CCNA 3 Chapter 3 Exam Answers
-
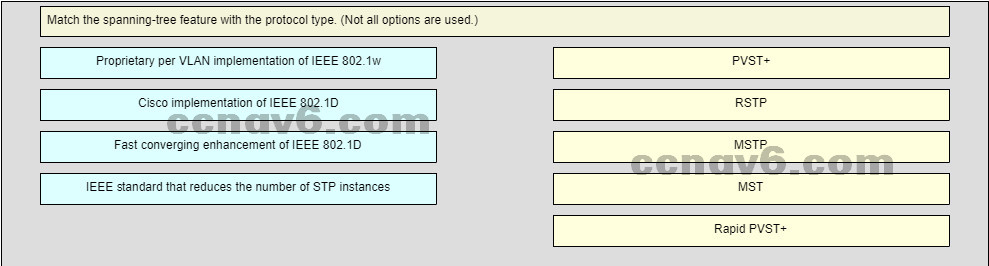
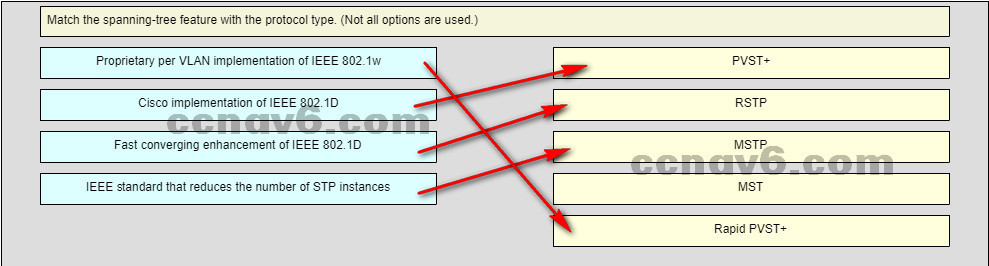
Which two network design features require Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to ensure correct network operation?
(Choose two.)
redundant links between Layer 2 switches*
link-state dynamic routing that provides redundant routes
implementing VLANs to contain broadcasts
static default routes
removing single points of failure with multiple Layer 2 switches*
-
Which STP priority configuration would ensure that a switch would always be the root switch?
spanning-tree vlan 10 root primary
spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 0*
spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096
spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 61440
-
What additional information is contained in the 12-bit extended system ID of a BPDU?
MAC address
port ID
VLAN ID*
IP address
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which trunk link will not forward any traffic after the root bridge election process is complete?
Trunk1
Trunk2*
Trunk3
Trunk4
-
Which protocol provides up to 16 instances of RSTP, combines many VLANs with the same physical and logical topology into a common RSTP instance, and provides support for PortFast, BPDU guard, BPDU filter, root guard, and loop guard?
STP
PVST+
MST*
Rapid PVST+
-
Fill in the blank. Do not use abbreviations.
The spanning-tree _______ global configuration command is used to enable Rapid PVST+.
Correct Answer: mode rapid-pvst
-
What port type is used to interconnect switches in a switch stack?
designated
StackWise*
root
edge
-
Which spanning tree standard supports only one root bridge so that traffic from all VLANs flows over the same path?
802.1D*
PVST+
Rapid PVST
MST
-
Which two types of spanning tree protocols can cause suboptimal traffic flows because they assume only one spanning-tree instance for the entire bridged network?
(Choose two.)
STP*
MSTP
RSTP*
PVST+
Rapid PVST+
-
What is the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)?
prevents Layer 2 loops*
prevents routing loops on a router
creates smaller broadcast domains
allows Cisco devices to exchange routing table updates
creates smaller collision domains
-
Which port state will switch ports immediately transition to when configured for PortFast?
learning
forwarding*
blocking
listening
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which switch will be elected the root bridge and which switch will place a port in blocking mode?
(Choose two.)
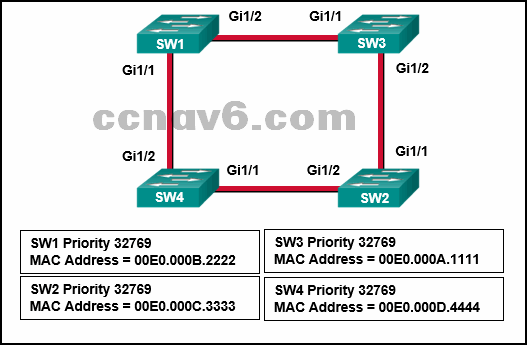
SW1 will become the root bridge.
SW2 will get a port blocked.
SW4 will become the root bridge.
SW2 will become the root bridge.
SW3 will become the root bridge.*
SW4 will get a port blocked.*
-
What is an advantage of PVST+?
PVST+ optimizes performance on the network through autoselection of the root bridge.
PVST+ reduces bandwidth consumption compared to traditional implementations of STP that use CST.
PVST+ requires fewer CPU cycles for all the switches in the network.
PVST+ optimizes performance on the network through load sharing.*
-
To obtain an overview of the spanning tree status of a switched network, a network engineer issues the show spanning-tree command on a switch. Which two items of information
will this command display?(Choose two.)
The role of the ports in all VLANs.*
The root bridge BID.*
The number of broadcasts received on each root port.
The IP address of the management VLAN interface.
The status of native VLAN ports.
-
A network administrator is preparing the implementation of Rapid PVST+ on a production network. How are the Rapid PVST+ link types determined on the switch interfaces?
Link types can only be determined if PortFast has been configured.
Link types are determined automatically.*
Link types must be configured with specific port configuration commands.
Link types can only be configured on access ports configured with a single VLAN.
-
If no bridge priority is configured in PVST, which criteria is considered when electing the root bridge?
highest MAC address
lowest MAC address*
lowest IP address
highest IP address
-
What is the outcome of a Layer 2 broadcast storm?
ARP broadcast requests are returned to the transmitting host.
CSMA/CD will cause each host to continue transmitting frames.
New traffic is discarded by the switch because it is unable to be processed.*
Routers will take over the forwarding of frames as switches become congested.
-
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question. Which switch is the root bridge?
Switch_4
Switch_1
Switch_3
Switch_2
-
In which two port states does a switch learn MAC addresses and process BPDUs in a PVST network?
(Choose two.)
disabled
blocking
listening
forwarding*
learning*
-
Which Cisco switch feature ensures that configured switch edge ports do not cause Layer 2 loops if a port is mistakenly connected to another switch?
PortFast
extended system ID
BPDU guard*
PVST+
-
What is a characteristic of a Layer 2 loop?
Broadcast frames are forwarded back to the sending switch.*
The Time-to-Live attribute of a frame is set to infinity.
Routers continually forward packets to other routers.
A switch is continually forwarding the same unicast frame.
-
Refer to the exhibit. What is the role of the SW3 switch?
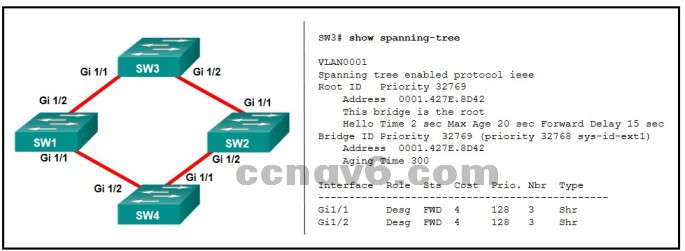
designated switch
root bridge*
enabled bridge
local bridge
edge switch
-
Which three components are combined to form a bridge ID?
MAC address*
extended system ID*
IP address
cost
bridge priority*
port ID
-
Which RSTP ports are connected to end devices?
edge ports*
designated ports
trunk ports
root ports
-
Question as presented: