0/24 | the second to the highest address in the network |
| Bldg3 | SVI | 10.10.25.0/24 | the third to the highest address in the network |
| Host 1 | NIC | 192.168.8.0/24 | any available address in the network |
| Host 2 | NIC | 192.168.9.0/24 | any available address in the network |
| NetAdmin 1 | NIC | 10.10.15.0/24 | any available address in the network |
| NetAdmin 2 | NIC | 10.10.15.0/24 | any available address in the network |
VLAN Switch Port Assignment Table:
| VLAN | Name | Network | Device | Switch Ports |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | LAB-A | 10.10.2.0/24 | Bldg1 | Fa0/5 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/7 | |||
| 4 | LAB-B | 10.10.4.0/24 | Bldg1 | Fa0/10 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/10 | |||
| 8 | LAB-C | 10.10.8.0/24 | Bldg1 | Fa0/15 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/15 | |||
| 15 | NetAdmin | 10.10.15.0/24 | Bldg1 | Fa0/24 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/24 | |||
| 25 | SW-Admin | 10.10.25.0/24 | Bldg1 | SVI |
| Bldg2 | SVI | |||
| Bldg3 | SVI | |||
| 99 | spare | N/A | Bldg1 | all unused ports |
Port-Channel Group Interfaces:
| Channel | Device | Interfaces |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bldg1 | Fa0/1, Fa0/2 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/1, Fa0/2 | |
| 2 | Bldg1 | Fa0/3, Fa0/4 |
| Bldg2 | Fa0/3, Fa0/4 | |
| 3 | Bldg2 | Fa0/5, Fa0/6 |
| Bldg3 | Fa0/5, Fa0/6 |

Instructions
All configurations must be performed through a direct terminal connection to the device console lines from an available host.
Part I: EIGRP Router Configuration
Step 1: Plan the Addressing.
Determine the IP addresses that you will use for the required interfaces on the devices and LAN hosts. Follow the configuration details provided in the Addressing Table.
Step 2: Configure East.
Configure East with initial settings:
- Configure the router host name: East. This value must be entered exactly as it appears here.
- Prevent the router from attempting to resolve command line entries to IP addresses.
- Protect device configurations from unauthorized access with an encrypted secret password.
- Secure the router console and remote access lines.
- Prevent system status messages from interrupting console output.
- Configure a message-of-the-day banner.
- Encrypt all clear text passwords.
Step 3: Configure the Router Interfaces.
Use the information in the addressing table to configure the interfaces of all routers for full connectivity with the following:
- Configure IP addressing.
- Descriptions for all physical interfaces.
- Configure DCE settings where required. Use a rate of 128000.
- The Ethernet subinterfaces on West will be configured later in this assessment.
Step 4: Configure inter-VLAN routing on West.
Configure router West to route between VLANs using information in the Addressing Table and VLAN Switch Port Assignment Table. The VLANs will be configured on the switches later in this assessment.
- Do not route the VLAN 99 network.
Step 5: Configure EIGRP Routing and a default route.
a. On all routers:
- Configure EIGRP for IPv4 to route between the internal networks. Use ASN 100.
- Use the precise wild card masks for all network statements.
- You are not required to route the SW-Admin VLAN network over EIGRP.
- Prevent routing updates from being sent on the LAN networks. Do not use the default keyword version of the command to do so.
- Prevent EIGRP for IPv4 from performing automatic route summarization on all routers.
b. On the Central router:
- Configure a default route to the Internet. Use the exit interface argument.
- Configure EIGRP for IPv4 to distribute the default route to the other routers.
Step 6: Customize EIGRP for IPv4.
Customize EIGRP for IPv4 by performing the following configuration tasks:
- Set the bandwidth of the link between East and Central to 128 kb/s.
- Create a summary route for the LANs connected to Bldg3. It should include all networks from 10.10.0.0 to 10.10.15.0.
- Do not include the SW-Admin VLAN network in the summary route.
- Configure EIGRP for IPv4 with the route summary so that it will be sent to the other routers. Be sure to configure the summary on all of the appropriate interfaces.
Step 7: Configure Access Control Lists.
You will configure two access control lists in this step. You should use the any and host keywords in the ACL statements where appropriate. The ACL specifications are as follows:
a. Restrict access to the vty lines on Central with an ACL:
- Create a named standard ACL using the name TELNET-BLOCK. Be sure that you enter this name exactly as it appears in this instruction.
- Allow only Test PC to access the vty lines of Central.
- No other Internet hosts (including hosts not visible in the topology) should be able to access the vty lines of Central.
- Your solution should consist of one ACL statement.
b. Block ping requests from the Internet with an ACL:
- Use access list number 101.
- Allow only Test PC to ping addresses within the Medical Company network. Only echo messages should be permitted.
- Prevent all other Internet hosts (not only the Internet hosts visible in the topology) from pinging addresses inside the Medical Company network. Block echo messages only.
- All other traffic should be allowed.
- Your ACL should consist of three statements.
- Your ACL should be placed in the most efficient location as possible to conserve network bandwidth and device processing resources.
c. Control access to the management interfaces (SVI) of the three switches attached to West as follows:
- Create a standard ACL.
- Use the number 1 for the list.
- Permit only addresses from the NetAdmin VLAN network to access any address on the SW-Admin VLAN network.
- Hosts on the NetAdmin VLAN network should be able to reach all other destinations.
- Your list should consist of one statement.
Part II: Switching and DHCP Configuration
Step 1: Create and name VLANs.
On all three switches that are attached to West, create and name the VLANs shown in the VLAN Table.
- The VLAN names that you configure must match the values in the table exactly.
- Each switch should be configured with all of the VLANs shown in the table.
Step 2: Assign switch ports to VLANs.
Using the VLAN table, assign the switch ports to the VLANs you created in Step 1, as follows:
- All switch ports that you assign to VLANs should be configured to static access mode.
- All switch ports that you assign to VLANs should be activated.
Step 3: Configure the SVIs.
Refer to the Addressing Table. Create and address the SVIs on all three of the switches that are attached to West. Configure the switches so that they can communicate with hosts on other networks. Full connectivity will be established after routing between VLANs has been configured later in this assessment.
Step 4: Configure Trunking and EtherChannel.
a. Use the information in the Port-Channel Groups table to configure EtherChannel as follows:
- Use LACP.
- The switch ports on both sides of Channels 1 and 2 should initiate negotiations for channel establishment.
- The switch ports on the Bldg2 side of the Channel 3 should initiate negotiations with the switch ports on Bldg3.
- The switch ports on the Bldg3 side of Channel 3 should not initiate negotiations with the switch ports on the other side of the channel.
- All channels should be ready to forward data after they have been configured.
b. Configure all port-channel interfaces as trunks.
c. Configure static trunking on the switch port on Bldg2 that is connected to West.
Step 5: Configure Rapid PVST+.
Configure Rapid PVST+ settings as follows:
a. Activate Rapid PVST+ and set root priorities.
- All three switches should be configured to run Rapid PVST+.
- Bldg1 should be configured as root primary for VLAN 2 and VLAN 4 using the default primary priority values.
- Bldg1 should be configured as root secondary for VLAN 8 and VLAN 15 using the default secondary priority values.
- Bldg3 should be configured as root primary for VLAN 8 and VLAN 15 using the default primary priority values.
- Bldg3 should be configured as root secondary for VLAN 2 and VLAN 4 using the default secondary priority values.
b. Activate PortFast and BPDU Guard on the active Bldg3 switch access ports.
- Configure PortFast on all access ports that are connected to hosts.
- Activate BPDU Guard on all access ports that are connected to hosts.
Step 6: Configure switch security.
You are required to complete the following only on some of the devices in the network for this assessment. In reality, security should be configured on all devices in the network.
a. Secure unused switch ports. Following security best practices, do the following on Bldg1 only:
- Shutdown all unused switch ports.
- Configure all unused switch ports as static access ports.
- Ensure that all unused switch ports have been assigned to VLAN 99.
b. Configure port security on all active access ports on Bldg1.
- Each switch port should accept only two MAC addresses before a security action occurs.
- The learned MAC addresses should be recorded in the running configuration.
- If a security violation occurs, the switch ports should provide notification that a violation has occurred but not place the interface in an err-disabled state.
c. On Bldg2, configure the virtual terminal lines to accept only SSH connections.
- Use a domain name of ccnaPTSA.com.
- Use a modulus value of 1024.
- Configure SSH version 2.
- Configure the vty lines to only accept SSH connections.
- Configure user-based authentication for the SSH connections with a user name of netadmin and a secret password of SSH_secret9. The user name and password must match the values provided here exactly in case, punctuation, and spelling.
Step 7: Configure West as a DHCP server for the hosts attached to the Bldg1 and Bldg2 switches.
Configure three DHCP pools as follows:
- Create a DHCP pool for hosts on VLAN 2 using the pool name vlan2pool.
- Create a DHCP pool for hosts on VLAN 4 using the pool name vlan4pool.
- Create a DHCP pool for hosts on VLAN 8 using the pool name vlan8pool.
- All VLAN pool names must match the provided values exactly.
- Exclude the first five addresses from each pool.
- Configure a DNS server address of 192.168.200.225.
- All hosts should be able to communication with hosts on other networks.
Step 8: Configure host addressing.
All hosts should be able to ping each other and the two external servers after they have been addressed.
- Hosts on VLANs 2, 4, and 8 should be configured to receive addresses dynamically over DHCP.
- Hosts on VLAN 15 should be addressed statically as indicated in the addressing table. Once configured, the hosts should be able to ping hosts on other networks.
- Hosts on the LANs attached to East should be statically assigned addressing that enables them to communicate with hosts on other networks.
Instruction:
1. Before begin please read the whole assesment.
2. And Replace the names on the code depending on the set you have. (replace the hostnames, access-list name, vlan names)
3. To apply theese commands in each device go to global Configuration mode { (config)# } and paste them all there without changing.
EAST or Site1
hostname Bldg-1
no ip domain-lookup
enable secret cisco
line console 0
logging synchronous
password cisco
login
line vty 0 4
password cisco
login
service password-encryption
banner motd #Authorized access only #
interface serial 0/0/0
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.21 255.255.255.252
description HQ
clock rate 128000
no shutdown
interface serial 0/0/1
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.29 255.255.255.252
description HQ
no shutdown
interface gi 0/0
ip address 192.168.8.1 255.255.255.0
description SITE
no shutdown
interface gi 0/1
ip address 192.168.9.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
router eigrp 100
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/1
network 192.168.100.20 0.0.0.3
network 192.168.100.28 0.0.0.3
network 192.168.8.0 0.0.0.255
network 192.168.9.0 0.0.0.255
no auto-summary
WEST or Site2
hostname Bldg-2
interface serial 0/0/0
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.30 255.255.255.252
description SITE
no shutdown
interface serial 0/0/1
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.38 255.255.255.252
description SITE
no shutdown
interface gig 0/1
description SITE
no shutdown
interface gi 0/1.2
encapsulation dot1q 2
ip address 10.10.2.1 255.255.255.0
interface gi 0/1.4
encapsulation dot1q 4
ip address 10.10.4.1 255.255.255.0
interface gi 0/1.8
encapsulation dot1q 8
ip address 10.10.8.1 255.255.255.0
interface gi 0/1.15
encapsulation dot1q 15
ip address 10.10.15.1 255.255.255.0
interface gi 0/1.25
encapsulation dot1q 25
ip address 10.10.25.1 255.255.255.0
exit
router eigrp 100
passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/1
network 192.168.100.28 0.0.0.3
network 192.168.100.36 0.0.0.3
network 10.10.2.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.4.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.8.0 0.0.0.255
network 10.10.15.0 0.0.0.255
no auto-summary
passive-interface g0/1.2
passive-interface g0/1.4
passive-interface g0/1.8
passive-interface g0/1.15
interface serial 0/0/0
ip summary-address eigrp 100 10.10.0.0 255.255.240.0
interface serial 0/0/1
ip summary-address eigrp 100 10.10.0.0 255.255.240.0
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.2.1 10.10.2.5
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.4.1 10.10.4.5
ip dhcp excluded-address 10.10.8.1 10.10.8.5
ip dhcp pool vlan2pool
network 10.10.2.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 10.10.2.1
dns-server 192.168.200.225
ip dhcp pool vlan4pool
network 10.10.4.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 10.10.4.1
dns-server 192.168.200.225
ip dhcp pool vlan8pool
network 10.10.8.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 10.10.8.1
dns-server 192.168.200.225
access-list 1 permit 10.10.15.0 0.0.0.255
interface gi0/1.25
ip access-group 1 out
Central or HQ
Hostname Main
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/1/0
interface serial 0/0/0
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.22 255.255.255.252
description SITE
no shutdown
interface serial 0/0/1
bandwidth 128
ip address 192.168.100.37 255.255.255.252
description SITE
clock rate 128000
no shutdown
interface serial 0/1/0
bandwidth 128
ip address 203.0.113.18 255.255.255.248
description INTERNET
no shutdown
router eigrp 100
redistribute static
network 192.168.100.20 0.0.0.3
network 192.168.100.36 0.0.0.3
no auto-summary
ip access-list standard telnetBlock
permit host 198.51.100.5
access-list 101 permit icmp 198.51.100.5 0.0.0.0 any echo
access-list 101 deny icmp any any echo
access-list 101 permit ip any any
line vty 0 4
access-class telnetBlock in
interface serial 0/1/0
ip access-group 101 in
BLDG1 or SWA
Hostname FL-A ip default-gateway 10.10.25.1 vlan 2 name dept1 vlan 4 name dept2 vlan 8 name dept3 vlan 15 name IT vlan 25 name manage vlan 99 name safe interface vlan 25 ip address 10.10.25.254 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface fa0/5 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 2 interface fa0/10 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 4 interface fa0/15 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 8 interface fa0/24 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 15 interface range fa0/6-9,fa0/11-14,fa0/16-23 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 99 shutdown interface range gi0/1-2 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 99 shutdown interface range fa0/1-2 channel-group 1 mode active interface port-channel 1 switchport mode trunk interface range fa0/3-4 channel-group 2 mode active interface port-channel 2 switchport mode trunk spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree vlan 2 root primary spanning-tree vlan 4 root primary spanning-tree vlan 8 root secondary spanning-tree vlan 15 root secondary interface fa0/5 switchport port-security switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security maximum 2 switchport port-security mac-address sticky interface fa0/10 switchport port-security switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security maximum 2 switchport port-security mac-address sticky interface fa0/15 switchport port-security switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security maximum 2 switchport port-security mac-address sticky interface fa0/24 switchport port-security switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security maximum 2 switchport port-security mac-address sticky
BLDG2 or SWB
hostname FL-B ip default-gateway 10.10.25.1 vlan 2 name dept1 vlan 4 name dept2 vlan 8 name dept3 vlan 15 name IT vlan 25 name manage vlan 99 name safe interface vlan 25 ip address 10.10.25.253 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface gi 0/1 switchport mode trunk interface range fa0/3-4 channel-group 2 mode active interface port-channel 2 switchport mode trunk interface range fa0/5-6 channel-group 3 mode active interface port-channel 3 switchport mode trunk spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst ip ssh version 2 ip domain-name ccnaPTSA.com crypto key generate rsa 1024 username netadmin secret SSHsecret9 line vty 0 4 login local transport input ssh line vty 5 15 login local transport input ssh
BLDG3 or SW-C
Hostname FL-C ip default-gateway 10.10.25.1 vlan 2 name dept1 vlan 4 name dept2 vlan 8 name dept3 vlan 15 name IT vlan 25 name manage vlan 99 name safe interface vlan 25 ip address 10.10.25.252 255.255.255.0 no shutdown interface fa0/7 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 2 interface fa0/10 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 4 interface fa0/15 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 8 interface fa0/24 switchport mode acces switchport acces vlan 15 interface range fa0/1-2 channel-group 1 mode active no shutdown interface port-channel 1 switchport mode trunk interface range fa0/5-6 channel-group 3 mode passive no shutdown interface port-channel 3 switchport mode trunk spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree vlan 2 root secondary spanning-tree vlan 4 root secondary spanning-tree vlan 8 root primary spanning-tree vlan 15 root primary interface range fa0/7, fa0/10, fa0/15, fa0/24 spanning-tree portfast spanning-tree bpduguard enable no shutdown
——————————————————————————
***HOSTS***
Assighn Ip addersses and Defauld gateways Accordingly.
For the hosts which do not have an IP address set them as dhcp.
