1.6.2 Lab – Configure Basic Router Settings
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address / Prefix | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0/0 | 192.168.0.1 /24 | N/A |
| 2001:db8:acad::1 /64 | |||
| fe80::1 | |||
| G0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 /24 | ||
| 2001:db8:acad:1::1 /64 | |||
| fe80::1 | |||
| Loopback0 | 10.0.0.1 /24 | ||
| 2001:db8:acad:2::1 /64 | |||
| fe80::1 | |||
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.10 /24 | 192.168.1.1 fe80::1 |
| NIC | 2001:db8:acad:1::10 /64 | ||
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.0.10 /24 | 192.168.0.1 fe80::1 |
| NIC | 2001:db8:acad::10 /64 |
Objectives
Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
• Cable equipment to match the network topology.
• Initialize and restart the router and switch.
Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
• Assign static IPv4 and IPv6 information to the PC interfaces.
• Configure basic router settings.
• Configure the router for SSH.
• Verify network connectivity.
Part 3: Display Router Information
• Retrieve hardware and software information from the router.
• Interpret the output from the startup configuration.
• Interpret the output from the routing table.
• Verify the status of the interfaces.
Background / Scenario
This is a comprehensive lab to review previously covered IOS router commands. In Parts 1 and 2, you will cable the equipment and complete basic configurations and interface settings on the router.
In Part 3, you will use SSH to connect to the router remotely and utilize the IOS commands to retrieve information from the device to answer questions about the router.
For review purposes, this lab provides the commands necessary for specific router configurations.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the router and switch have been erased and have no startup configurations. Consult with your instructor for the procedure to initialize and reload a router and switch.
Required Resources
• 1 Router (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
• 1 Switch (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
• 2 PCs (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
• Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
• Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Note: The Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on Cisco 4221 routers are autosensing and an Ethernet straightthrough cable may be used between the router and PC-B. If using another model Cisco router, it may be necessary to use an Ethernet crossover cable.
Instructions
Part 1: Set Up the Topology and Initialize Devices
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
a. Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
b. Power on all the devices in the topology.
Step 2: Initialize and reload the router and switch.
Part 2: Configure Devices and Verify Connectivity
Step 1: Configure the PC interfaces.
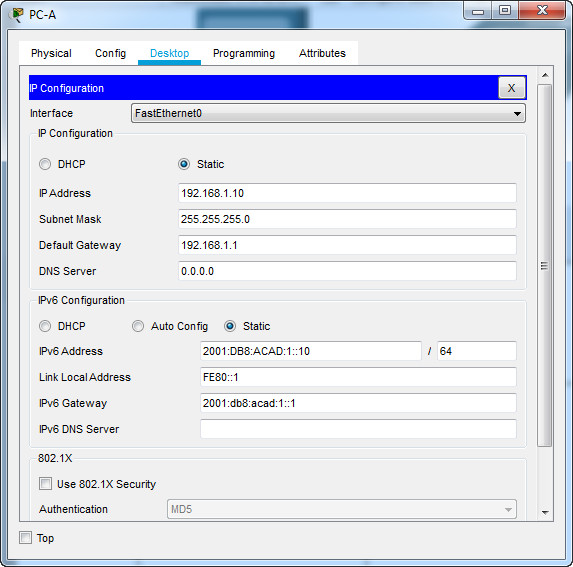
a. Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-A.
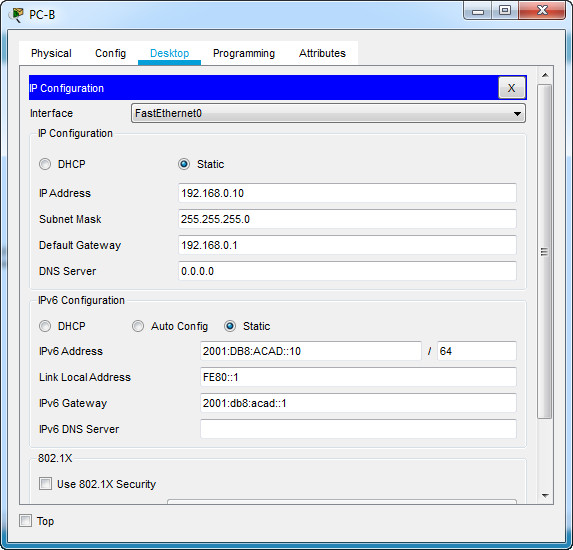
b. Configure the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings on PC-B.
Step 2: Configure the router.
Open configuration window
a. Console into the router and enable privileged EXEC mode.
b. Enter configuration mode.
Router>enable Router#config terminal
c. Assign a device name to the router.
d. Set the router’s domain name as ccna-lab.com.
R1(config)#ip domain-name ccna-lab.com
e. Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
R1(config)#no ip domain-lookup
f. Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
R1(config)#service password-encryption
g. Configure the system to require a minimum 12-character password.
R1(config)#security passwords min-length 12
h. Configure the username SSHadmin with an encrypted password of 55Hadm!n2020.
i. Generate a set of crypto keys with a 1024 bit modulus
R1(config)#crypto key generate rsa How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024 R1(config)#username SSHadmin secret 55Hadm!n2020
j. Assign the privileged EXEC password to $cisco!PRIV*
R1(config)#enable secret $cisco!PRIV*
k. Assign $cisco!!CON* as the console password, configure sessions to disconnect after four minutes of inactivity, and enable login.
R1(config)#line console 0 R1(config-line)#password $cisco!!CON* R1(config-line)#exec-tim R1(config-line)#exec-timeout 4 R1(config-line)#login
l. Assign $cisco!!VTY* as the vty password, configure the vty lines to accept SSH connections only, configure sessions to disconnect after four minutes of inactivity, and enable login using the local database.
R1(config)#line vty 0 4 R1(config-line)#transport input ssh R1(config-line)#exec-timeout 4 R1(config-line)#login local
m. Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
R1(config)#banner motd #Unauthorized access to this device is prohibited!#
n. Enable IPv6 Routing
R1(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
o. Configure all three interfaces on the router with the IPv4 and IPv6 addressing information from the addressing table above. Configure all three interfaces with descriptions. Activate all three interfaces.
R1(config)#interface g0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 add 2001:db8:acad::1/64 R1(config-if)#description Link to PC-B R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface g0/0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1::1/64 R1(config-if)#description Link to PC-A R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface loopback 0 R1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:2::1/64 R1(config-if)#description Connect to loopback 0 R1(config-if)#exit
p. The router should not allow vty logins for two minutes if three failed login attempts occur within 60 seconds.
R1(config)#login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60
q. Set the clock on the router.
R1#clock set 15:37:00 5 JUL 2020
r. Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
R1#copy running-config startup-config
What would be the result of reloading the router prior to completing the copy running-config startupconfig command?
Step 3: Verify network connectivity.
a. Using the command line at PC-A, ping the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for PC-B.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PCs firewall.
Were the pings successful?
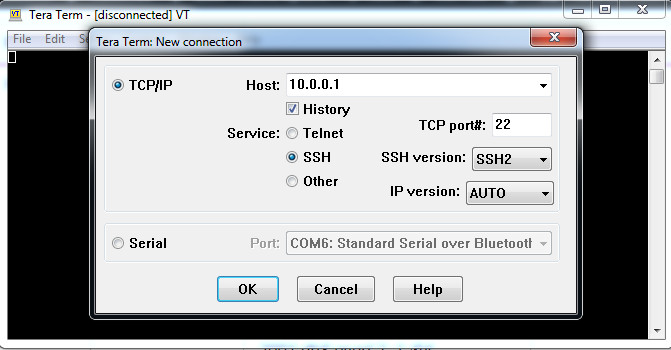
b. Remotely access R1 from PC-A using the Tera Term SSH client.
Using Tera Term on PC-A, open an SSH session to the R1 Loopback interface IPv4 address. Ensure that the SSH radio button is selected and then click OK to connect to the router. Log in as SSHadmin with the password 55Hadm!n2020.
Open Tera Term and enter the Loopback 0 interface IP address of R1 in the Host: field of the Tera Term: New Connection window. Ensure that the SSH radio button is selected and then click OK to connect to the router.
In this case, i’m only use Packet Tracer to remotely access R1 from PC-A.
From PC-A, go to Desktop tab –> Telnet / SSH Client
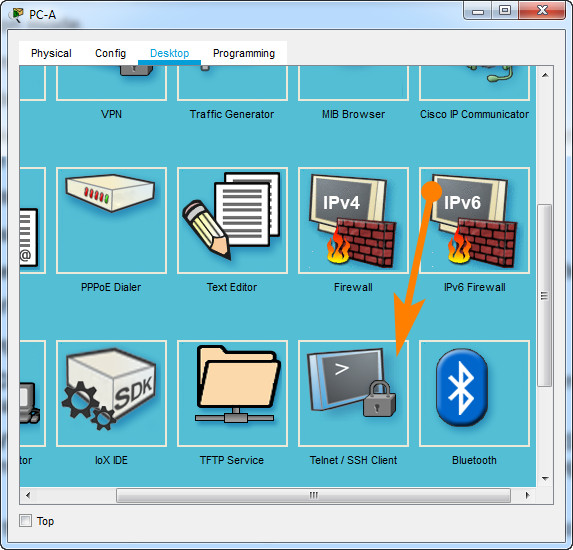
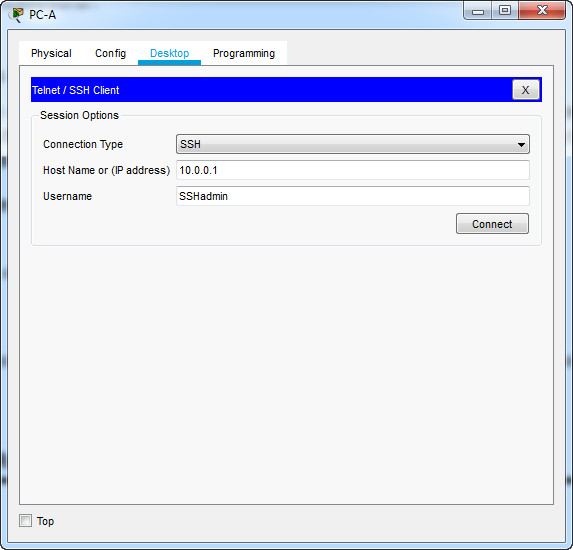
Was remote access successful?
Using Tera Term on PC-A, open an SSH session to the R1 Loopback interface IPv6 address. Ensure that the SSH radio button is selected and then click OK to connect to the router. Log in as SSHadmin with the password 55Hadm!n2020. Note: The IPv6 address should be surrounded with square brackets, i.e. [IPv6 address]
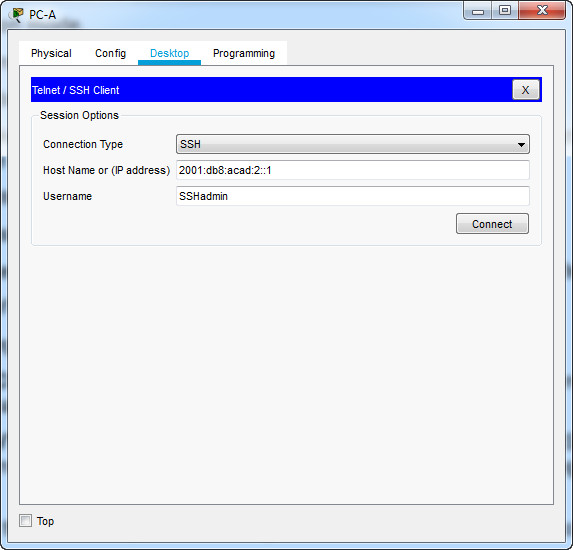
Was remote access successful?
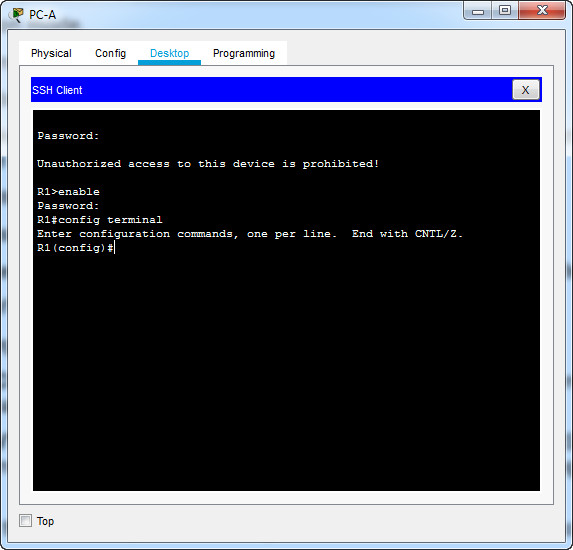
Why is the Telnet protocol considered to be a security risk?
Part 3: Display Router Information
In Part 3, you will use show commands from an SSH session to retrieve information from the router.
Step 1: Establish an SSH session to R1.
Using Tera Term on PC-B, open an SSH session to the R1 Loopback interface IPv6 address and log in as SSHadmin with the password 55Hadm!n2020.
Step 2: Retrieve important hardware and software information.
a. Use the show version command to answer questions about the router.
R1#show version
Cisco IOS XE Software, Version 03.16.05.S - Extended Support Release
Cisco IOS Software, ISR Software (X86_64_LINUX_IOSD-UNIVERSALK9-M), Version Version 15.5 (3)S5, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc2)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2017 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thu 19-Jan-17 11:24 by mcpre
Cisco IOS-XE software, Copyright (c) 2005-2017 by cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved. Certain components of Cisco IOS-XE software are
licensed under the GNU General Public License ("GPL") Version 2.0. The
software code licensed under GPL Version 2.0 is free software that comes
with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. You can redistribute and/or modify such
GPL code under the terms of GPL Version 2.0. For more details, see the
documentation or "License Notice" file accompanying the IOS-XE software,
or the applicable URL provided on the flyer accompanying the IOS-XE
software.
ROM: IOS-XE ROMMON
Router uptime is 1 hours, 1 minutes, 18 seconds
Uptime for this control processor is 1 hours, 1 minutes, 18 seconds
System returned to ROM by power-on
System image file is "bootflash:/isr4300-universalk9.03.16.05.S.155-3.S5-ext.SPA.bin"
Last reload reason: PowerOn
This product contains cryptographic features and is subject to United
States and local country laws governing import, export, transfer and
use. Delivery of Cisco cryptographic products does not imply
third-party authority to import, export, distribute or use encryption.
Importers, exporters, distributors and users are responsible for
compliance with U.S. and local country laws. By using this product you
agree to comply with applicable laws and regulations. If you are unable
to comply with U.S. and local laws, return this product immediately.
A summary of U.S. laws governing Cisco cryptographic products may be found at:
http://www.cisco.com/wwl/export/crypto/tool/stqrg.html
If you require further assistance please contact us by sending email to
[email protected].
Suite License Information for Module:'esg'
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Suite Suite Current Type Suite Next reboot
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FoundationSuiteK9 None None None
securityk9
appxk9
AdvUCSuiteK9 None None None
uck9
cme - srst
cube
Technology Package License Information:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Technology Technology-package Technology-package
Current Type Next reboot
------------------------------------------------------------------------
appxk9 None None None
uck9 None None None
securityk9 securityk9 Permanent securityk9
ipbase ipbasek9 Permanent ipbasek9
security securityk9 Permanent securityk9
ipbase ipbasek9 Permanent ipbasek9
cisco ISR4321/K9 (1RU) processor with 1687137K/6147K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID FLM2041W2HD
2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
32768K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
4194304K bytes of physical memory.
3223551K bytes of flash memory at bootflash:.
Configuration register is 0x2142 (will be 0x2102 at next reload)
What is the name of the IOS image that the router is running?
How much non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) does the router have?
How much Flash memory does the router have?
b. The show commands often provide multiple screens of outputs. Filtering the output allows a user to display certain sections of the output. To enable the filtering command, enter a pipe (|) character after a show command, followed by a filtering parameter and a filtering expression. You can match the output to the filtering statement by using the include keyword to display all lines from the output that contain the filtering expression. Filter the show version command, using show version | include register to answer the following question.
R1#show version | include register Configuration register is 0x2142
What is the boot process for the router on the next reload?
Step 3: Display the startup configuration.
Use the show startup-config command on the router to answer the following questions.
R1#show startup-config Using 1436 bytes ! version 15.4 no service timestamps log datetime msec no service timestamps debug datetime msec service password-encryption security passwords min-length 12 ! hostname R1 ! login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 ! ! enable secret 5 $1$mERr$2q6B19eTeuK92k7m8Bhgz/ ! ! ! ! ! ! ip cef ipv6 unicast-routing ! no ipv6 cef ! ! ! username SSHadmin secret 5 $1$mERr$fuFUxOtVJZMfnQOcoB7vt/ ! ! ! ! ! ! ! ! no ip domain-lookup ip domain-name ccna-lab.com ! ! spanning-tree mode pvst ! ! ! ! ! ! interface Loopback0 description Connect to loopback 0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/64 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 description Link to PC-B ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD::1/64 ipv6 enable ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1 description Link to PC-A ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/64 ipv6 enable ! interface Vlan1 no ip address shutdown ! ip classless ! ip flow-export version 9 ! ! ip access-list extended sl_def_acl deny tcp any any eq telnet deny tcp any any eq www deny tcp any any eq 22 permit tcp any any eq 22 ! no cdp run ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized access to this device is prohibited!^C ! ! ! ! ! line con 0 exec-timeout 4 0 password 7 08654F471A1A0A565328232A60 login ! line aux 0 ! line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 4 0 login local transport input ssh ! ! ! end
How are passwords presented in the output?
$cisco!!CON* is encrypted as 08654F471A1A0A565328232A60. The SSHadmin password of 55Hadm!n2020 is
encrypted as $1$mERr$fuFUxOtVJZMfnQOcoB7vt/.
Use the show startup-config | section vty command.
R1#show running-config | section vty line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 4 0 login local transport input ssh
What is the result of using this command?
Step 4: Display the routing table on the router.
Use the show ip route command on the router to answer the following questions.
R1#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.0.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback0
L 10.0.0.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback0
192.168.0.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L 192.168.0.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
What code is used in the routing table to indicate a directly connected network?
How many route entries are coded with a C code in the routing table?
Step 5: Display a summary list of the interfaces on the router.
a. Use the show ip interface brief command on the router to answer the following question.
R1#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol GigabitEthernet0/0/0 192.168.0.1 YES NVRAM up up GigabitEthernet0/0/1 192.168.1.1 YES NVRAM up up Loopback0 10.0.0.1 YES NVRAM up up Vlan1 unassigned YES NVRAM administratively down down
What command changed the status of the Gigabit Ethernet ports from administratively down to up?
b. Use the show ipv6 int brief command to verify IPv6 settings on R1.
R1#show ipv6 int brief
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 [up/up]
FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE15:4201
2001:DB8:ACAD::1
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 [up/up]
FE80::2E0:B0FF:FE15:4202
2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
Loopback0 [up/up]
FE80::203:E4FF:FE4A:7AC8
2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
Vlan1 [administratively down/down]
unassigned
R1#
What is the meaning of the [up/up] part of the output?
c. On PC-B, change its configuration so that it no longer has a static IPv6 address. You may have to reboot the machine. Then, issue the ipconfig command on PC-B to examine the IPv6 configuration.
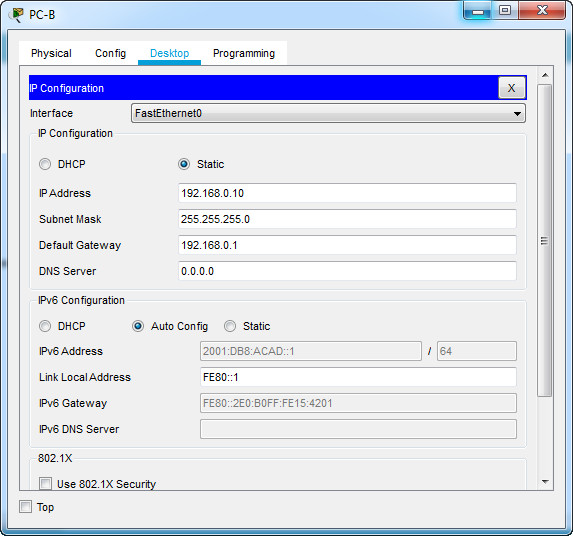
What is the IPv6 address assigned to PC-B?
What is the default gateway assigned to PC-B?
Issue a ping from PC-B to the R1 default gateway link local address. Was it successful?
Issue a ping from PC-B to the R1 IPv6 unicast address 2001:db8:acad::1. Was it successful?
Reflection Questions
1. In researching a network connectivity issue, a technician suspects that an interface was not enabled. What show command could the technician use to troubleshoot this issue?
2. In researching a network connectivity issue, a technician suspects that an interface was assigned an incorrect subnet mask. What show command could the technician use to troubleshoot this issue?
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 4221 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 4300 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device.
The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
End of document
Download PDF & PKT file Completed 100% Score:
[sociallocker id=”54558″][wpdm_package id=’49899′][/sociallocker]
