Lab – Implement Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
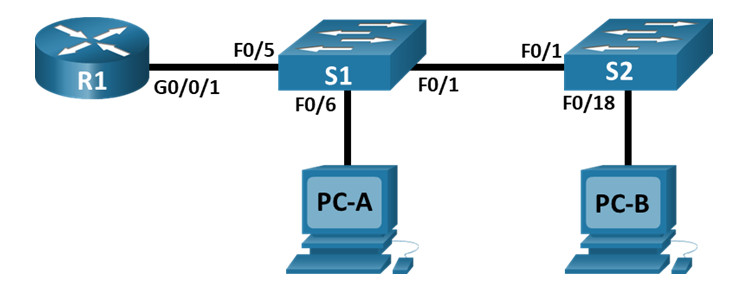
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/1.10 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| G0/0/1.20 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| G0/0/1.30 | 192.168.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | ||
| G0/0/1.1000 | N/A | N/A | ||
| S1 | VLAN 10 | 192.168.10.11 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| S2 | VLAN 10 | 192.168.10.12 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.20.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.30.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.30.1 |
VLAN Table
| VLAN | Name | Interface Assigned |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | Management | S1: VLAN 10
S2: VLAN 10 |
| 20 | Sales | S1: F0/6 |
| 30 | Operations | S2: F0/18 |
| 999 | Parking_Lot | S1: F0/2-4, F0/7-24, G0/1-2
S2: F0/2-17, F0/19-24, G0/1-2 |
| 1000 | Native | N/A |
Objectives
- Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
- Part 2: Create VLANs and Assign Switch Ports
- Part 3: Configure an 802.1Q Trunk between the Switches
- Part 4: Configure Inter-VLAN Routing on the Router
- Part 5: Verify Inter-VLAN Routing is working
Background / Scenario
Modern switches use virtual local-area networks (VLANs) to improve network performance by separating large Layer 2 broadcast domains into smaller ones. VLANs can also be used as a security measure by separating sensitive data traffic from the rest of the network. In general, VLANs make it easier to design a network to support the goals of an organization. Communication between VLANs requires a device operating at Layer 3 of the OSI model. Adding an inter-VLAN router allows the organization to segregate and separate broadcast domains while simultaneously allowing them to communicate with each other.
VLAN trunks are used to span VLANs across multiple devices. Trunks allow the traffic from multiple VLANs to travel over a single link, while keeping the VLAN identification and segmentation intact. A particular kind of inter-VLAN routing, called “Router-on-a-Stick”, uses a trunk from the router to the switch to enable all VLANs to pass to the router.
In this lab, you will create VLANs on both switches in the topology, assign VLANs to switch access ports, verify that VLANs are working as expected, create VLAN trunks between the two switches and between S1 and R1, and configure Inter-VLAN routing on R1 to allow hosts in different VLANs to communicate, regardless of which subnet the host resides.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your instructor.
Required Resources
- 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 2 PCs (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and switches.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Configure basic settings for the router.
a. Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode.
router> enable
b. Enter configuration mode.
router# config terminal
c. Assign a device name to the router.
router(config)# hostname R1
d. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
R1(config)# no ip domain lookup
e. Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
R1(config)# enable secret class
f. Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
R1(config)# line console 0 R1(config-line)# password cisco R1(config-line)# login
g. Assign cisco as the vty password and enable login.
R1(config)# line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)# password cisco R1(config-line)# login
h. Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
R1(config)# service password-encryption
i. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
R1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
j. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
R1(config)# exit R1# copy running-config startup-config
k. Set the clock on the router.
R1# clock set 15:30:00 27 Aug 2019
Step 3: Configure basic settings for each switch.
a. Assign a device name to the switch.
switch(config)# hostname S1 switch(config)# hostname S2
b. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
S1(config)# no ip domain-lookup S2(config)# no ip domain-lookup
c. Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
S1(config)# enable secret class S2(config)# enable secret class
d. Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
S1(config)# line console 0 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S2(config)# line console 0 S2(config-line)# password cisco S2(config-line)# login
e. Assign cisco as the vty password and enable login.
S1(config)# line vty 0 4 S1(config-line)# password cisco S1(config-line)# login S2(config)# line vty 0 4 S2(config-line)# password cisco S2(config-line)# login
f. Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
S1(config)# service password-encryption S2(config)# service password-encryption
g. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
S1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $ S2(config)# exit S2(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $ S2(config)# exit
h. Set the clock on the switch.
S1# clock set 15:30:00 27 Aug 2019 S2# clock set 15:30:00 27 Aug 2019
i. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration.
S1# copy running-config startup-config S2# copy running-config startup-config
Step 4: Configure PC hosts.
Refer to the Addressing Table for PC host address information.
Part 2: Create VLANs and Assign Switch Ports
In Part 2, you will create VLANs as specified in the table above on both switches. You will then assign the VLANs to the appropriate interface and verify your configuration settings. Complete the following tasks on each switch.
Step 1: Create VLANs on both switches.
a. Create and name the required VLANs on each switch from the table above.
S1(config)# vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)# name Management S1(config-vlan)# vlan 20 S1(config-vlan)# name Sales S1(config-vlan)# vlan 30 S1(config-vlan)# name Operations S1(config-vlan)# vlan 999 S1(config-vlan)# name Parking_Lot S1(config-vlan)# vlan 1000 S1(config-vlan)# name Native S1(config-vlan)# exit S2(config)# vlan 10 S2(config-vlan)# name Management S2(config-vlan)# vlan 20 S2(config-vlan)# name Sales S2(config-vlan)# vlan 30 S2(config-vlan)# name Operations S2(config-vlan)# vlan 999 S2(config-vlan)# name Parking_Lot S2(config-vlan)# vlan 1000 S2(config-vlan)# name Native S2(config-vlan)# exit
b. Configure the management interface and default gateway on each switch using the IP address information in the Addressing Table.
S1(config)# interface vlan 10 S1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.11 255.255.255.0 S1(config-if)# no shutdown S1(config-if)# exit S1(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1 S2(config)# interface vlan 10 S2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.12 255.255.255.0 S2(config-if)# no shutdown S2(config-if)# exit S2(config)# ip default-gateway 192.168.10.1
c. Assign all unused ports on the switch to the Parking_Lot VLAN, configure them for static access mode, and administratively deactivate them.
Note: The interface range command is helpful to accomplish this task with as few commands as necessary.
S1(config)# interface range f0/2 - 4 , f0/7 - 24 , g0/1 - 2 S1(config-if-range)# switchport mode access S1(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 999 S1(config-if-range)# shutdown S2(config)# interface range f0/2 - 17 , f0/19 - 24 , g0/1 - 2 S2(config-if-range)# switchport mode access S2(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 999 S2(config-if-range)# shutdown
Step 2: Assign VLANs to the correct switch interfaces.
a. Assign used ports to the appropriate VLAN (specified in the VLAN table above) and configure them for static access mode.
S1(config)# interface f0/6 S1(config-if)# switchport mode access S1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 20 S2(config)# interface f0/18 S2(config-if)# switchport mode access S2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 30
b. Verify that the VLANs are assigned to the correct interfaces.
S1# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/5
10 Management active
20 Sales active Fa0/6
30 Operations active
999 Parking_Lot active Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/7
Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11
Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15
Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19
Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23
Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
1000 Native active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
S2# show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1
10 Management active
20 Sales active
30 Operations active Fa0/18
999 Parking_Lot active Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/5
Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9
Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13
Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17
Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22
Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
1000 Native active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 token-ring-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trnet-default act/unsup
Part 3: Configure an 802.1Q Trunk Between the Switches
In Part 3, you will manually configure interface F0/1 as a trunk.
Step 1: Manually configure trunk interface F0/1 on switch S1 and S2.
a. Configure static trunking on interface F0/1 for both switches.
S1(config)# interface f0/1 S1(config-if)# switchport mode trunk S2(config)# interface f0/1 S2(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
b. Set the native VLAN to 1000 on both switches.
S1(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 1000 S2(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 1000
c. Specify that VLANs 10, 20, 30, and 1000 are allowed to cross the trunk.
S1(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30,1000 S2(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30,1000
d. Verify trunking ports, the Native VLAN and allowed VLANs across the trunk.
S1# show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1000 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000 S2# show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/1 on 802.1q trunking 1000 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000 Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Fa0/1 10,20,30,1000
Step 2: Manually configure S1’s trunk interface F0/5
a. Configure S1’s interface F0/5 with the same trunk parameters as F0/1. This is the trunk to the router.
b. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
S1# copy running-config startup-config S2# copy running-config startup-config
c. Verify trunking.
What happens if G0/0/1 on R1 is down?
Part 4: Configure Inter-VLAN Routing on the Router
Step 1: Configure the router.
a. Activate interface G0/0/1 as necessary on the router.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# no shutdown R1(config-if)# exit
b. Configure sub-interfaces for each VLAN as specified in the IP addressing table. All sub-interfaces use 802.1Q encapsulation. Ensure the sub-interface for the native VLAN does not have an IP address assigned. Include a description for each sub-interface.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1.10 R1(config-subif)# description Management Network R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 10 R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-subif)# interface g0/0/1.20 R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 20 R1(config-subif)# description Sales Network R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-subif)# interface g0/0/1.30 R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 30 R1(config-subif)# description Operations Network R1(config-subif)# ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-subif)# interface g0/0/1.1000 R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1000 native R1(config-subif)# description Native VLAN
c. Verify the sub-interfaces are operational
R1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0/0 unassigned YES NVRAM down down GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned YES NVRAM up up Gi0/0/1.10 192.168.10.1 YES manual up up Gi0/0/1.20 192.168.20.1 YES manual up up Gi0/0/1.30 192.168.30.1 YES manual up up Gi0/0/1.1000 unassigned YES unset up up GigabitEthernet0 unassigned YES NVRAM down down
Part 5: Verify Inter-VLAN Routing is Working
Step 1: Complete the following tests from PC-A. All should be successful.
Note: You may have to disable the PC firewall for pings to work
a. Ping from PC-A to its default gateway.
b. Ping from PC-A to PC-B
c. Ping from PC-A to S2
Step 2: Complete the following test from PC-B
From the Command Prompt window on PC-B, issue the tracert command to the address of PC-A.
What intermediate IP addresses are shown in the results?
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
Device Configs – Final
Switch S1
S1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3232 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$i9s4$16rO8XteeFVjmCcZIgmeV0 ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! ! no ip domain-lookup ! ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30,1000 switchport trunk native vlan 1000 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30,1000 switchport trunk native vlan 1000 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 20 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! interface Vlan10 ip address 192.168.10.11 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 110A1016141D login line vty 0 4 password 7 110A1016141D login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Switch S2
S2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 3181 bytes ! version 15.2 no service pad service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname S2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$Egw6$KhQsKEMbfcGBIoVHJ2Q8F. ! no aaa new-model system mtu routing 1500 ! ! no ip domain-lookup ! ! spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst spanning-tree extend system-id ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending ! ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk allowed vlan 10,20,30,1000 switchport trunk native vlan 1000 switchport mode trunk ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/5 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/13 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/14 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/16 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/17 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/18 switchport access vlan 30 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/19 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/20 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/21 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/22 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/23 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/24 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 999 switchport mode access shutdown ! interface Vlan1 no ip address ! interface Vlan10 ip address 192.168.10.12 255.255.255.0 ! ip http server ip http secure-server ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 00071A150754 login line vty 0 4 password 7 00071A150754 login line vty 5 15 login ! end
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 4347 bytes ! version 16.9 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption platform qfp utilization monitor load 80 no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! vrf definition Mgmt-intf ! address-family ipv4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 exit-address-family ! enable secret 5 $1$1Al2$hVlCY2CB18CBDtaHd48hq/ ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ! ip dhcp pool webuidhcp ! login on-success log ! subscriber templating ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! spanning-tree extend system-id ! redundancy mode none ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 no ip address negotiation auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.10 description Management Network encapsulation dot1Q 10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.20 description Sales network encapsulation dot1Q 20 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.30 description Operations Network encapsulation dot1Q 30 ip address 192.168.30.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1.1000 description Native VLAN encapsulation dot1Q 1000 native ! interface Serial0/1/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface Serial0/1/1 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0 vrf forwarding Mgmt-intf no ip address negotiation auto ! ip forward-protocol nd no ip http server ip http secure-server ip tftp source-interface GigabitEthernet0 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C ! line con 0 password 7 070C285F4D06 login transport input none stopbits 1 line aux 0 stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password 7 104D000A0618 login ! end
Download PDF & PKT file Completed 100% Score:
[sociallocker id=”54558″][wpdm_package id=’**’][/sociallocker]
