6.2.7 Packet Tracer – Investigate NAT Operation (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
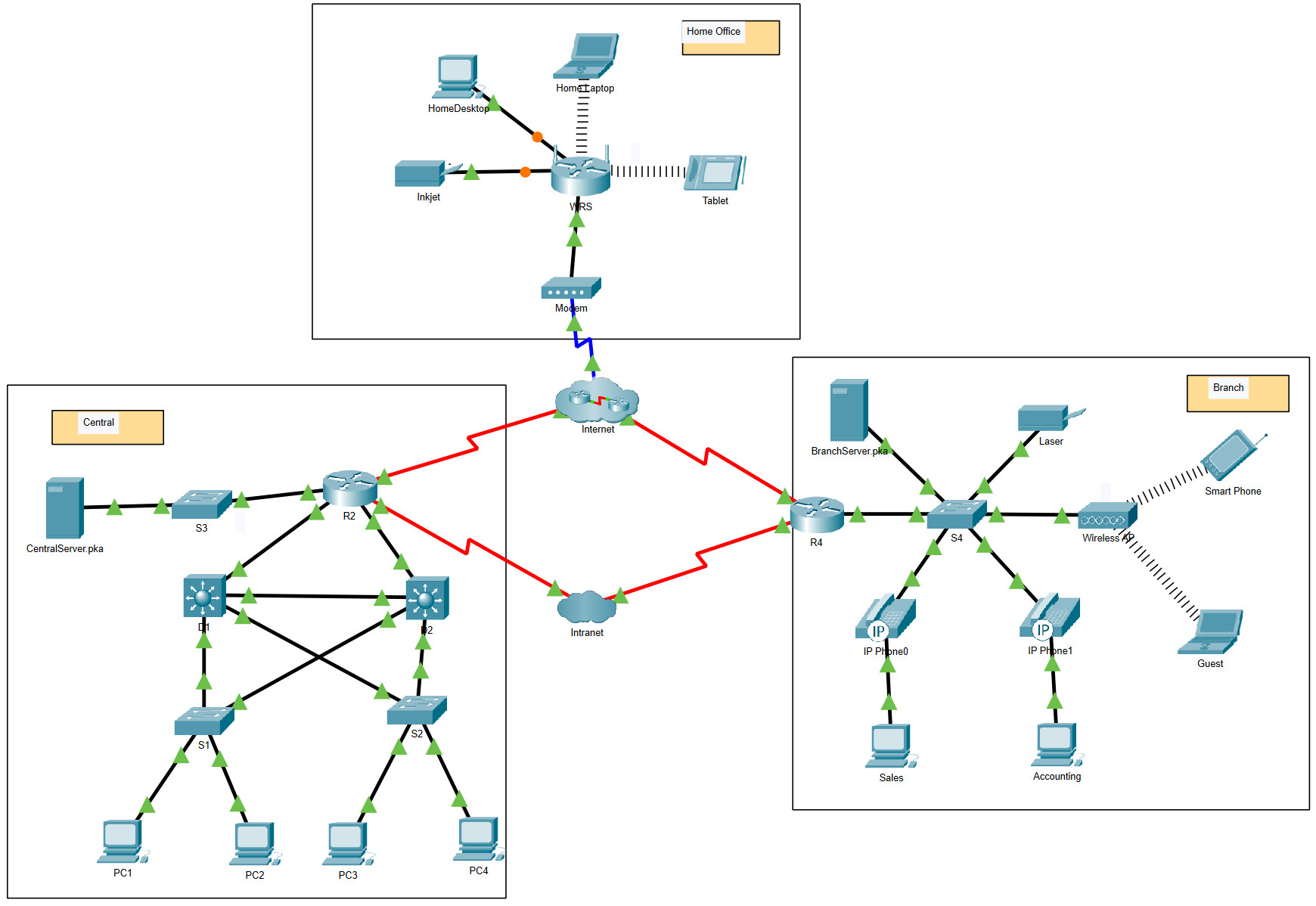
Addressing Table
The following table provides addressing for networking device interfaces only.
| Device | Interface | IP Address and Prefix |
|---|---|---|
| R2 | G0/0 | 10.255.255.245/30 |
| G0/1 | 10.255.255.249/30 | |
| G0/2 | 10.10.10.1/24 | |
| S0/0/0 | 64.100.100.2/27 | |
| S0/0/1.1 | 64.100.200.2/30 | |
| R4 | G0/0 | 172.16.0.1/24 |
| S0/0/0 | 64.100.150.1/30 | |
| S0/0/1.1 | 64.100.200.1/30 | |
| WRS | LAN | 192.168.0.1/24 |
| Internet | 64.104.223.2/30 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Investigate NAT Operation Across the Intranet
- Part 2: Investigate NAT Operation Across the Internet
- Part 3: Conduct Further Investigations
Scenario
As a frame travels across a network, the MAC addresses may change. IP addresses can also change when a packet is forwarded by a device configured with NAT. In this activity, we will investigate what happens to IP addresses during the NAT process.
Instructions
Part 1: Investigate NAT Operation Across the Intranet
Step 1: Wait for the network to converge.
It might take a few minutes for everything in the network to converge. You can speed the process up by clicking Fast Forward Time.
Step 2: Generate an HTTP request from any PC in the Central domain.
a. Switch to Simulation mode and edit the filters to show only HTTP requests.
b. Open the Web Browser of any PC in the Central domain and type the URL http://branchserver.pka and click Go. Minimize the browser window.
c. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over D1 or D2. Click on the most recent PDU in the Event List. Record the source and destination IP addresses.
To what devices do those addresses belong?
d. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over R2. Record the source and destination IP addresses in the outbound packet.
To what devices do those addresses belong?
e. Login to R2 from the CLI using the password class to enter privileged EXEC and issue the following command:
R2# show run | include pool ip nat pool R2Pool 64.100.100.3 64.100.100.31 netmask 255.255.255.224 ip nat inside source list 1 pool R2Pool
The address came from the NAT pool R2Pool.
f. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over R4. Record the source and destination IP addresses in the outbound packet.
To what devices do those addresses belong?
g. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over Branchserver.pka. Record the source and destination TCP port addresses in the outbound segment.
h. On both R2 and R4, run the following command and match the IP addresses and ports recorded above to the correct line of output:
R2# show ip nat translations R4# show ip nat translations
What do the inside local IP addresses have in common?
Did any private addresses cross the intranet?
i. Click the Reset Simulation button and remain in Simulation Model.
Part 2: Investigate NAT Operation Across the Internet
Step 1: Generate an HTTP request from any computer in the home office.
a. Open the Web Browser of any PC in the Home Office domain and type the URL http://centralserver.pka and click Go.
b. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over WRS. Record the inbound source and destination IP addresses and the outbound source and destination addresses.
To what devices do those addresses belong?
c. Click Capture / Forward until the PDU is over R2. Record the source and destination IP addresses in the outbound packet.
To what devices do those addresses belong?
d. On R2, run the following command and match the IP addresses and ports recorded above to the correct line of output:
R2# show ip nat translations
e. Return to Realtime mode.
Did all of the web pages appear in the browsers?
Part 3: Conduct Further Investigations
Experiment with more packets, both HTTP and HTTPS and answer the following questions.
Do the NAT translation tables grow?
Does WRS have a NAT pool of addresses?
Is this how the computers in the classroom connect to the internet?
Why does NAT use four columns of addresses and ports?
Where are the networks are inside global and inside local?
On which devices are NAT services operating? What do they have in common?
Download Packet Tracer Completed File
[sociallocker id=”54558″]
[wpdm_package id=’55925′]
[wpdm_package id=’55926′]
[/sociallocker]
[alert-note][one_half]
Previous Lab
5.5.1 Packet Tracer – IPv4 ACL Implementation Challenge
[/one_half][one_half_last]
Next Lab
6.4.5 Packet Tracer – Configure Static NAT
[/one_half_last][/alert-note]
